
- •The size of molecules
- •Aggregative states of matter
- •Ideal gas model
- •Three methods in molecular physics
- •Thermodynamical systems
- •Temperature
- •If objects a and b are separately in thermal equilibrium with a third object c, then a and b are in thermal equilibrium with each other.
- •The Constant-Volume Gas Thermometer and the Absolute Temperature Scale
- •The Celsius, Fahrenheit, and Kelvin Temperature Scales
- •Summary
- •Work in t/d processes
- •Heat capacity
- •The adiabatic constant and internal energy
- •Polytropic process
- •Work in polytropic process
- •Adiabatic process
- •The table for iso-processes
- •The classical theory of heat capacity
- •Internal energy
- •Barometrical formula
- •Gas of Van der Waals
- •Statistical physics. Probability. Distribution functions
- •Maxwell's distribution
- •Maxwell's distribution for modulus of velocity
- •The characteristic speeds
- •Boltzmann's distribution
- •Thermal apparatuses
- •Entropy on a Microscopic Scale
- •Equilibrium and phase transformations of matter
- •Van der Waals isotherms
- •The theory of skating
- •The foundations of kinetics
- •Thermodynamic potentials
- •Internal energy.
- •Liquid state
- •Surface tension
- •Laplace's formula
- •4. Reflection about a point.
- •5. Rotation-reflection symmetry.
The theory of skating

The increasing of pressure on the ice is decreased the melting temperature of ice. The nascent thin film of water decreases the friction appreciably!
![]() ,
,
where
![]() - it is a difference between specific volume of water and ice.
- it is a difference between specific volume of water and ice.
![]()
where m – it is the mass of man;
S – it is the area of skate.
Calculate the minimal temperature for skating!
The pVT - diagram
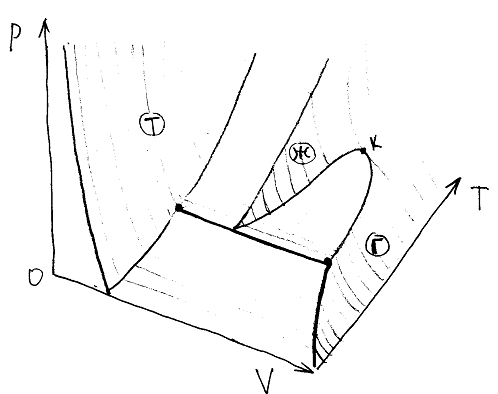
The foundations of kinetics
The physical kinetics deals with the TD system near the equilibrium.
The local equilibrium.
The disequilibrium reduces to arising of substance flux, energy flux and momentum flux. There are so called transport phenomena.
The subject of investigation there are three transport phenomena:
diffusion;
viscosity;
heat transfer.
The flux of physical value through the area.
T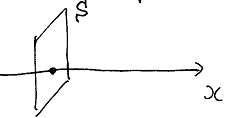 he
heterogeneity of the physical value is a course of the flux of this
value.
he
heterogeneity of the physical value is a course of the flux of this
value.
Diffusion
Diffusion – it is a mutual penetration of the different substances in there mixture.
T he
experimental law:
he
experimental law:
![]()
![]() - it is the
density of mass flux
- it is the
density of mass flux
![]() ;
;
D
– is the coefficient of diffusion
![]() ;
;
![]() - it is the
gradient of the density.
- it is the
gradient of the density.
![]() and
and
![]() .
.
Viscosity
Viscosity – it is the transport of momentum due to the chaotic thermal motion of the molecules.
T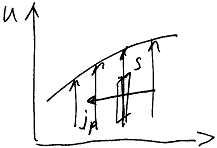 he
experimental law (Newton's law):
he
experimental law (Newton's law):
![]()
![]() - it is the
viscosity's tension
- it is the
viscosity's tension
![]() ;
;
x
- it is a
viscosity
![]() .
.
![]()
- it is kinematical viscosity.
![]() ,
,
![]() and
and
![]()
Thermal conductivity
Thermal conductivity – it is the energy transfer due to the chaotic thermal motion of the molecules.
T he
experimental law (Fourier's law):
he
experimental law (Fourier's law):
![]()
![]() - it is the
density of heat flux
- it is the
density of heat flux
![]() ;
;
![]() - it is the
thermo conductivity
- it is the
thermo conductivity
![]() .
.
![]() - it is the
gradient of the temperature.
- it is the
gradient of the temperature.
![]() and
and
![]() .
.
The molecular mechanism of the transport phenomena in gases
The mean free path of the molecule
L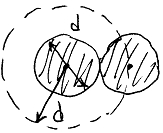 et
us introduce the effective
diameter
d
of molecule and effective
cross section
et
us introduce the effective
diameter
d
of molecule and effective
cross section![]() :
:
![]()
Put
is an mean
frequency of collisions
and
![]() is an
mean
free path of the molecule:
is an
mean
free path of the molecule:

![]()
![]()
![]() - it is an
average relative velocity of the molecule;
- it is an
average relative velocity of the molecule;
n – it is a concentration of the molecules;
![]() - it is the
volume of the tube with cross section
that molecule moves inside for one second.
- it is the
volume of the tube with cross section
that molecule moves inside for one second.
![]() ;
; ![]() ;
;
![]() ,
,
because![]() due to chaotic motions.
due to chaotic motions.
![]()
![]()
![]() - it is a mean free path of molecule.
- it is a mean free path of molecule.
For ideal gas therefore:
![]()
The evaluation of mean free path:
![]() ;
;
![]()
![]()
We can fined the mean distance between the molecules l from the volume per one molecule:
![]() ;
;
![]() ;
; ![]() ;
;
So ![]() .
.
The general transport equation
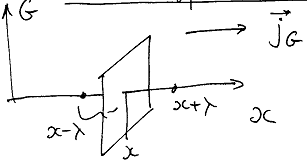
The density flux of molecules along x axis:
![]()
The property G may be energy, momentum, charge…
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
it is a general equation for transport phenomena.
Diffusion (self diffusion)
![]()
n – it is the concentration of marked particles;
![]() -
it is the concentration of all
particles.
-
it is the concentration of all
particles.
![]()
![]()
![]()
For oxygen
and nitrogen at normal conditions
![]()
Viscosity
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
The
viscosity of gases at normal conditions
![]()
Thermal conductivity
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() - it is a specific heat at constant volume
- it is a specific heat at constant volume
![]() - it is a density.
- it is a density.
![]()
![]()
![]()
The dependence of the coefficients of transfer on TD parameters
![]()
![]()
![]() ;
;
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Vacuum
Knudsen's number:
![]()
![]() - it is vacuum;
- it is vacuum;
![]() - it is a solid medium.
- it is a solid medium.
Dewar Flask
Thermodynamic relations and potentials
All calculations in thermodynamics are based on functions of state that called thermodynamic potentials. For any set of independent parameters there are own thermodynamic potential. The changing of the potentials at the process defines the work done by the system or the quantity of heat received by the system. Below we shall use the inequality:
![]()
The equality sign corresponds to the reversible processes, the inequality sign – to the irreversible. Thermodynamic potentials are the functions of state.
Let us consider an example for this calculation.
![]()
If
![]() then
then
![]()
![]() ;
; ![]()
If
![]() then
then
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() ;
; ![]()
![]()

![]()
![]()
Thermal radiation.
The pressure of the photon gas:
![]() ;
;
![]() ;
;
![]() - it is a density of energy radiation.
- it is a density of energy radiation.
![]() ;
;
![]() ;
;
![]() (
(![]() is
independent on volume);
is
independent on volume);
![]() ;
;
![]() ;
;
![]() - it is Stefan-Boltzmann law for radiation.
- it is Stefan-Boltzmann law for radiation.
