
Nanoparticles
Nanoparticles are at the heart of UV protection. They have a significant increase in their effectiveness of blocking UV light compared to natural material due to their large surface area to volume ratio. Figure 3 illustrates this effect: Incoming UV radiation is unblocked and penetrates the stratum conium. (B) An UV reflective material in bulk form (ex. ZnO) is applied to the surface of the stratum corneum. Some incoming UV radiation is blocked by reflection/scattering and some UV radiation is unblocked/deflected to the stratum corneum. (C) UV reflective nanoparticles (ex. ZnO) are appliedto the surface of the stratum corneum. The incoming UV radiation is reflected by the nanoparticles.
This
review will cover the use of organic and inorganic nanoparticle
components in sunscreen and the use of solid lipid nanoparticles in
UV protection. This review also touches upon the use of these
particles in novel UV protection applications.

Inorganic nanoparticle components
Titanium dioxide
Titanium dioxide is a mineral which isprepared as ultra-fine nanoparticles with a diameter on the order of 14nm. These articles form aggregates which reflect UVlight most efficiently with aggregates sized at 60-120 nm . In sunscreens, TiO2 is usually treated with coating materials such as silicon oils, SiO2, or Al2O3 in order to make it more passive in relation to the organic components and improve its dispersion in the overall formulation. Additionally, TiO2 nanoparticles can be coated with silica to increase UV absorption.
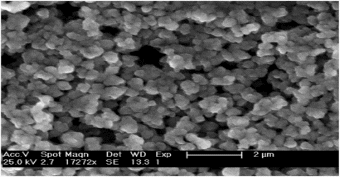

Zinc Oxide
Zinc oxide (ZnO) is a mineral and prepared in particles that have an optimal size of 20-30 nm [13]. ZnO is also usually coated with silicon oils, SiO2, or Al2O3 in sunscreen formulations. Additionally, ZnO is considered a better sunscreen ingredient than TiO2 because it is more transparent for a given concentration and is more protective against UVA light.

Advantages/disadvantages of inorganics
Inorganics used in sunscreen are beneficial because they have been shown to reflect and scatter UV light, which is gnerally considered safer and more effective than absorption of UV light. Inorganics cover a broad spectrum, so their addition can simplify the sunscreen formulation by minimizing the necessary number of organic components. This can be beneficial for those with sensitivity or skin irritation issues [15].Inorganic UV sunscreens have relatively high consumer acceptance because of their transparency, which increases the usage of sunscreen [7]. A drawback of using inorganics is their dispersion issues, which often require an additional material for coating the inorganic material [10]. The most considerable drawback is the potential risk caused by the generation of free radicals through oxidation when exposing inorganic molecules to UV radiation.
Organic nanoparticle components
Avobenzone
Butyl methoxydibenzoylmethane(BMDM), more commonly known as avobenzone, is an oil soluble product used to absorb the full spectrum of UVA rays. It is considered one of the best sunscreen agents because of its ability to absorb UV light over a very broad spectrum. Since, avobenzone is highly degradable in the presence of sunlight it is often paired with a photo stabilizer in sunscreen formulations.
Oxybenzone
Oxybenzone is also used in sunscreen formulations because of its ability o absorb UVA light. It is considered potentially harmful and a likely photocarcinogen because of its ability to penetrate through the stratum corneum and generate free radicals when illuminated with UV light. Oxybenzone is a derivative of benzophenone, a known photo-carcinogen.
Phenylbenzimidazole sulfonic acid
This acid is a common sunscreen agent also known as ensulizole. It protects
against UVB and minimally against UVA. It is water soluble and is used in formulations for
a light, non-greasy feeling.
Octyl methoxycinnamate
This organic, also known as Octinoxate, is used in sunscreen and lip balms for its ability to absorb UVB light and reduce the appearance of scars. It is insoluble in water, making it useful in
waterproof formulations.
