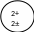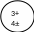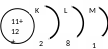- •The characteristics of matter
- •Matter construction
- •Atomic structure
- •Matter is everything that has mass & volume.
- •Density
- •Melting point:
- •The boiling point is the temperature at which a substance begins to change from the liquid into the gaseous state.
- •Thermal conduction
- •Rusting of metals:
- •Complete the following statements:
- •Explain why:
- •Problems :
- •What’s meant by:
- •Melting point
- •A solid substance (ice) melts when heated.
- •A liquid (water) evaporates when heated.
- •Vaporization is the change of liquid into gas.
- •Explain why:
- •Write the scientific term:
- •Match the figure with the following molecules:
- •Match the figure with the process:
- •Fill in the blanks:
- •Give reasons:
- •Choose the right answer:
- •Figure………………………is an excited atom while, figure…………………is for the atom in the ground state.
A solid substance (ice) melts when heated.
The molecules gain energy & move apart.
T he
intermolecular spaces increase & the intermolecular forces
weaken, ice becomes water.
he
intermolecular spaces increase & the intermolecular forces
weaken, ice becomes water.
A liquid (water) evaporates when heated.
The energy of the molecules increases by heating the spaces between them increase & they overcome the intermolecular forces. And some of them escaped as vapour
Melting is the change of
solid substance into liquid substance.
Vaporization is the change of liquid into gas.
A molecule consists of atoms.
I f
the atoms in the molecule are similar , this substance is an element.
An element is the simplest form of a substance.
f
the atoms in the molecule are similar , this substance is an element.
An element is the simplest form of a substance.
A compound results from the combination of 2 or more different elements.

Gaseous elements |
A molecule consists of 1 atom |
Inert gases (noble gases) |
Helium, xenon , neon argon, krypton, radon |
A molecule consists of 2 atoms |
|
Oxygen Chlorine Fluorine Hydrogen Nitrogen
|
|
Liquid elements |
Bromine |
||
A molecule consists of one atom |
Mercury |
||
Solid elements |
Magnesium ,aluminium, iron & carbon |
||
Points of comparison |
Structure of the molecule |
Examples |
|
Explain why:
The table salt dissolved in water disappears.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
The volume of a mixture of water & alcohol is less than the sum of their volumes before being mixed.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
The smell of perfume spreads in the room.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Write the scientific term:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Match the figure with the following molecules:
1. Hydrogen molecule 2. Water molecule 3. Helium molecule
4 .
Sodium molecule 5. Ammonia molecule 6. Iron
molecule
.
Sodium molecule 5. Ammonia molecule 6. Iron
molecule
Match the figure with the process:
Figure………………………………..indicates the vaporization process.
Figure……………………………….indicates the melting process.

Chemists use symbols to express elements.
Some symbols come from the Italian name of the element (Latin is an old European language).
The symbol is a capital letter, if the symbol consists of 2 letters only the first one is a capital letter.
Element |
Atom symbol |
Element |
Atom symbol |
Lithium |
Li |
Hydrogen |
H |
Potassium |
K |
Oxygen |
O |
Sodium |
Na |
Nitrogen |
N |
Calcium |
Ca |
Fluorine |
F |
Magnesium |
Mg |
Chlorine |
Cl |
Aluminium |
Al |
Bromine |
Br |
Zinc |
Zn |
Iodine |
I |
Iron |
Fe |
Helium |
He |
Lead |
Pb |
Argon |
Ar |
Copper |
Cu |
Sulphur |
S |
Mercury |
Hg |
Phosphorous |
P |
Silver |
Ag |
Carbon |
C |
Gold |
Au |
Silicon |
Si |
S cientists found that atoms consist
of a nucleus & electrons.
The nucleus |
The electrons |
|
|
Protons |
Neutron |
|
1. Neutral (carry no charge) |
|
2. Exist in the nucleus |
|
|
The number of protons in the atom of an element is unique & characterizes the element.
The atomic number is the number of protons in an atom.
The mass number is the sum of protons & neutrons in an atom.
![]() Atomic
number (written at the left side below the symbol is 8) = 8 protons.
Atomic
number (written at the left side below the symbol is 8) = 8 protons.
Mass number (written at the left side above the symbol is 16)
No. of neutrons = 16 – 8 = 8
Nitrogen
![]()
Atomic number = no. of protons = 7
Mass number = protons + neutrons = 14
Number of neutrons = 14 - 7 = 7
Complete the following table:
Element symbol |
Atomic number |
Mass number |
Number of protons |
Number of neutrons |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
An atom is electrically neutral because the number of protons = the number of electrons. The positive charge of the proton is opposite to that of the electrons.
Electrons revolve around the nucleus in orbits called energy levels.
E
 nergy
levels are places around the nucleus where electrons exist.
nergy
levels are places around the nucleus where electrons exist.There are 7 energy levels represented from the nearest to the nucleus to the farthest by the letters K, L, M, N, O , P, Q .
The energy of the level increases by the increase of the distance from the nucleus.
Each level is saturated (completely filled) with a certain number of electrons.
The number of electros which saturate energy levels 1-4 is calculated by the rule 2n2
Where n is the number of the energy level.
No. of energy level |
It symbol |
The number of electrons that saturate the levels |
1 |
K |
2 (1)2 = 2 |
2 |
L |
2 (2)2 = 8 |
3 |
M |
2 (3)2 = 18 |
4 |
N |
2 (4)2 = 32 |
5 |
O |
32 electrons. The equation isn’t applied because a number of electrons larger than 32 makes the atom unstable. |
6 |
P |
|
7 |
Q |
W
 hen
an electron gains a quantum
of energy,
it moves to a higher energy level. The atom is excited by gaining
energy.
hen
an electron gains a quantum
of energy,
it moves to a higher energy level. The atom is excited by gaining
energy.The excited atom loses the quantum of energy & electrons return to the original level (ground state)
Distributing electrons in energy levels electronic configuration.
Mass number symbol atomic |
Electronic configuration |
|
K
1
|
|
K
1
|
|
K
L
1
2
|
|
K
L
5
2
|
|
|
Complete the following table:
Symbol
Mass number Atomic number |
Electronic configuration |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The atom is the basic unit of matter which goes into in a chemical reaction
Substances react together producing new substances. The activity which changes the substance into a new material is called chemical reaction.
An atom is the unit of the substance which undergoes a chemical reaction.
An atom that has less than 8 electrons in the last energy level is active.
It reacts with atoms of other elements to complete the last energy level with 8 electrons. An example: sodium atoms are active because each has an electron in the last energy level. In a chemical reaction sodium gives this electrons to atoms of another element & end up with 8 electrons in the last energy level.
I
 nert
gases such as Argon 18Ar
has 8 electrons in the last energy level. They are stable &
don’t react with other substances.
nert
gases such as Argon 18Ar
has 8 electrons in the last energy level. They are stable &
don’t react with other substances.