
- •Unit I Petroleum Industry
- •1. Read and learn the following words.
- •2. Read the text and translate it into Russian.
- •3. Find in the text and read out English equivalents of these words and word-combinations.
- •4. Answer the following questions.
- •5. Match the terms and their definitions.
- •6. Answer the following questions using the information from the exercise 5:
- •7. Fill in the gaps in the following sentences with the appropriate word or word-combination:
- •9. Translate into English.
- •10. Speak about the petroleum industry according to the following plan:
- •Unite II. Petroleum Origin
- •1. Read and learn the following words.
- •Quantity – количество
- •Mixture – смесь
- •2. Read and translate the following words and word-combinations. Practice your pronunciation.
- •3. Read and translate the words of the same root:
- •4. Read the text and translate it into Russian.
- •5. Find in the text and read out English equivalents of these words and word-combinations.
- •6. Answer the following questions.
- •8. Fill in the blanks with the appropriate prepositions: between, on, in, to, of, for, by, with, over, from.
- •9. Translate into English.
- •9. Read the text, arrange the paragraphs logically and give a heading to the text.
- •11. Speak about the petroleum origin according to the following plan:
- •Unit III Light and Heavy Crude Oil
- •1. Read and learn the following words.
- •2. Read and translate the words of the same root:
- •3. Read and translate the following words. Pay attention to the pronunciation.
- •4. Read the text and translate it into Russian.
- •4. Find in the text and read out English equivalents of these words and word-combinations.
- •5. Answer the following questions.
- •6. React to the statements (true or false).
- •7. Match the terms and their definitions.
- •8. Fill in the gaps in this paragraph about light crude oil.
- •9. Translate into English.
- •10. Speak about crude oil according to the following plan:
- •Unit IV The Search for Oil and Gas
- •1. Read and learn the following words.
- •2. Read and translate the words of the same root:
- •3. Read and translate the following words. Pay attention to the pronunciation.
- •4. Read the text and translate it into Russian. The Search for Oil
- •5. Find in the text and read out English equivalents of these words and word-combinations.
- •6. Answer the following questions.
- •7. Match the words and word-combinations from the first column with the words and word-combinations that have the same meaning from the second column.
- •8. React to the statements (true or false).
- •9. Translate into English.
- •10. Speak about the oil exploration according to the following plan:
- •1. Read and learn the following words.
- •2. Read and translate the words and word-combinations of the same root.
- •3. Read the following words and word-combinations and give their Russian equivalents.
- •4. Read the text and translate it into Russian.
- •5. Find in the text and read out English equivalents of these words and word-combinations.
- •6. Answer the following questions.
- •7. Match the words and word-combinations from the first column with the words and word-combinations that have the same meaning from the second column.
- •8. Agree or disagree with the following statements.
- •9. Fill in the blanks choosing the proper English word from those given above the text.
- •9. Translate into English.
- •10. Speak about the petroleum geology according to the following plan:
- •A Petroleum Geologist
- •1. Read and learn the following words.
- •2. Read the text and translate it into Russian.
- •3. Find in the text and read out English equivalents of these words and word-combinations.
- •4. Answer the following questions.
- •5. Translate into English.
- •6. Translate the text in writing. Use the dictionary.
- •7. Speak about the work of a petroleum geologist.
- •Английский язык
- •Библиотечно-издательский комплекс
- •625000, Тюмень, ул. Володарского, 38. Типография библиотечно-издательского комплекса.
- •625039, Тюмень, ул. Киевская, 52.
10. Speak about the petroleum industry according to the following plan:
importance of fossil fuels in the modern world;
history of the petroleum industry;
oil and oil products;
problems of the petroleum industry.
Unite II. Petroleum Origin
Start-up
What theories on the origin of hydrocarbons do you know?
1. Read and learn the following words.
origin – происхождение
Quantity – количество
hydrocarbons – углеводороды
organic matter – органическое вещество
to form from – образовывать(ся) из
to float – плавать, держаться на поверхности воды
mud – ил, грязь, буровой раствор
to decay – гнить, разлагаться
to convert to (into) – превращать(ся) в
formation – пласт (породы)
Mixture – смесь
compound – соединение
composition - состав
to contain – содержать
viscous – вязкий
associated gas – попутный газ
pressure differential – перепад давления
to migrate – мигрировать, перемещаться
source rock – материнская порода
reservoir rock – горная порода, обладающая способностью накапливать нефть; пористая порода; порода-коллектор
porous rock – пористая порода
impermeable layer - непроницаемый пласт; флюидоупор
to accumulate – накапливать(ся)
oil pool – нефтяной пласт, залежь нефти
to use – использовать
to saturate – насыщать, пропитывать
to generate – порождать, образовывать
2. Read and translate the following words and word-combinations. Practice your pronunciation.
associated natural gas [ə’səuʃɪeɪtɪd ‘nætʃərəl gæs]
sufficient quantity [sə’fɪʃənt ’kwɒntətɪ]
extraordinary theory [ɪk’strɔ:dənərɪ ‘θɪəri]
geoscientist [d3i:əu’saɪəntɪst]
ancient ocean [‘eɪnʃənt ‘əuʃən]
hydrogen [’haɪdrədʒən]
hydrocarbons [haɪdrə’ka:bənz]
sulphur [’sʌlfə]
oxygen [’ɒksɪdʒən]
nitrogen [’naɪtrədʒən]
viscous product [vɪskəs ’prɒdəkt]
source rock [sɔ:s rɒk]
pressure differential [’preʃə ‚dɪfə’renʃəl]
reservoir rock [’rezə‚vwa: rɒk]
saturate [’sætʃə‚reɪt]
impermeable layer [ɪm’pɜ:mɪəbəl ’leɪə]
3. Read and translate the words of the same root:
To compose – composition; to add – addition; to accumulate – accumulation; to move – movement; to mix – mixture; to migrate – migration; to form – formation; to combine – combination; to associate – association; to differ – different – difference – differential.
4. Read the text and translate it into Russian.
Petroleum Origin
The general term “petroleum” includes both crude oil and natural gas. Crude oil nearly always has more or less natural gas associated with it, but in some places considerable quantities of gas may exist alone.
Petroleum geologists have written more on the origin of petroleum than on any other subject. Speculation in this field was initiated in the 1860-s, but the problem of oil origin is still with us. Even extraordinary theories on the origin of hydrocarbons have surfaced over years. Some geologists believe petroleum to be of inorganic origin.
But most geoscientists consider petroleum to result from the breakdown of organic matter (plants and animals). Most geologists today agree that oil formed over million of years from the remains of tiny aquatic plants and animals that were exposed to the combined effects of time and temperature. In other words, oil formed from organic matter that was either "cooked" deep within the earth for long periods of time at low temperatures, or "cooked" for short periods of time at high temperatures.
Most crude oils formed from one-celled plants and animals, which floated on the surfaces of ancient oceans. As these organisms died, they settled to the ocean floor and were covered with mud. If the mud did not contain enough oxygen for the soft parts of these organisms to decay, with sufficient time and temperature, and over probably millions of years, the organic materials were slowly converted to oil.
Crude oils are mixtures of many different compounds. Most of the compounds found in oil are composed of hydrogen and carbon. In addition to these materials, called hydrocarbons, other compounds containing small amounts of sulphur, oxygen and nitrogen are also present.
Oil is a black viscous product of composition:
carbon |
80% to 89% |
hydrogen |
12% to 14% |
nitrogen |
0,3% to 1% |
sulphur |
0,3% to 3% |
oxygen |
2% to 3% |
The chemical composition itself, the kinds of rocks with which petroleum is associated, and certain optical tests, all point to the organic origin of petroleum.
Petroleum is not necessarily found where it was generated, but instead may have migrated from its source rock over large distance. Temperature changes, earth movements and differences in density between oil and salt water, caused the oil to migrate from the source rock, to accumulate in favourable geological formations. Under the pressure differential petroleum moves outward and upward along zones of increased permeability to a reservoir rock and accumulates there. Although the term “oil pool” is commonly used, there is really no actual pool or underground lake, but rather there is a porous rock saturated with oil and covered with an impermeable layer.
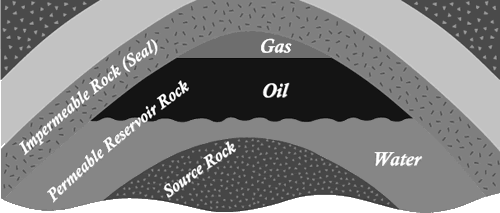
Therefore, several geologic elements are necessary for oil and gas to accumulate in sufficient quantities to create a pool large enough to be worth producing. These elements include an organic-rich source rock to generate the oil or gas, a porous reservoir rock to store the oil and gas in, and some sort of trap to prevent the oil and gas from leaking away.
