
- •Traffic alert and collision avoidance system General
- •Abbreviations and Acronyms
- •Tcas - general description General
- •Tcas - component location General Description
- •Radio Altimeter Inputs
- •Signal Processor
- •Suppression
- •Speech Processor
- •Receiver Processor
- •Transmitter
- •Beam Steering and Attenuator Circuits
- •Directional Antenna
- •Tcas - basic operation General
- •Whisper-Shout Interrogation
- •Mode s Interrogation
- •Tcas Data Calculation
- •Tcas - surveillance area General
- •Ra and ta Groups
- •Atc/tcas Control Panel
- •Tcas - navigation display General
- •Range Data
- •Altitude Readout
- •Altitude Separation
- •Absolute Altitude
- •Vertical Motion Arrow
- •Tcas Messages
- •Offscale
- •Traffic
- •Ra and ta No-Bearing Traffic
- •Corrective Action ra
- •Corrective Action ra
- •Increase Corrective Action ra
- •Tcas Self-Test Indications – ai
- •Tcas - self-test indications on tcas computer front panel Front Panel Self-Test
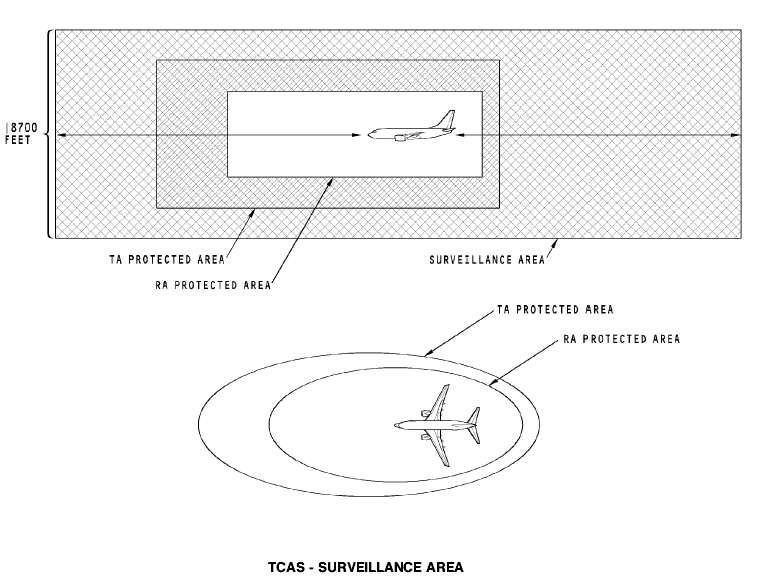
Tcas - surveillance area General
The TCAS tracks and evaluates up to 30 airplanes that are in the surveillance area. Airplanes in the surveillance area are put into one of these four groups:
Resolution advisory (RA) group
Traffic advisory (TA) group
Proximate traffic
Other traffic.
TCAS has a maximum surveillance area that is 8700 feet above and below your airplane. It has a range of 40 nm.
Ra and ta Groups
The TCAS forms two protected areas around its own airplane. The dimensions of these protected areas change with airspeed and altitude of the TCAS airplane and the closure rate of the target.
The protected area represents the time until the target will be at the closest point of approach (CPA) to the TCAS airplane. This protected area is called the TAU area.
To calculate the TAU, the TCAS computer uses this data:
Own airplane altitude
Target closure rate
Target range and altitude.
Traffic advisory TAU and resolution advisory TAU define areas around the TCAS airplane that, if penetrated by a target within the required altitude restrictions, would produce the appropriate warning from the TCAS computer.
The TCAS computer uses six sensitivity levels (2-7). Level 7 is the most sensitive. At level 2, no resolution advisories may occur. Below 1000 feet, level 2 is used and above 20000 feet, level 7 is used. Sensitivity levels are set by the TCAS computer based on own airplane altitude.
The TA and RA times vary with sensitivity level. At sensitivity level 3, RA TAU is 15 seconds while at sensitivity level 7, RA TAU is 35 seconds.
Proximate Traffic and Other Traffic
Proximate traffic is an airplane with a relative altitude
separation less than 1200 feet, is in a 6 nm radius of your
airplane, and is not a TA or RA threat.
Other traffic is an airplane with a range more than 6 nm that is not a TA or RA threat. If the range is less than 6 nm, the relative altitude must be more than 1200 feet.
TCAS - CONTROL AND DISPLAY
General
The EFIS control panel and the ATC control panel control the TCAS data that shows on the displays.
EFIS Control Panel
To show the TCAS data on the display, put the mode selector on the EFIS control panel in one of these modes:
Expanded approach
Expanded VOR
Expanded map
Centered map.
The range selector selects the range for the ND.
Push the TFC (traffic) switch on the range selector to let the ND show the TCAS data. When you do this, the TFC message and the TCAS symbols of any targets show on the display.
If the function selector on the ATC control panel is not in the TA or TA/RA position, the display does this:
Shows an amber message, TCAS OFF (TCAS OFF shows in all ND modes)
Removes all TCAS target symbols.
To remove the TCAS messages and symbols from the display, push the TFC switch again.
Atc/tcas Control Panel
The ATC/TCAS control panel sends control data through the ATC Mode S transponder to the TCAS computer. The TCAS computer sends this data to the DEU for display.
The function selector puts the TCAS computer in the TA only or TA/RA mode. In the TA only mode, the TCAS does not supply RA traffic symbols or advisories. It also does not supply RA aural messages. The function selector can also put the TCAS computer in the test mode.
The ND shows the relative altitude of the target above or below the symbol.
