
- •Atomic Structure Atomic structure - Summary Atomic structure
- •Classification of Elements Classification of Elements and the long periodic table
- •Chemical Combination Chemical Combination
- •The Main Groups Elements of the Periodic Table (Representative Elements) The Representative Elments
- •The group 5 - a:
- •The Transition Elements and Iron Transition Elements and Iron
- •Chemical calculation and quantitative analysis
- •Chemical Equilibrium
- •Electro- Chemistry
- •Organic Chemistry Hydrocarbon
- •Alkenes (CnH2n)
- •Nutrition Chemistry
Nutrition Chemistry
-
Nutrition chemistry is called boichemistry, because it connects
chemistry science with biology one.
- Saccharides or mono
charbohydrates have the general formula
![]() .
The ratio between hydrogen and oxygen is semilar to that in water ( 2
: 1).
- Saccharides are called carbohydrate i.e carbon hydrate,
because its general formula is [Cn(H2O)n]
- Monosaccharides are named simple saccharides as they do not
undergo hydrolysis into simpler units i.e they are in the simplest
form.
.
The ratio between hydrogen and oxygen is semilar to that in water ( 2
: 1).
- Saccharides are called carbohydrate i.e carbon hydrate,
because its general formula is [Cn(H2O)n]
- Monosaccharides are named simple saccharides as they do not
undergo hydrolysis into simpler units i.e they are in the simplest
form.
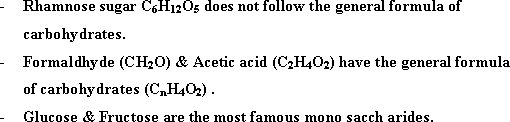 -
Mono saccarides are polyhydroxy compounds, because they contain many
hydroxyle groups in the sugar molecule. They dissolve easily in water
because they form hydrogen bonds with water molecules.
-
Mono saccarides are polyhydroxy compounds, because they contain many
hydroxyle groups in the sugar molecule. They dissolve easily in water
because they form hydrogen bonds with water molecules.
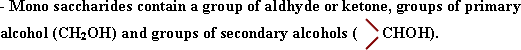 -
Glucose is from aldoses due to the prsence of aldhyde group in the
sugar molecule.
- Fructose is from ketoses due to the presence
of ketone group in the sugar molecule.
- Monosaccharides are
reduced to polyhydric alcohols by sodium amalgam (Glucose is reduced
to sorbitol) as the aldhyde group in the sugar molecule is reduced to
primary alcohol group.
- Glucose is oxidized by mild oxidizing
agent e.g (Br2/H2O)
to gluconic acid (monobasicity) and oxidized to saccharic acid
(di-basicity) by strong oxidizing agent eg. Dil HNO3.
- Disaccharides (sucrose, maltose and lactose) are
oligosaccarides, because each molecule is formed from condensation of
two monomsaccharides units.
- Disaccharides decompose by
hydrolysis to two units of monosaccharides which have no fermentation
characteristics.
- Maltose & lactose have areducing
property. They reduce the solutions of Fehling or Benedict to red
brick ppt, and reduce the ammonical silver nitrate to silver mirror.
- Sucrose has no reducing power, since the aldhydic and ketonic
groups in glucose and fructose are linked with each other, so their
characteristics disappear.
- Osazone compounds are used to
differentiate between the different types of sugar.
- The poly
saccharide molecule is formed from the condensation of more than ten
units of mono-saccharides (starch, cellulose or glycogene).
-
Polysaccharides are natural polymers, as they form from the
condenstation of unlimited numbers of units of glucose sugar.
-
Polysaccarides neither have reducing property nor fermentation
characteristic. The general formula is (C6H10O5)n
-
Starch dissolve in hot water. Its particles swell and explode.
-
starch does not melt by heating, its colour becomes blue when adding
drops of iodine.
- Cellulose is insoluble in water, acids or
alkalies, but it dissolves in ammoniacal copper II hydroxide
[Cu(NH4)2](OH)
2
and precipitate in a glossy form by adding dil. HCl (because the acid
is neutralized with ammonical copper II hydroxidel.
- Cellulose
reacts with acetic acid and cellulose acetate is produced (starting
material of synthetic silk)
-
Glucose is from aldoses due to the prsence of aldhyde group in the
sugar molecule.
- Fructose is from ketoses due to the presence
of ketone group in the sugar molecule.
- Monosaccharides are
reduced to polyhydric alcohols by sodium amalgam (Glucose is reduced
to sorbitol) as the aldhyde group in the sugar molecule is reduced to
primary alcohol group.
- Glucose is oxidized by mild oxidizing
agent e.g (Br2/H2O)
to gluconic acid (monobasicity) and oxidized to saccharic acid
(di-basicity) by strong oxidizing agent eg. Dil HNO3.
- Disaccharides (sucrose, maltose and lactose) are
oligosaccarides, because each molecule is formed from condensation of
two monomsaccharides units.
- Disaccharides decompose by
hydrolysis to two units of monosaccharides which have no fermentation
characteristics.
- Maltose & lactose have areducing
property. They reduce the solutions of Fehling or Benedict to red
brick ppt, and reduce the ammonical silver nitrate to silver mirror.
- Sucrose has no reducing power, since the aldhydic and ketonic
groups in glucose and fructose are linked with each other, so their
characteristics disappear.
- Osazone compounds are used to
differentiate between the different types of sugar.
- The poly
saccharide molecule is formed from the condensation of more than ten
units of mono-saccharides (starch, cellulose or glycogene).
-
Polysaccharides are natural polymers, as they form from the
condenstation of unlimited numbers of units of glucose sugar.
-
Polysaccarides neither have reducing property nor fermentation
characteristic. The general formula is (C6H10O5)n
-
Starch dissolve in hot water. Its particles swell and explode.
-
starch does not melt by heating, its colour becomes blue when adding
drops of iodine.
- Cellulose is insoluble in water, acids or
alkalies, but it dissolves in ammoniacal copper II hydroxide
[Cu(NH4)2](OH)
2
and precipitate in a glossy form by adding dil. HCl (because the acid
is neutralized with ammonical copper II hydroxidel.
- Cellulose
reacts with acetic acid and cellulose acetate is produced (starting
material of synthetic silk)
 Mercerization:
Spun
cotton fibers are treated with caustic soda solution, the cotton
threads become more tolerant, brightes and easily to be dye.
-
Herbivorous intestine can hydrolize cellulose into glucose, by the
action of some bacteria that they contain.
- Oils and fats are
triglyceride esters, since they form from the combination between
trihydric alcohol and three molecules of fatty acids.
Saponification:
The
hydrolysis of esters iin the presence of strong alkali (NaOH) or
(KOH) to form sodium or pottasium salt of the fatty acid (soap).
-
The iodine number:
The
amount of iodine in grams needed to saturated 100 grams of the
triglyceride.
- The iodine number of stearic acid = zero
because it is saturated.
-
rancidity of oils or fat:
A
chemical reaction that produced a change in colour, odour and taste
of fats and oil as a result of oxidation .
- Artificial fats
are produced from the hydrogenation of vegetable oils.
-
Margarine (butter substitutes) are produced by mixing hydrogenated
oil with milk.
- Proteins are natural polymers, as they are
produced from the condensation of unlimited number of amino acids.
They combine together forming a chain of polypeptide.
Amino
acid is the basic unit of protein molecule.
- Amino acids are
considered as the amino derivatives of organic acids, since a
hydrogen atom in the alkyle group of organic acid is replaced with an
amino group.
- eg: Glycine is amino acetic acid.
- Amino
acids are amphoteric compounds since they react with an acid as a
base and react with the base as an acid to give salt and water.
Mercerization:
Spun
cotton fibers are treated with caustic soda solution, the cotton
threads become more tolerant, brightes and easily to be dye.
-
Herbivorous intestine can hydrolize cellulose into glucose, by the
action of some bacteria that they contain.
- Oils and fats are
triglyceride esters, since they form from the combination between
trihydric alcohol and three molecules of fatty acids.
Saponification:
The
hydrolysis of esters iin the presence of strong alkali (NaOH) or
(KOH) to form sodium or pottasium salt of the fatty acid (soap).
-
The iodine number:
The
amount of iodine in grams needed to saturated 100 grams of the
triglyceride.
- The iodine number of stearic acid = zero
because it is saturated.
-
rancidity of oils or fat:
A
chemical reaction that produced a change in colour, odour and taste
of fats and oil as a result of oxidation .
- Artificial fats
are produced from the hydrogenation of vegetable oils.
-
Margarine (butter substitutes) are produced by mixing hydrogenated
oil with milk.
- Proteins are natural polymers, as they are
produced from the condensation of unlimited number of amino acids.
They combine together forming a chain of polypeptide.
Amino
acid is the basic unit of protein molecule.
- Amino acids are
considered as the amino derivatives of organic acids, since a
hydrogen atom in the alkyle group of organic acid is replaced with an
amino group.
- eg: Glycine is amino acetic acid.
- Amino
acids are amphoteric compounds since they react with an acid as a
base and react with the base as an acid to give salt and water.
 -
The isoelectric point is the pH value at which the amino acid exists
in the form of dipolar ion and precipetate.
- The amino acids
exist in the neutral medium in the form of dipolar ion, in alkaline
medium they are presented as anions and in acidic medium as cations.
- The essential amino acids are ten in number. They must be
taken in diet since they cannot be synthesized in the body, while the
non essential amino acids are not essential to be taken in diet, as
they are synthesized in the body.
-
The isoelectric point is the pH value at which the amino acid exists
in the form of dipolar ion and precipetate.
- The amino acids
exist in the neutral medium in the form of dipolar ion, in alkaline
medium they are presented as anions and in acidic medium as cations.
- The essential amino acids are ten in number. They must be
taken in diet since they cannot be synthesized in the body, while the
non essential amino acids are not essential to be taken in diet, as
they are synthesized in the body.
