
- •Atomic Structure Atomic structure - Summary Atomic structure
- •Classification of Elements Classification of Elements and the long periodic table
- •Chemical Combination Chemical Combination
- •The Main Groups Elements of the Periodic Table (Representative Elements) The Representative Elments
- •The group 5 - a:
- •The Transition Elements and Iron Transition Elements and Iron
- •Chemical calculation and quantitative analysis
- •Chemical Equilibrium
- •Electro- Chemistry
- •Organic Chemistry Hydrocarbon
- •Alkenes (CnH2n)
- •Nutrition Chemistry
Organic Chemistry Hydrocarbon
1-In
1806, the scientist Berzelius divided all compounds into two
categories:
a-
Organic compounds:
They are compounds that extracted from animal or plant origin.
b-
Inorganic compounds:
They are compounds originate from mineral sources in earth.
2-Vital
Force theory: Brezelius considered that organic compounds are formed
by vital force which is found in living cells of the body and it is
impossible to synthesized them in laboratories.
3-In 1828, The
German scientistWohler
destroyed the vital force theory, when he prepared urea by heating an
aqueous solution of two inorganic compounds, ammonium chloride and
silver cyanate.
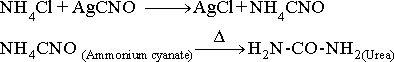 4-Organic
chemistry focused on the study of carbon element with exception of
carbon oxides, carbonate and cyanides salt.
5- The number of
organic compounds are more than the organic ones. The ratio between
the organic and inorganic compounds is approximately 20 : 1 .
6-The
abundance of organic compounds is due to the ability of carbon atom
to combine with itself or with others atoms by different kinds of
bond, it might connect through single, double, triple bonds.
7-Carbon atoms can join together with different methods, either
straight chains, branched chains, homocyclic or heterocyclic.
4-Organic
chemistry focused on the study of carbon element with exception of
carbon oxides, carbonate and cyanides salt.
5- The number of
organic compounds are more than the organic ones. The ratio between
the organic and inorganic compounds is approximately 20 : 1 .
6-The
abundance of organic compounds is due to the ability of carbon atom
to combine with itself or with others atoms by different kinds of
bond, it might connect through single, double, triple bonds.
7-Carbon atoms can join together with different methods, either
straight chains, branched chains, homocyclic or heterocyclic.
 9-
Molecular Formula: It is the formula which indicates the number and
kind of the elements which form the chemical compound, and doesn't
show the kind of the linkage between the atoms in the molecule.
10-Structural Formula: It's the formula which indicates the
number and kind of each element in the molecule, and the kind of
linkage between the atoms by the covalent bonds.
11-The number
of covalent bonds around the atom indicates its valancy .Each single
covalent bond represents one pair of valency.
12-Isomerism:
many organic compounds are different in the physical and chemical
properties and also in structural formula but they have the same
molecular formula.
13- The structural formula show that the
molecule has a stereostructure shape i.e. its atoms are directed in
the three dimensions.
14- Detection
of carbon and hydrogen in organic compounds:
1-The
white colour of anhydrous copper sulphate turns into blue which
indicates the absorption of (CuSO4)
to water vapour which is formed from combination of oxygen of CuO
with the hydrogen of organic compound.
2-Lime water turns
turbid due to the evolution of carbon dioxide (CO2),
which is formed from combination of oxygen of (CuO) with the carbon
of the organic compound.
Conclusion:The
organic compound contains carbon and hydrogen.
9-
Molecular Formula: It is the formula which indicates the number and
kind of the elements which form the chemical compound, and doesn't
show the kind of the linkage between the atoms in the molecule.
10-Structural Formula: It's the formula which indicates the
number and kind of each element in the molecule, and the kind of
linkage between the atoms by the covalent bonds.
11-The number
of covalent bonds around the atom indicates its valancy .Each single
covalent bond represents one pair of valency.
12-Isomerism:
many organic compounds are different in the physical and chemical
properties and also in structural formula but they have the same
molecular formula.
13- The structural formula show that the
molecule has a stereostructure shape i.e. its atoms are directed in
the three dimensions.
14- Detection
of carbon and hydrogen in organic compounds:
1-The
white colour of anhydrous copper sulphate turns into blue which
indicates the absorption of (CuSO4)
to water vapour which is formed from combination of oxygen of CuO
with the hydrogen of organic compound.
2-Lime water turns
turbid due to the evolution of carbon dioxide (CO2),
which is formed from combination of oxygen of (CuO) with the carbon
of the organic compound.
Conclusion:The
organic compound contains carbon and hydrogen.
![]() 15-
Hydrocarbons are organic compounds consist of carbon and hydrogen
only.
16- Alkanes
(CnH2n+2)saturated
aliphatic open chain hydrocarbons .The carbon atoms are combined
together by a single bond called sigma bond which is strong and
difficult to be broken therefore they are relatively chemically
inactive.
17- Each alkane compound exceeds the previous one by
(-CH2)
group.
18-Members of alkanes are ended by the suffix (ane)
which indicates that the compound is belonging to (alkanes chain) ,
The prefix of the name indicates the number of carbon atoms in the
molecule . For example the prefix Meth = 1 , Eth = 2 , Prop = 3 , But
= 4 , Pent =5 and so on . Alkanes form a homologous series.
19-Homologous series: It is a group of compounds that having
the same molecular formula , chemical properties and graduated
physical properties.
20-Alkanes have a very important role as a
fuel, as natural gas which is used now as fuel in homes.
21-
The Alkyl Radical (R -)
:It is an organic atomic group which does not found alone. It is
derived from the corresponding alkane by removing one hydrogen atom
.Alkyl radicals are given the symbol "R".Their general
formula is (CnH2n+1).Its
name is derived from the corresponding alkane by replacing the suffix
(ane) by (yl).
22-
The nomenclature of alkanes: (IUPAC system)
International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry.
23-The
nomenclature of alkanes by the IUPAC system may be summarized as
follows:
1-The name of the hydrocarbon is determined according
to the longest continuous carbon chain .
2-The carbon atoms are
given numbers in the longest chain.
3- If the longest
hydrocarbon chain free from any branches or side chain the carbon
atoms are given numbers from any side (left or right side).
4-If
the longest hydrocarbon chain attached to an alkyl group or any other
atoms. The numbering of carbon atoms in the hydrocarbon chain begins
from the side which is nearer to the branch. The nomenclature begins
by the number of the carbon atom from which the chain arises, then
the name of the branch, and ending by the name of the alkane.
If
the side group is repeated in the hydrocarbon chain we use prefix Di
- or Tri - or Tetra - to indicate the number of repetition.
1-If
the branch is a (-ve) group such as. Cl
-
, Br
-
or NO2
-
, the name of this group is ended by the letter (O) so we say chloro
, bromo or nitro.
2-If the side groups are different (alkyl
group and halogens). the groups are arranged according to their
alphabetical Latin names.
24-Methane can be prepared in lab. by
dry distillation of anhydrous sodium acetate with soda lime
15-
Hydrocarbons are organic compounds consist of carbon and hydrogen
only.
16- Alkanes
(CnH2n+2)saturated
aliphatic open chain hydrocarbons .The carbon atoms are combined
together by a single bond called sigma bond which is strong and
difficult to be broken therefore they are relatively chemically
inactive.
17- Each alkane compound exceeds the previous one by
(-CH2)
group.
18-Members of alkanes are ended by the suffix (ane)
which indicates that the compound is belonging to (alkanes chain) ,
The prefix of the name indicates the number of carbon atoms in the
molecule . For example the prefix Meth = 1 , Eth = 2 , Prop = 3 , But
= 4 , Pent =5 and so on . Alkanes form a homologous series.
19-Homologous series: It is a group of compounds that having
the same molecular formula , chemical properties and graduated
physical properties.
20-Alkanes have a very important role as a
fuel, as natural gas which is used now as fuel in homes.
21-
The Alkyl Radical (R -)
:It is an organic atomic group which does not found alone. It is
derived from the corresponding alkane by removing one hydrogen atom
.Alkyl radicals are given the symbol "R".Their general
formula is (CnH2n+1).Its
name is derived from the corresponding alkane by replacing the suffix
(ane) by (yl).
22-
The nomenclature of alkanes: (IUPAC system)
International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry.
23-The
nomenclature of alkanes by the IUPAC system may be summarized as
follows:
1-The name of the hydrocarbon is determined according
to the longest continuous carbon chain .
2-The carbon atoms are
given numbers in the longest chain.
3- If the longest
hydrocarbon chain free from any branches or side chain the carbon
atoms are given numbers from any side (left or right side).
4-If
the longest hydrocarbon chain attached to an alkyl group or any other
atoms. The numbering of carbon atoms in the hydrocarbon chain begins
from the side which is nearer to the branch. The nomenclature begins
by the number of the carbon atom from which the chain arises, then
the name of the branch, and ending by the name of the alkane.
If
the side group is repeated in the hydrocarbon chain we use prefix Di
- or Tri - or Tetra - to indicate the number of repetition.
1-If
the branch is a (-ve) group such as. Cl
-
, Br
-
or NO2
-
, the name of this group is ended by the letter (O) so we say chloro
, bromo or nitro.
2-If the side groups are different (alkyl
group and halogens). the groups are arranged according to their
alphabetical Latin names.
24-Methane can be prepared in lab. by
dry distillation of anhydrous sodium acetate with soda lime
![]() 25-
Soda lime is a mixture of Na OH and quick lime CaO which doesn't take
part in the reaction but it helps in reducing the melting points of
the reaction mixture .
26-The first four members of alkanes are
gases in normal temperature. Alkanes ,which contain from
[5-17]
carbon atoms are liquids e.g gasoline and kerosine which are used as
liquid fuel .The compounds which contain more than 17 carbon atoms
are solids e.g. paraffin wax.
27-Alkanes are non polar
compounds insoluble in water, so the metals are covered by heavy
alkanes to protect them against rust and corrosion.
28-The
carbon atoms in alkanes are combined together by the strong sigma
bonds , These bonds cannot be broken easily except under certain
conditions, Therefore, alkanes are comparatively, inactive compounds.
29 -All alkanes burn giving water vapour and carbon dioxide,
these reactions are highly exothermic, that is
25-
Soda lime is a mixture of Na OH and quick lime CaO which doesn't take
part in the reaction but it helps in reducing the melting points of
the reaction mixture .
26-The first four members of alkanes are
gases in normal temperature. Alkanes ,which contain from
[5-17]
carbon atoms are liquids e.g gasoline and kerosine which are used as
liquid fuel .The compounds which contain more than 17 carbon atoms
are solids e.g. paraffin wax.
27-Alkanes are non polar
compounds insoluble in water, so the metals are covered by heavy
alkanes to protect them against rust and corrosion.
28-The
carbon atoms in alkanes are combined together by the strong sigma
bonds , These bonds cannot be broken easily except under certain
conditions, Therefore, alkanes are comparatively, inactive compounds.
29 -All alkanes burn giving water vapour and carbon dioxide,
these reactions are highly exothermic, that is
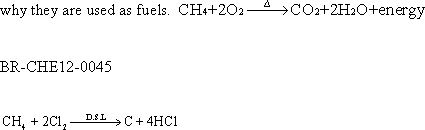 30-The
reactions with Halogens:
a. In direct sunlight : If methane
reacts with chlorine or fluorine in the direct sun light, the halogen
eliminates hydrogen from methane and black carbon is remained . The
reaction is accompanied by explosion ( this reaction is called
elimination reaction
30-The
reactions with Halogens:
a. In direct sunlight : If methane
reacts with chlorine or fluorine in the direct sun light, the halogen
eliminates hydrogen from methane and black carbon is remained . The
reaction is accompanied by explosion ( this reaction is called
elimination reaction
![]() 31-In
indirect sunlight : Alkanes react with halogens in indirect sun light
in a series of substitution reactions these are :
31-In
indirect sunlight : Alkanes react with halogens in indirect sun light
in a series of substitution reactions these are :
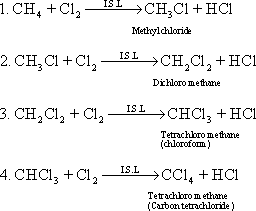 32-
Chloroform was used for a long time as anesthetic substance but its
uses stopped because the inaccurate estimation of the dose for each
patient causes the death. Halothane is used now as anesthetic
substance with safety and its formula CHBrCl - CF3
33-The
compound 1,1,1 trichloro ethane is used in the dry cleaning.
34-Freons were used in air conditions and fridges, also as a
rushed substance to liquid and perfumes and as a cleaner of
electronic sets.
35-Freons are consider as halogenated
derivative of alkanes as CF4
tetra flouro methane but the famous one is dichloro, diflouromethane
CF2
Cl2
or1-bromo 1-chloro-2,2,2 triflouroethane . Freons are used by large
quantities due to its sheep price, easily to be liquefied, non
poisonous and non corrosive for metals, however Freon's cause the
decay of the ozone layer which protect the earth against harmful
effect of ultra violet rays .
36.Thermal catalytic cracking:
heating the heavy petroleum products under high pressure and
temperature in the presence of a catalyst to produce two kind of
products. This process usually takes place during the refining of
petroleum oil to convert the heavy long petroleum chains to the daily
used lighter short chain products .
37-Methane is used to
obtain finely divided carbon, (black carbon ).The black carbon is
produced by heating methane to 1000?C in the absence of air.
32-
Chloroform was used for a long time as anesthetic substance but its
uses stopped because the inaccurate estimation of the dose for each
patient causes the death. Halothane is used now as anesthetic
substance with safety and its formula CHBrCl - CF3
33-The
compound 1,1,1 trichloro ethane is used in the dry cleaning.
34-Freons were used in air conditions and fridges, also as a
rushed substance to liquid and perfumes and as a cleaner of
electronic sets.
35-Freons are consider as halogenated
derivative of alkanes as CF4
tetra flouro methane but the famous one is dichloro, diflouromethane
CF2
Cl2
or1-bromo 1-chloro-2,2,2 triflouroethane . Freons are used by large
quantities due to its sheep price, easily to be liquefied, non
poisonous and non corrosive for metals, however Freon's cause the
decay of the ozone layer which protect the earth against harmful
effect of ultra violet rays .
36.Thermal catalytic cracking:
heating the heavy petroleum products under high pressure and
temperature in the presence of a catalyst to produce two kind of
products. This process usually takes place during the refining of
petroleum oil to convert the heavy long petroleum chains to the daily
used lighter short chain products .
37-Methane is used to
obtain finely divided carbon, (black carbon ).The black carbon is
produced by heating methane to 1000?C in the absence of air.
![]() Black
carbon is used in the manufacture of car tiers, black painting,
polishes, and printing ink .
38- Methane is used to obtain to
obtain " water gas".water gas is a mixture of hydrogen and
carbon monoxide which is used as reducing agent or as a flammable
fuel.
Black
carbon is used in the manufacture of car tiers, black painting,
polishes, and printing ink .
38- Methane is used to obtain to
obtain " water gas".water gas is a mixture of hydrogen and
carbon monoxide which is used as reducing agent or as a flammable
fuel.
![]()
