
- •Mr. Ahmed mabrouk second term 2011
- •1(A Metal substitutes water hydrogen or acid:
- •2) The substitution of a metal instead of another one into its salt
- •1) Reaction between acid and Alkali. (Neutral)
- •2) The reaction of acid with salt
- •3 ) The Reaction of salt with salt
- •L esson 1 exercises
- •L esson 2: Speed of Chemical reactions
- •The definition of the speed of chemical reaction
- •The speed of chemical reaction:
- •Type of coherence in reactants
- •C atalysts have some common properties:
- •Biology
- •L esson 2 Exercise
- •Lesson 3: Solution
- •Solutions of acids, bases and minerals
- •Economic importance of some common acids
- •E conomic importance of some common bases
- •Economic importance of some common minerals
- •Lesson 3 Exercise
- •L esson 3 Exercise
- •Science, Technology and Society
- •A) Shinning metal
- •B) In the Kitchen
- •C) In the garden
- •D) In the medical field
- •Electromotive force ( emf )
- •T ypes of electric resistance:
- •The relationship between the current intensity and the potential difference (Ohm’s law):
- •Lesson 1 exercises
- •1 Complete the following sentences:
- •2 Choose the correct answer for each of the following statements:
- •3 Write the scientific term corresponding to each of the following statements:
B) In the Kitchen
● Add a small amount of it in the bottom of a waste basket before putting the bag to prevent the bad odors
● soak the legumes in water and add a small amount of sodium bicarbonate to help in decreasing the bloating that accompanies eating legumes.
● Add a small amount of sodium bicarbonate in the kitchens sink الحوض and pour on it boiling water, and notice that the draining of the sink is faster.
C) In the garden
● Place sodium bicarbonate without addition in the places where ants come out, and with time you will notice their disappearance.
D) In the medical field
● Clean your teeth with it by means of immersing a piece of cotton wet with water in sodium bicarbonate. With time you will notice the teeth’s w
U nit
2 Lesson 1: The Physical Properties of the Electric Current
nit
2 Lesson 1: The Physical Properties of the Electric Current
Electricity is a hidden energy that can not accurately describe yet, we identify it through its various effects and phenomena.
You might know that the electric current is generated in electric power stations that are away from your house by hundreds or thousands of kilometers.
How is the electric current generated? What does the electric current mean?

![]() You
knew that the protons are present in the nucleus atom while the
electrons revolve around it in outer orbits affected by an attraction
force??
You
knew that the protons are present in the nucleus atom while the
electrons revolve around it in outer orbits affected by an attraction
force??
(resulting from the attraction between positively charged protons and negatively charged electrons). In the presence of an outer attraction force (other atoms or positive charges) the electrons will leave the atom and move in the wires (conductors) creating the electric current.
Physical properties of the electric current:

It is the quantity of the electric charges passing through a cross - section of the conductor in one second.

It is measured by using instrument called an Ammeter that has a symbol
. The measuring unit of the current intensity is known as Ampere.
 (Ampere)
is a quantity of charge of 1 coulomb passing through any cross
section of the conductor in one second.
(Ampere)
is a quantity of charge of 1 coulomb passing through any cross
section of the conductor in one second.
![]()

Q :
Calculate the current intensity due to the flow of 5400 coulomb in 5
min
:
Calculate the current intensity due to the flow of 5400 coulomb in 5
min
Through a cross - section of a conductor.
Solution: ……………………………………………………………………………………..
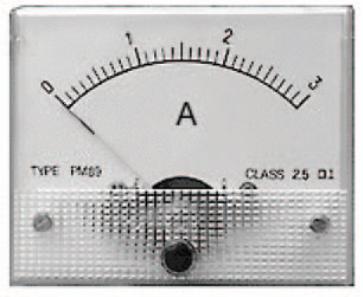
Q: How is the Ammeter connected? Why?
Ammeter is connected in series connection to measure the electric current intensity.

What does the electric potential of a conductor mean?
I t
is the condition of an electric conductor that shows the transfer of
the electricity to and from it when it is connected to another
conductor.
t
is the condition of an electric conductor that shows the transfer of
the electricity to and from it when it is connected to another
conductor.
H ow
does electricity move from one conductor to another, try to
understand the following example:
ow
does electricity move from one conductor to another, try to
understand the following example:
The temperature moves from a hot object to a cold object when they are connected.
the temperature continues to move until their temperatures are equal.
The movement of temperature does not depend on the size of the two objects, but on the difference in their temperatures.
The same goes for electricity:
The difference of electric potential between two conductors determines the transfer of the electric charges to and from an object if it is connected to another conductor.
If two charged conductors touch the electric current will move from the high conductor to the low conductor until they become equal.
The flow of the charges does not depend on their amount, but on the conductor potential in comparison to the other conductor.
A joule is the amount of work done by a force of one newton moving an object through a distance of one meter.
![]()
Q: If the work done to transfer electric charge of 300 coulomb between two points is 33300 Joule, calculate the potential difference between the two points .
Solution: ……………………………………………………………………………………..
The coulomb: is the charge transferred by a constant current of one ampere in one second.
Volt: is the potential difference between the two poles of a conductor on doing a work of 1 joule to transfer a quantity of electricity (1 coulomb).
 **
The potential difference is measured by using instrument called
Voltmeter
that has a symbol.
**
The potential difference is measured by using instrument called
Voltmeter
that has a symbol.
** The measuring unit of the potential difference is known as Volt.

Q: How is the Voltmeter connected? Why?
Voltmeter is connected in parallel connection to measure the electric potential difference.
