
- •Mr. Ahmed mabrouk second term 2011
- •1(A Metal substitutes water hydrogen or acid:
- •2) The substitution of a metal instead of another one into its salt
- •1) Reaction between acid and Alkali. (Neutral)
- •2) The reaction of acid with salt
- •3 ) The Reaction of salt with salt
- •L esson 1 exercises
- •L esson 2: Speed of Chemical reactions
- •The definition of the speed of chemical reaction
- •The speed of chemical reaction:
- •Type of coherence in reactants
- •C atalysts have some common properties:
- •Biology
- •L esson 2 Exercise
- •Lesson 3: Solution
- •Solutions of acids, bases and minerals
- •Economic importance of some common acids
- •E conomic importance of some common bases
- •Economic importance of some common minerals
- •Lesson 3 Exercise
- •L esson 3 Exercise
- •Science, Technology and Society
- •A) Shinning metal
- •B) In the Kitchen
- •C) In the garden
- •D) In the medical field
- •Electromotive force ( emf )
- •T ypes of electric resistance:
- •The relationship between the current intensity and the potential difference (Ohm’s law):
- •Lesson 1 exercises
- •1 Complete the following sentences:
- •2 Choose the correct answer for each of the following statements:
- •3 Write the scientific term corresponding to each of the following statements:
L esson 2: Speed of Chemical reactions
A chemical reaction is a process in which a chemical substance turns to another one.
Chemical reactions differ in the time they take to occur. For example:
Some reactions take very short time like fireworks.
Some reactions are a bit slower like the reaction of oil with caustic soda.
Some reactions are the slowest and need several months such as iron rust.
Some reactions may take tens or hundreds of years like reactions inside the earth to form oil.
The definition of the speed of chemical reaction
To identify the speed of a chemical reaction, we will study the following equation:
 N2O5
2NO2
+ 1/2 O2
N2O5
2NO2
+ 1/2 O2
Nitrogen pent oxide breaks up into nitrogen dioxide & oxygen
Oxygen atoms collect together to from molecules that rise.
The following graph illustrates:
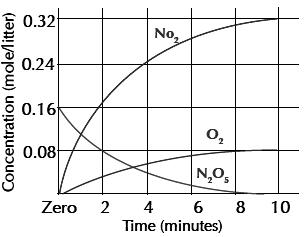
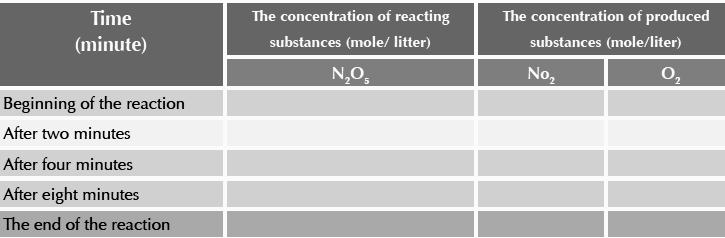
The breaking up of nitrogen pent oxide with time.
The concentration (mole/liter) is represented on the vertical axis while time (minute) is represented on the horizontal axis.
The blue graphical line shows the change in the concentration of N2O5.
The red graphical line shows the change in the concentration of nitrogen dioxide.
The green graphical line shows the change in the concentration of oxygen.
We notice that at the start of the reaction, the concentration of N2O5 is 0.16 mole/liter (100%) while the concentration of both NO2 and O2 is zero%.
A
 s
time passes,
the concentration of nitrogen pent oxide starts to decrease whereas
the concentration of both nitrogen dioxide and oxygen starts to
increase.
s
time passes,
the concentration of nitrogen pent oxide starts to decrease whereas
the concentration of both nitrogen dioxide and oxygen starts to
increase.By the end of the reaction, the concentration of N2O5 becomes zero mole/liter (zero %) whereas the concentration of both NO2 and O2 increases (100%).
The speed of chemical reaction:
“The change in the concentration of the reactants and resultants at a time unit”
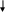 The
speed of chemical reaction can be practically measured by the rate of
disappearance of a reactant or the rate of appearance of a resultant.
The
speed of chemical reaction can be practically measured by the rate of
disappearance of a reactant or the rate of appearance of a resultant.
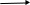 Example:
2 NaOH + Cu SO4
Na2
SO4
+ Cu (OH)2
Example:
2 NaOH + Cu SO4
Na2
SO4
+ Cu (OH)2On adding sodium hydroxide to blue copper sulphate, colorless sodium sulphate forms and blue precipitate of copper hydroxide is formed.
The speed of this reaction is measured by the disappearance rate of copper sulphate color or the appearance rate of the precipitate.
Factors affecting the speed of chemical reaction:
The nature of reactants.
The concentration of reactants.
The temperature of the reactants.
Catalysts.

The nature of reactants means.
The kind of coherence تماسكin reactants.
The area of reactants exposed to reaction.
Type of coherence in reactants
Covalent compounds: are slow in reacting because they do not break up in ions.
The reactions are between molecules.
Such as the reaction between organic compounds.
Ionic compounds: are fast in reaction because they break up in ions.
The reactions are between the ions.
Such as the reaction of sodium chloride with silver nitrates:
Each of the two compounds breaks up into its ions and then the reaction occurs between the ions.
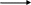 NaCl
+ AgNO3 NaNO3
+ AgCl
NaCl
+ AgNO3 NaNO3
+ AgCl
Na+ + Cl- + Ag+ + NO3 - Na+ + NO3- + AgCl
T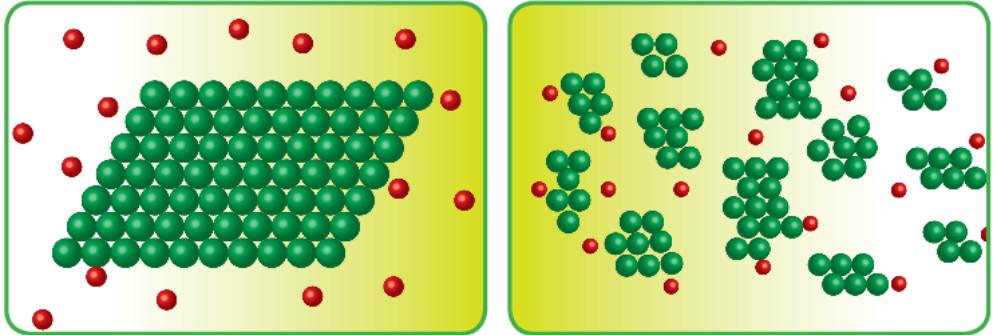
 he
area of reactants exposed to reaction:
he
area of reactants exposed to reaction:
The bigger the area exposed to the reaction,
the faster the chemical reaction is.
 Activity:
Effect of surface area on the speed of chemical reaction
Activity:
Effect of surface area on the speed of chemical reaction
Procedures:
Put iron fillings in test tube (1) and a piece of iron in test tube (2).
Put equal amount of diluted hydrochloric acid in both tubes.
Observation:
The rate of the reaction of hydrochloric acid with the iron filling is faster than the one piece of iron.
The reaction ends in case of iron fillings in shorter time than that of the one piece.
Conclusion:
 Fe
+ 2HCl FeCl2
+ H2
Fe
+ 2HCl FeCl2
+ H2
Iron Hydrochloric acid Iron chloride Hydrogen

The area exposed to the reaction in case of the iron filling is bigger than that in case of the piece of iron.
The bigger the area exposed to the reaction is, the faster the reaction is.

One factor of the increase in the speed of chemical reaction is the increase in the concentration of reactants. This increases the number of collisions between molecules and consequently the speed of the reaction increases.
One small spoon of sugar makes a glass of lemon juice sweet but if we add a big spoon, it tastes sweeter. Thus, we can say that in the second glass of lemon the sugar molecules are more concentrated.
In a quiet street, the probability of collisions decreases like in the molecules of a substance with a low concentration.
In a crowded street, the probability of collisions increases like the molecules of a substance with a high concentration.
The burning of the aluminium coil in pure oxygen (high concentration) is faster than its burning in oxygen in the air (less oxygen concentration).


Activity: The effect of reactants concentration on the speed of the chemical.
Procedures
Put diluted hydrochloric acid in tube “A”.
Put the same amount of concentrated hydrochloric acid in tube “B”.
Put a piece of magnesium in each tube
Observation: Tube B contains more bubbles.
Conclusion:
We can deduce through this activity that the speed of a chemical reaction increases when the concentration of the reactants increases.

Most of the chemical reactions speed up when temperature increases.
Because the number of collisions between molecules increases.
If you want to cook eggs faster, you increase the temperature to increase the speed of chemical reaction that helps in cooking of food.
Food gets spoilt quickly if not frozen because of the chemical reactions done by bacteria. Cooling of food at low temperature slows down those reaction.
 Activity:
The effect of temperature on chemical reactions
Activity:
The effect of temperature on chemical reactions
Steps:
Fill half of the first glass with hot water and the second one with cold water.
Add an effervescent tablet to each of the glasses.
Observation: The first glass of hot water is faster in effervescence فوران.
Conclusion: the speed of a chemical reaction increases if the temperature of the reaction increases.

A catalyst is a substance which speeds up the chemical reaction without sharing in it or being used up.
Some chemical reactions are so slow but they speed up when a catalyst is added.
Most catalysts speed up the chemical reaction and they are called a positive catalyst.
Other catalysts are used to slow down a chemical reaction and they are called a negative catalyst.
