
- •Section 1. Aerodynamics of lifting surfaces Topic 6. The aerodynamic characteristics of Wings in a supersonic gas flow. Wing in transonic range of speeds
- •6.1. Rectangular wings.
- •6.1.1. Lift.
- •6.1.2. Drag.
- •6.1.3. Location of aerodynamic center.
- •6.2. Triangular wings with subsonic leading edges.
- •6.2.1. Analysis of the aerodynamic characteristics.
- •6.3. Triangular wing with supersonic leading edges.
- •6.4. Wings of any plan form. The qualitative analysis of the aerodynamic characteristics.
- •6.4.1. Lift.
- •6.4.2. Wave drag.
- •6.4.3. Induced drag.
- •6.4.4. Location of aerodynamic center.
- •6.5. Wing in transonic range of speeds.
- •6.6. Wing induced drag at with taking into account local supersonic flows.
Section 1. Aerodynamics of lifting surfaces Topic 6. The aerodynamic characteristics of Wings in a supersonic gas flow. Wing in transonic range of speeds
The
wing aerodynamic characteristics in supersonic gas flow (![]() )
depend on edges type: subsonic or supersonic. In the beginning we
shall consider the aerodynamic characteristics of wings of the
individual plan forms and on their example we shall reveal some
common properties characteristic for wings of derived plan forms.
Then we shall consider features of the aerodynamic characteristics of
wings with various plan forms.
)
depend on edges type: subsonic or supersonic. In the beginning we
shall consider the aerodynamic characteristics of wings of the
individual plan forms and on their example we shall reveal some
common properties characteristic for wings of derived plan forms.
Then we shall consider features of the aerodynamic characteristics of
wings with various plan forms.
6.1. Rectangular wings.
Fig.
6.1. Pressure distribution
On
a surface of a wing
![]() and trailing edge
and trailing edge
![]() - supersonic, lateral edges
- supersonic, lateral edges
![]() and
and
![]() - subsonic on a wing (Fig. 6.1). The influence of lateral edges
(pressure equalization between the lower and upper surface) has an
effect only in areas
- subsonic on a wing (Fig. 6.1). The influence of lateral edges
(pressure equalization between the lower and upper surface) has an
effect only in areas
![]() and
and
![]() ,
limited by Mach cones, in difference from subsonic flow where the
pressure equalization (influence of lateral edges) occurs all
spanwise. Outside of area of influence (surface of a wing
,
limited by Mach cones, in difference from subsonic flow where the
pressure equalization (influence of lateral edges) occurs all
spanwise. Outside of area of influence (surface of a wing
![]() )
the flow is similar to flow about flat plate in two-dimensional flow.
The pressure factor in any point of wing surface outside of areas of
influence of lateral edges is equal
)
the flow is similar to flow about flat plate in two-dimensional flow.
The pressure factor in any point of wing surface outside of areas of
influence of lateral edges is equal
![]() .
(6.1)
.
(6.1)
In the field of influence of lateral edges the factor of pressure is determined
Fig.
6.2.
![]() .
(6.2)
.
(6.2)
(Here wing is considered as a flat plate). The last formula is recorded for case when there is no mutual influence of the right-hand and left-hand lateral edges (Fig. 6.2). This influence appears at such Mach numbers, when the Mach cone of the left-hand (or the right-hand) lateral edge crosses the right-hand (left-hand) lateral edge.
Limit
case of mutual influence absence is determined by a condition
![]() .
Fig. 6.3. shows probable cases of lateral edges mutual influence.
.
Fig. 6.3. shows probable cases of lateral edges mutual influence.
![]()
Fig. 6.3.
The factor of pressure in the field of mutual influence of lateral edges is determined by more complex formulae; they are shown in the special literature.
Summarizing distributed pressure we shall define the aerodynamic characteristics.
The
following formulas are received for the case when
![]() :
:
![]() ;
(6.3)
;
(6.3)
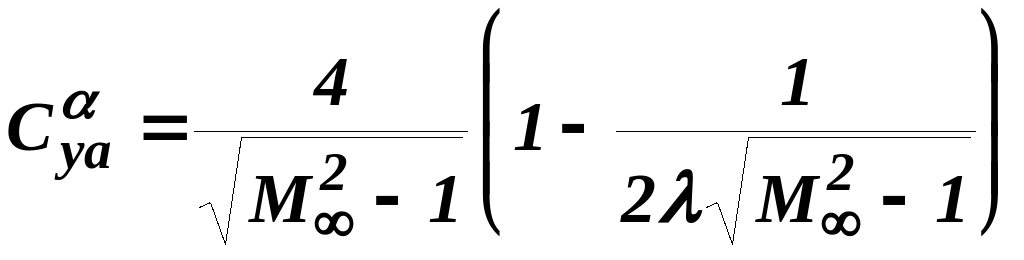 ;
(6.4)
;
(6.4)
![]() ;
(6.5)
;
(6.5)
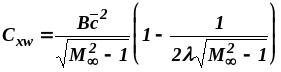 ;
(6.6)
;
(6.6)
![]() ;
(6.7)
;
(6.7)
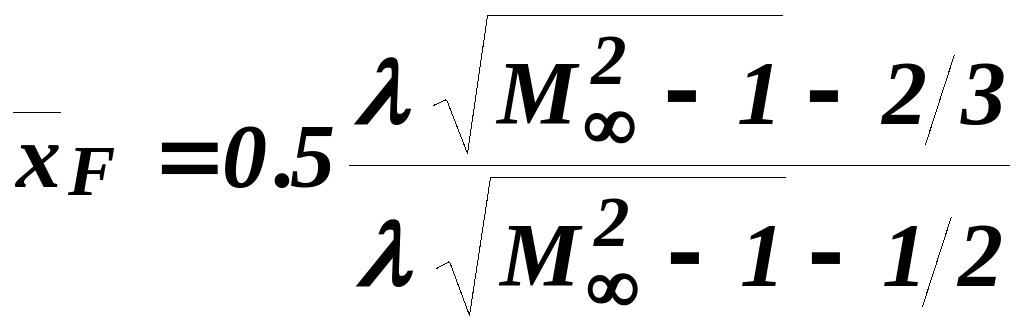 .
(6.8)
.
(6.8)
At equations for the aerodynamic characteristics for rectangular wings become considerably complicated.
Let's analyze the aerodynamic characteristics.
6.1.1. Lift.
1.
The dependence
![]() is linear for any aspect ratio wing (
is linear for any aspect ratio wing (![]() ).
).
2.
With increasing of
![]() the value of a derivative
the value of a derivative
![]() grows and at
grows and at
![]() tends to the airfoil characteristic
tends to the airfoil characteristic
![]() (Fig. 6.4). This tendency takes place faster than in subsonic flow,
that is explained by limited area of the lateral edges influence at
(Fig. 6.4). This tendency takes place faster than in subsonic flow,
that is explained by limited area of the lateral edges influence at
![]() .
.
3.
The value of derivative
decreases and tends to
![]() with increasing of Mach numbers
with increasing of Mach numbers
![]() ,
that is connected to narrowing of Mach cones at growth of
and reduction of lateral edges influence (Fig. 6.5). It is
possible to assume, that
,
that is connected to narrowing of Mach cones at growth of
and reduction of lateral edges influence (Fig. 6.5). It is
possible to assume, that
![]() already at
already at
![]() (difference is less than
(difference is less than
![]() at
at
![]() ,
at
,
at
![]() - less than
- less than
![]() ).
).


Fig.
6.4. Dependence
|
Fig.
6.5. Dependence
at
|
4.
The ratio
![]() is the universal dependence on reduced aspect ratio
is the universal dependence on reduced aspect ratio
![]() .
.
