
- •Topic: "Electromagnetic induction"
- •The phenomenon of electromagnetic induction. Faraday's Law. Lenz rule.
- •2. Explanation of the phenomenon of electromagnetic induction by the Lorentz force
- •3. Виникнення вихрового електричного поля при зміні магнітного поля. Пояснення явища електромагнітної індукції на його основі
- •4. Вихрові струми. Їх роль у техніці
- •5. Кількість електрики, що переноситься індукційним струмам. Балістичний метод вимірювання індукції магнітного поля
Lecture 5
Topic: "Electromagnetic induction"
Questions of the lecture:
The phenomenon of electromagnetic induction. Faraday's Law. Lenz rule.
Explanation of the phenomenon of electromagnetic induction by the Lorentz force.
 The
emergence of vortex electric field by changing the magnetic field.
Explanation
of the phenomenon of electromagnetic induction on that basis.
The
emergence of vortex electric field by changing the magnetic field.
Explanation
of the phenomenon of electromagnetic induction on that basis.Vortex currents. Their useful and harmful role in engineering.
Amount of electricity that is transferred by the induction current. Ballistic Stoletov method of measuring the magnetic field.
The phenomenon of electromagnetic induction. Faraday's Law. Lenz rule.
Рис.
5.1

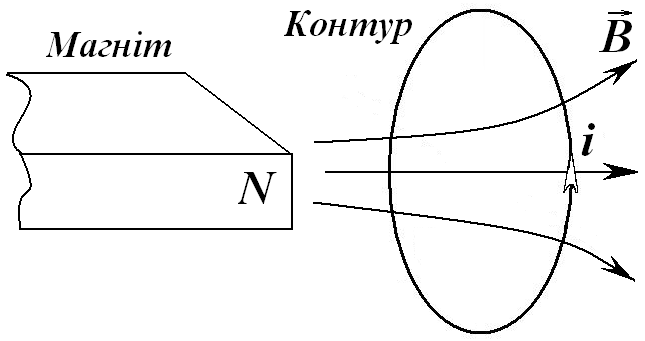 The
phenomenon of electromagnetic induction can be demonstrated by
experiments with a magnet, approaching or distancing it from the
circuit (рис. 5.1), or changing the current and the magnetic field
in the coil (Fig. 5.2).
The
phenomenon of electromagnetic induction can be demonstrated by
experiments with a magnet, approaching or distancing it from the
circuit (рис. 5.1), or changing the current and the magnetic field
in the coil (Fig. 5.2).
Рис.
5.2
The
magnitude
εі
does not depend on how the magnetic flux changes
Ф, and is determined only by the speed of this change (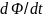 ).
The
sign
ЕРС of
the
induction
εі
is
determined
by the change in the flow direction, i.e.
the ascending or descending order.
This
can be written
in
a formula as follows:
).
The
sign
ЕРС of
the
induction
εі
is
determined
by the change in the flow direction, i.e.
the ascending or descending order.
This
can be written
in
a formula as follows:
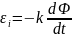
The
proportionality factor k
depends
on the choice of units
of measurement.
In
the international system (SI)
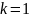 .
The
sign
"
.
The
sign
"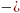 "
takes into account the direction of ЕРС
Thus, in
the
system SI
it
can be written as:
"
takes into account the direction of ЕРС
Thus, in
the
system SI
it
can be written as:
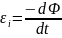
This is Faraday's law of electromagnetic induction.
We examined the occurrence of emf induction in the simplest circuit of one turn. If the path consists of N turns connected in series, then the EMF is equal to the EMF of each induction coil (Fig. 5.Z):
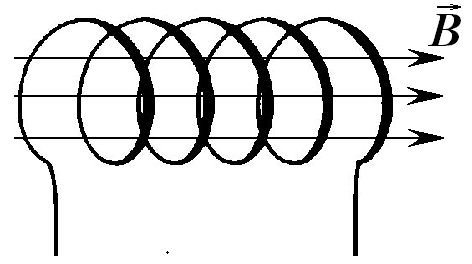
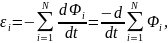
Let:
Fig.
5.3
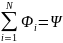
 Then:
Then:
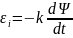
The
magnitude
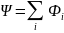 ,
is
referred
to as full
magnetic flux.
,
is
referred
to as full
magnetic flux.
Fig.
5.4

Рис.
5.5
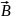 1,
whose
field
lines penetrate the
circuits
1 and
2
(fig.
5.4). If
the
current
І1
increases
(
1,
whose
field
lines penetrate the
circuits
1 and
2
(fig.
5.4). If
the
current
І1
increases
(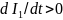 ),
then the flux of magnetic induction Ф2
through the circuit 2 also increases, and it arises emf
induction and the
current
),
then the flux of magnetic induction Ф2
through the circuit 2 also increases, and it arises emf
induction and the
current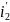 ,
a direction to counteract the reason that it has caused, that is, to
counter increasing flux of magnetic induction. This means that the
current
in
the
circuit
2 flows
in the
,
a direction to counteract the reason that it has caused, that is, to
counter increasing flux of magnetic induction. This means that the
current
in
the
circuit
2 flows
in the  opposite
direction relative to the current I1
and creates a stream of F_2 ', directed against the flow
of
F1.
opposite
direction relative to the current I1
and creates a stream of F_2 ', directed against the flow
of
F1.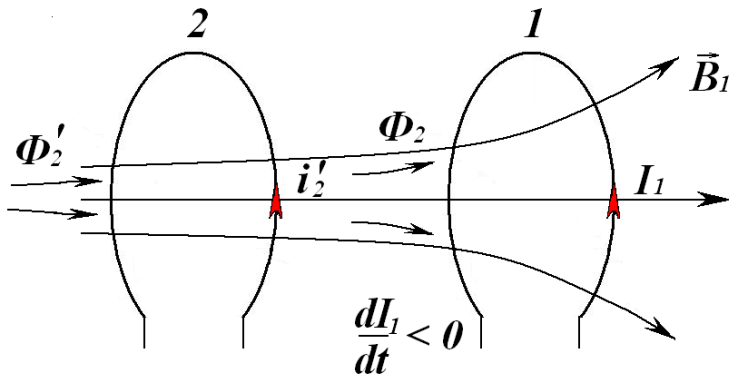 Now
consider the case of reducing the current
I1
(Fig.
5.5). The
current
Ф1,
while also decreases
(
Now
consider the case of reducing the current
I1
(Fig.
5.5). The
current
Ф1,
while also decreases
(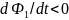 )
and circuit 2 according to Lenz's rule, there is an induction current
of
such a
direction
so the
created current
)
and circuit 2 according to Lenz's rule, there is an induction current
of
such a
direction
so the
created current
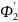 opposed to
reducing
the flow Ф2,
i.e.
to complement it. In this case,
should have the same direction as the current І1.
opposed to
reducing
the flow Ф2,
i.e.
to complement it. In this case,
should have the same direction as the current І1.
