
- •Введение
- •Contents
- •Introduction to legal english Before you start
- •Concept
- •Part 1.Terminology basics
- •Fundamentals
- •I. Origin of some basic words
- •1. Law and Legal
- •3. The word jury has a different origin
- •2. Impersonal sentences
- •3. Passive constructions
- •Development Exercise 1
- •Exercise 2
- •Exercise 3
- •Part 2.The concept of law and areas of law fundamentals
- •Exercise 3
- •Exercise 4
- •Areas of law
- •Exercise 5
- •Exercise 6
- •Exercise 7 Business Law
- •Part 3. How to look up words in a dictionary
- •Unit II state structure: legislative branch of power Before you start
- •Part 1. Legislation process in the united kingdom fundamentals The uk Parliament
- •Exercise 1
- •Exercise 4
- •How laws are made in the uk Parliament
- •Exercise 5
- •Exercise 6
- •Exercise 7
- •Exercise 8
- •Video script
- •Uk Executive Branch of Power
- •How Bill Becomes Law in the usa
- •Exercise 10
- •Exercise 14
- •Internet Search. Visiting the site of the Congress.
- •The Executive Branch of Power in the usa
- •The russian federation chapter
- •Part 3. How to make presentations
- •Presentation
- •Introduction
- •Unit III state structure: judicial branch of power Before you start
- •Part 1. The uk justice system
- •Exercise 1
- •Exercise 2
- •Exercise 4
- •Exercise 5
- •Exercise 6
- •Exercise 7
- •Development Exercise 8
- •Part 2. The us justice system
- •Fundamentals
- •Exercise 9
- •Exercise 10
- •Development State court system
- •Exercise 11
- •Exercise 12
- •Exercise 13
- •Internet research
- •Exercise 14
- •The russian federation chapter
- •Part 3. How to conduct discussions and hold meetings
- •1. Chairperson conducts a meeting or discussion
- •2. Audience’s interaction with the speaker
- •3. The speaker’s reaction to the questions and comments.
- •Sequencing and connecting ideas
- •Unit IV legal systems Before you start
- •Exercise 2
- •Henry II of England
- •The third criterion
- •Exercise 6
- •Exercise 7
- •Exercise 8
- •Exercise 9
- •Sources of Civil Law Exercise 10
- •Part 2. Precedent
- •Fundamentals
- •Exercise 11
- •Development Exercise 12
- •Exercise 13
- •Exercise 14
- •Miranda V. Arizona (1966)
- •Gideon V Wainwright (1963)
- •Brown V. Board of Education, 347 u.S. 483 (1954)
- •The russian federation chapter
- •Information that law students search in Internet
- •Unit V. Wrongs and offences. Before you start
- •Part 1. Torts as civil wrongs fundamentals Exercise 1
- •Exercise 2
- •Intentional torts
- •Exercise 3
- •Exercise 4
- •Exercise 7
- •Exercise 8
- •Exercise 9
- •Internet research
- •Exercise 12
- •Exercise 13
- •Exercise 14
- •Exercise 15
- •Development Exercise 16
- •Exercise 17
- •4. Note hate crime – преступление на почве ненависти; преступление на почве этнической ненависти
- •Exercise 18
- •Internet research
- •The russian federation chapter
- •Part 3. How to provide arguments in a dispute
- •Unit VI legal education Before you start
- •Part 1. Becoming an attorney (us) fundamentals
- •How to become a lawyer in the usa
- •Interview with an American attorney
- •Exercise 1
- •Exercise 2
- •Exercise 3
- •Exercise 4
- •Development Exercise 5
- •Internet Research
- •Exercise 6
- •Exercise 7.
- •Part 2. Becoming a solicitor or barrister (uk) fundamentals
- •Exercise 8
- •Exercise 9
- •Exercise 10
- •Internet research.
- •Exercise 11
- •The russian federation chapter
- •Part 3. How law students keep up legal correspondence
- •Internship advertisement
- •Unit VII legal professionals Before you start
- •Concept
- •Part 1. Law and law-related professions
- •Exercise 1
- •Fundamentals
- •Exercise 2
- •Exercise 3
- •Development Exercise 4
- •Exercise 5
- •Exercise 6
- •Exercise 7
- •Interview with a Finance Lawyer
- •Exercise 8
- •Part 2. Law firms and legal departments Exercise 9
- •Exercise 10
- •Exercise 11
- •Exercise 12
- •Exercise 13
- •Exercise 14
- •1. Providing legal advice and guidance
- •2. Prosecution of cases in courts and litigation management
- •3. Documentation preparation and drafting
- •The russian federation chapter
- •Part 3. How law professionals keep up legal correspondence
- •Correspondence phrase bank basics
- •The russian federation chapter
- •Bibliography
- •Заключение
Exercise 7.
Prepare a Presentation about one of the American law schools and the courses. Use information from Internet. But you need to process this information and while speaking use more active vocabulary of the Unit Part 1.
Part 2. Becoming a solicitor or barrister (uk) fundamentals
Core vocabulary 3
compulsory – обязательный foundation (adj) - основной vocational stage – стадия профессионального образования workshop – семинар, тренинг pupilage - ученичество chamber – палата-кабинет адвоката under the guidance / supervision – под руководством |
tenancy – работа по договору training contract – договор о профессиональном обучении call to Bar – присвоение звания барристера/ прием в адвокатуру LPC – курс юридической практики BPTC – курс адвокатской профессиональной практики PSC – курс повышения профессиональных навыков |
The system of legal education in the United Kingdom has its peculiarities. First, the modes of legal education are slightly different in England /Wales and Scotland or Northern Ireland. But the major distinction in the ways to obtain appropriate qualification is the existence of two professions – solicitors and barristers.
Solicitor is a lawyer who advises clients on matters of law, draws up legal documents, prepares cases for barristers, etc, and who may represent clients in certain courts
Barrister is a one of two types of practicing lawyers in Britain (the other is the solicitor). Barristers engage in advocacy (trial work), and only they may argue cases before a high court.
A barrister must be a member of one of the four Inns of Court. Inns of Court the four legal societies in England founded about the beginning of the 14th century and having the exclusive right to confer the title of barrister on law students.
Examine the following diagram that represents the system of legal education in England and Wales. Get ready to speak about the stages of the represented educational system using words and phrases from Core Vocabulary 1 and this Core Vocabulary 3.
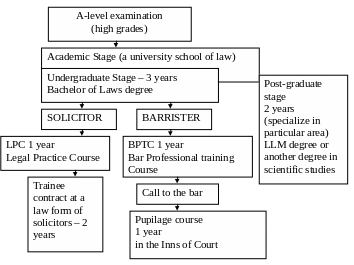
Exercise 8
The detailed information on each stage of legal education in the UK. While scanning the extracts restore the proper order according to the diagram above. Then read again attentively.
(From the site LawCareers.Net www. lawcareers.net)
A) The Legal Practice Course (LPC) is the vocational stage of training to be a solicitor. It is a one-year, full-time (or two-year, part-time) course designed to provide a bridge between academic study and training in a law firm. The LPC is practical in nature and the focus is firmly on mastering relevant skills. The emphasis is on workshops, continuous assessment, independent research and group discussions. It also allows you a certain amount of specialization through a range of optional subjects. The majority of courses are delivered in two stages. Stage one is the compulsory study of core areas of law and practice, while stage two is comprised of three vocational electives.
B) For many of the students, LLM study is a stepping stone to developing academic and professional expertise in a particular field of law. For others, it is an opportunity to gain postgraduate knowledge and skills across a broad range of subjects. The programmes of study provide a flexible mix of classroom based teaching (assessed by formal examinations or coursework) in three taught modules, followed by more self-directed work on a 15,000 word dissertation
C) The Bar Professional Training Course (BPTC), formerly the Bar Vocational Course (BVC), is the vocational stage of training that must be completed if you wish to become a barrister. It is a one-year, practical course, designed to provide training that is specific to the work of a junior barrister (a two-year, part-time course is also available at some law schools). Students are encouraged to participate in a range of activities (including mock trials, debating and extra mini-pupilages) that will help them to develop the necessary skills. The BPTC helps to prepare you for the 12-month pupilage and beyond.
D) The standard LLB (Bachelor of Law) is a three-year law programme. It includes compulsory modules in the first and second year: property, trusts, contract, criminal law, tort, constitutional and administrative law and EU law. These satisfy professional requirements for the foundations of legal knowledge and skills. From these strong foundations, you are in a good position to choose options for your second and third years.
E) Pupilage is the final stage of training to be a barrister. During this time, you put into practice everything you have learnt so far. Although you will be a fully qualified barrister (and called to the Bar) on passing the Bar Professional Training Course (BPTC), pupilage is essential for all those who wish to practise. Pupilage usually takes a year to complete, with the year divided into two six-month periods or 'sixes'. Each six is spent in a set of chambers (although a small number of places are available in companies and other institutions), under the guidance and supervision of a junior barrister of at least five years' experience - your pupil supervisor. It is not uncommon for each six to be spent in a different chamber and/or with a different pupil supervisor. With competition for tenancies so high, sometimes a third six is undertaken.
F) The training contract, which includes the Professional Skills Course (PSC), is the final stage on the path to qualifying as a solicitor. It is the stage at which you put into practice all the knowledge and skills you have learnt so far, and develop these still further within a working environment. The training contract is a two-year period spent working at a law firm. You should always be under the supervision of a qualified solicitor who will manage your workload, monitor your progress and help to train you. These two years provide an opportunity for a law firm to build on what the trainee has already learnt through practical work experience and training. It also gives the firm the chance to assess the trainee's prospects for a job as a solicitor after the training period is over.
G) Call to the Bar is the graduation ceremony for BPTC students. There are four Call Nights each year (March, July, October and November). In order to qualify for Call a student must have successfully completed the vocational stage and have completed the requisite number of qualifying sessions. After that the students can be admitted for pupilage. (Inner Temple information)
