
- •Опись учебно-методический комплекс дисциплины
- •Второй год обучения
- •Предметное содержание речи
- •2. Внутренняя и внешняя политика сия и Казахстана.
- •3. Социальные проблемы
- •1. Устные контакты
- •2. Современные проблемы развития избранной отрасли (по специальности).
- •Аудирование
- •Аудирование
- •Итоговый контроль второго года обучения состоит из 2-х частей:
- •Третий год обучения
- •Предметное содержание речи
- •1. Образование и наука.
- •2. Профессиональная подготовка будущего инженера (технического работника) в сия и Казахстане.
- •3. Диалог культур в обучении ия
- •Уровень с2
- •Говорение
- •Письменная речь
- •Аудирование
- •Аудирование
- •1. Сафронова ю.В. - ст. Преподаватель юкгу им.М.Ауезова.
- •2. Карбозова г.К. - к.Ф.Н., доцент юкгу им.М.Ауезова.
- •Министерство образования и науки республики казахстан
- •Рабочая учебная программа
- •1. Цель, задачи и место дисциплины в учебном процессе
- •2. Выписка из учебного плана
- •2.1 Выписка из учебного плана
- •3. Содержание дисциплины
- •3.1. Номера и название лабораторных работ, практических работ, тем семинарских занятий по каждому модулю.
- •3.2. Номера и название срс по модулям
- •History of building and architecture
- •Building materials
- •Structural elements
- •Building and architecture
- •4. Методическое обеспечение дисциплины и тсо
- •5.Дополнения и изменения в рабочей учебной программе на 201__/201__ учебный год в рабочую учебную программу вносятся следующие изменения:
- •1. Цели и задачи дисциплины «Английский язык»
- •2.Политика курса:
- •3. Тематический план практических занятий
- •Module 1.
- •Module 2.
- •5. График выполнения и сдачи заданий
- •6. Список рекомендуемой литературы:
- •6.1 Основная литература
- •1. Цели и задачи дисциплины «Английский язык»
- •2.Политика курса:
- •Тематический план практических занятий
- •Module 3.
- •Module 4.
- •5. График выполнения и сдачи заданий по дисциплине английский язык (рекомендуемый)
- •6. Список рекомендуемой литературы:
- •6.1 Основная литература
- •1. Цели и задачи дисциплины «Английский язык»
- •2.Политика курса:
- •3. Тематический план практических занятий
- •Module 1.
- •Module 2.
- •5. График выполнения и сдачи заданий
- •6. Список рекомендуемой литературы:
- •6.1 Основная литература
- •Входной конроль Put the words in brackets in the possessive case using –‘s or of:
- •The history of building.
- •From the history of building.
- •Vocabulary
- •From the history of architecture.
- •II. Active vocabulary
- •III. Answer the following questions
- •Types of Buildings
- •1. What types of buildings do you know ?
- •2. What do you know about their functions ?
- •3. What do you think about requirements to types of buildings ?
- •I From the list of types of buildings, try to label the drawings below:
- •II. Look at this table and complete the examples:
- •III. Ask and answer questions like the following:
- •IV . Look at this example:
- •I Read the text and tell about types of buildings Types of buildings
- •Vocabulary
- •V With your partner, speak on the different types of buildings
- •Control work
- •Properties and Shapes
- •II. Look at these drawings of two-dimensional shapes:
- •III. Now answer these questions about the drawings in exercise I:
- •I V. Look and read:
- •V. Now describe the shapes of the buildings in exercise I, and compare them with the buildings around you.
- •I. Look at these examples:
- •II. Make sentences about four other properties of materials from this table:
- •III. Answer the following questions:
- •Building materials.
- •1. What is it necessary for the designer to know in order to select the most effective building materials ?
- •2. What do you think about the most widely used material ?
- •I Read and find which passage reveals the content of the title: The Most Important and Widely Used Building Materials
- •Vocabulary
- •Variations - өзгерістер - изменения
- •II Read the text again and find out if the following statements are true or false:
- •III Complete the sentences with the infinitive forms given bellow:
- •IV What passages do the following titles belong to ?
- •V Find verbs to the following nouns:
- •VI Match the translations of the terms:
- •Concrete – a Yearning for the Monolithic
- •Vocabulary List
- •Plastic house looks to the future.
- •I. Read the text and tell about the qualities of plastic.
- •Cement: Man’s miracle mix
- •Control work
- •Vocabulary
- •Circle a), b), or c) to complete the sentences.
- •2.Complete the sentences
- •Exercises
- •Give the Russian equivalents
- •Divide the verbs in the box into two groups: regular or irregular. Give three forms of the verb.
- •Prove the following statements using to the information from the text.
- •Vocabulary
- •1. Complete the sentences.
- •Exercises
- •1. Suggested the Russian equivalents.
- •2. Fill in the gaps with the words from the text.
- •3.Match the beginning of the sentences to their ends using the information from the text.
- •4. Discuss in your group these questions
- •5. Give the English equivalents.
- •Domes and realated elements
- •Vocabulary
- •I. Complete the following sentences
- •II. Choose the right synonym.
- •Exercises
- •I. Suggest the Russian equivalents
- •II. Put the verbs in brackets into appropriate form in the following sentences.
- •III. Make some sentences of your own with these expressions.
- •IV. Fill the gaps with the words from the text.
- •Floor system
- •Vocabulary
- •I. Choose the right word
- •II. Complete the following sentences
- •III. Make the right choice.
- •Exercises
- •I. Match the terms (a) and their definitions (b).
- •II. Explain in English
- •Foundations
- •Vocabulary
- •I. Choose the right form of the adjective.
- •II. Complete the following sentences
- •Exercises
- •I. Suggest the Russian equivalents
- •II. There are some notes the student made after reading the text “Foundation”. Did he remember everything right? Read his notes and correct them if necessary.
- •Vocabulary
- •I. Choose the right verb
- •II. Complete the following sentences.
- •Exercises
- •Architectural design
- •Planning a house.
- •III. Answer the following questions
- •C olours in your home
- •Some building professions.
- •Vocabulary
- •II Match the beginnings (1-5) of the sentences to their ends using group (a-e)
- •III Answer the following questions:
- •IV Translate the following sentences into Kazakh or Russian:
- •Types of building.
- •Control work
- •High-Strength Concrete
- •High - Strength Concrete
- •Vocabulary List
- •I Answer the following questions.
- •II Give synonyms.
- •III True or false?
- •Rendered Facades, but with What Finish? Coloured, Painted or Coated?
- •Vocabulary List
- •I Answer the following questions.
- •II Give definitions to the following words and phrases.
- •Industrial Building Typology
- •Vocabulary List
- •I Answer the following questions.
- •II Give synonyms.
- •Control work
- •1. Make the written translation of the third paragraph of the text.
- •2. Give antonyms.
- •3. Find the English equivalents in the text.
- •Water Supply
- •Water supply
- •Sewerage
- •Sewerage
- •Panel Heating
- •Panel heating
- •Principles of Air-Conditioning
- •Principles of air-conditioning
- •Материалы для самостоятельной работы обучающего Модуль 1 history of building and architecture
- •I’ve chosen building as a career because …
- •Модуль 2 building materials
- •Модуль 3 structural elements
- •Модуль 4 building and architecture
- •Architectural design
- •Модуль 5
- •Модуль 6
- •Материалы для срсп
- •II Use the right prepositions where necessary.:
- •III. Use “some, any, no”:
- •IV. Choose the necessary word given in the brackets:
- •V. Use the verbs given in the brackets in right Tenses:
- •5. Put the following sentences in the negative form:
- •6. Use the verb in the Present Continuous:
- •Причастие (The Participle)
- •Формы Participle I
- •Функции причастия I в предложении
- •To cry, to shake, to shine, to sit, to laugh, to fall, to run, to sleep, to smoke, to wait, to speak, to stand, to follow, to play, to lose, to leave
- •The early houses in Great Britain. Dialogue.
- •The Syntax of the Sentence
- •Participle II
- •1. Определение
- •2. Обстоятельство.
- •Предикативный член
- •Независимый причастный оборот
- •Способы перевода независимого причастного оборота
- •To trust, to bother, to employ, to explain, to wash, to respect, to impress, to cook, to decorate, to dress, to love
- •Страдательный залог (The Passive Voice)
- •Struсtures
- •The dialogue
- •I. Read this:
- •II. Complete this following diagram:
- •III. Problem solving:
- •Present perfect tense
- •VI Put in gone or been.
- •VII Complete these sentences.
- •The Past Perfect Tense
- •1.Read the sentences. In each case, tick (V) which happened first, a) or b). Example
- •2.Make sentences in the past perfect using the verbs in brackets. Example
- •3.Put the verb in brackets into Past Perfect Tense.
- •4.Make the sentences: a) negative b) interrogative.
- •5.Read the sentences. In each case, tick (V) which happened first, a) or b). Example
- •Types of plastics.
- •Epoxy resin
- •Pvc (polyvinyl chloride)
- •Polystyrene.
- •Vocabulary
- •The Future Perfect
- •Инфинитив (the infinitive)
- •Формы инфинитива
- •Инфинитивный оборот с предлогом for
- •The millenium dome
- •Vocabulary
- •I. Choose the right preposition
- •II. Complete the following sentences
- •Exercises
- •I. Suggest the Russian equivalents
- •II. Fill the gaps with the words from the text.
- •IV. Choose the right verb and put it in the right form
- •Terms terminology
- •I. Suggest the Russian equivalents
- •II. Match the terms (a) and their definitions (b).
- •III. Explain in English
- •IV. Discuss with your partner the following questions.
- •V. Ask you r friend to prove that the reinforced-concrete slab has a great advantage over the most earlier systems. Use the following word combinations.
- •Leaning tower of pisa begins to be stabilized.
- •Vocabulary
- •I. Choose the right synonym
- •II. Complete the following sentences
- •Making up a dialogue
- •VI. Agree with the following statements using the appropriate passive form.
- •Discussion of the latest shell structures
- •Visual Vocabulary
- •The Compound Sentence
- •Формы герундия
- •Функция герундия в предложении
- •Перевод герундия
- •Перевод герундия с различными предлогами
- •Perfect tenses
- •The Complex Sentence
- •Grammar revision Ex.1 Compose sentences using verbs from left column:
- •A. Model
- •Trades of building professions
- •I Look and read:
- •Week number
- •II.Read this:
- •III.Complete these sentences with the name of a building trade:
- •IV.Read this:
- •The tools and instruments used in building construction.
- •II. Look at these drawings of instruments:
- •5 Модуль
- •Типы вопросов в английском языке
- •Обороты there is / there are
- •Основные модальные глаголы и их заменители в английском языке
- •Форма и основные функции сослагательного наклонения
- •Неопределенные местоимения some, any, отрицательное местоимение по и их производные
- •Отличие местоимений little и few и местоименных выражений a little и a few
- •Отличие временных групп Indefinite, Continuous и Perfect
- •Согласование времен в главном и придаточном предложениях
- •Преобразование прямой речи в косвенную
- •Материалы по контролю и оценке учебных достижений обучаящихся
- •Экзаменационный билет № 1 по дисциплине « Английский язык»
- •Экзаменационный билет № 2 по дисциплине « Английский язык»
- •Экзаменационный билет № по дисциплине « Английский язык»
- •I. Read the text
- •II. The terms.
- •Экзаменационный билет № по дисциплине « Английский язык»
- •I. Read the text
- •II. The terms.
Present perfect tense
have
done (present perfect 1)
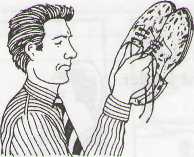

He is cleaning his shoes.
He has cleaned his shoes. (= his shoes are clean now)



They are going out.
They have gone out.
(= they are not at home now)
has cleaned / have gone etc. is the present perfect (have + past participle):
past participle

I we you they |
have fve) have not (haven't) |
cleaned finished started lost done been gone |
|
||
|
I |
cleaned? |
have |
we |
finished? |
|
you |
started? |
|
they |
lost? |
1 |
'he |
done? |
has < |
she |
been? |
1 |
. it |
goner |
Present Perfect образуется при помощи вспомогательного глагола to have в настоящем времени ( have, has ) и причастия прошедшего времени смыслового глагола:
I ( we, you, they ) have worked.
He ( she, it ) has worked.
Вопросительная форма образуется путем постановки вспомогательного глагола to have перед подлежащим например:
Have I worked?
Has he worked?
Отрицательная форма образуется путем постановки отрицания not после вспомогательного глагола например:
I have not worked.
He has not worked.
Present Perfect употребляется для выражения закончившегося действия, когда время совершения его указывается неопределенно, а результат действия налицо
в настоящий момент. ( В тех случаях, когда время совершения действия в прошлом указывается определенно, употребляется Past Indefinite. ) Present Perfect
чаще всего переводится на русский язык глаголами совершенного вида в прошедшем времени:
I have written a letter. Я написал письмо. ( Письмо написано, но
не сказано, когда оно написано, поэтому
употребляем Present Perfect. )
We have bought a TV set. Мы купили телевизор. ( Телевизор куплен.
Он в комнате. Нас интересует результат
в настоящем, а время совершения действия
не указано. )
Pete has broken his pencil. Петя сломал карандаш. ( Результат действия
налицо: карандаш сломан и им писать
нельзя. Время совершения действия не
указано. )
Present Perfect часто употребляется с наречиями неопределенного времени, которые ставятся между вспомогательным глаголом и причастием прошедшего времени спрягаемого глагола:
Ann has just come in. Аня только что вошла.
We have already seen this film. Мы уже видели этот фильм.
Наиболее часто употребляемые наречия неопределенного времени:
Ever [ ' evә ] когда- либо
Never [ nevә] никогда
Just [ dzast ] только что
Already [o l redi ] уже
( not ) yet ( not ) jet ) еще (не)
Различия употребления Present Perfect и Past Simple
Present Perfect |
Past Simple |
• Обозначает действие в прошлом, имеющее результат в настоящем, при этом время действия не указывается или неясно из контекста: We've bought a house. — Мы купили новый дом. They've invited me to their party. Can I go? — Они пригласили меня на вечеринку. Я могу пойти? • Употребляется с обстоятельствами времени today, this morning, this week, this month, this year и т. п., если период времени еще не окончен: / haven't seen my e-mail today. I'm going to do it now. — Я еще не ви- |
• Обозначает законченное действие в прошлом, никак не связанное с настоящим, при этом время действия указано словами или ясно из контекста: We bought the house in the 1970s. — Мы купили этот дом в семидесятых. They invited me to their party, but I refused to go there. — Они пригласили меня на вечеринку, но я отказалась туда пойти. • Употребляется с обстоятельствами времени today, this morning, this week, this month, this year и т. п., если период времени уже окончен: / didn't see my e-mail today. I was busy all day. — Я не видел сегод- |
Present Perfect |
Past Simple |
дел сегодня электронную почту. Я собираюсь это сделать сейчас. • Не употребляется в вопросах, начинающихся со слов When и How. • Часто употребляется в тех случаях, когда говорящий хочет сообщить или узнать информацию общего характера: He's already seen this film. — Он уже видел этот фильм. Have you ever been to the Tower? — Ты бывал в Тауэре? |
ня электронную почту. Я был занят весь день. • Употребляется в вопросах, начинающихся со слов When и How: When did you meet him? — Когда вы с ним встретились? How did they learn my address? — Как они узнали мой адрес? • Употребляется, если говорящий хочет сообщить или узнать подробности: Where did he see this film? — Где он видел этот фильм? |
Характерные слова и фразы
already, just, ever, never, up to now, so far, for long, for seven years, for ages, since January, since last year, since 1945, yet.
Exercises.
I Complete the sentences with a verb from the list.
break buy decide finish go go invite see not/see take tell
Can I have this newspaper? Yes, I’ ve finished with it.
I…………….some new shoes. Do ypu want to see them?
Where’s Liz? She …………..out.
I’m looking for Paula. …………….you……………..her?
Look! Somebody ………………..that window.
Does Lisa know that you’re going away? Yes, I …………..her.
I can’t find my umbrella. Somebody …………….it.
I’ m looking for Sarah. Where ………..she…………..?
I know that woman but I …………………her name.
Sue is having a party tonight. she …………a lot of people.
What are you going to do? …………….you ……………..?
Where are my glasses? I don’t know. I …………….them.
II Complete the sentences. Use already + present perfect.
What time is Paul arriving? He’s already arrived.
Do Sue and Bill want to see the film? No, they ……………….it.
Don’t forget th phone Tom. I …………………. .
When is Martin going away? He …………….. .
Do you want to read the newspaper? I ………………. .
When does Linda start her new job? She …………… .
III Write questions with yet.
Your friend has got a new job. Perhaps she has started it. You ask her:
Have you started your new job yet?
your friend has some new neighbours. Perhaps he has met them. You ask him:
…………………..you ………………?
your friend must write a letter. Perhaps she has written it now. You ask her:
…………………………………………?
Tom was trying to sell his car. Perhaps he has sold it now. You ask a freind about Tom: …………………………..?
IV You are asking Helen questions beginning Have you ever……? Write the questions.
(London?) – Have you ever been to London? - No, never.
(play/golf?) - ………………………………………..? – Yes, many times.
(Australia?) - …………………………………………? – No. Never.
(lose/your passport?)………………………………..? – Yes, once.
(fly/in a helicopter?)…………………………………? – No, never.
(eat/Chinese food?)………………………………….? – Yes, a few times.
(New York?)……………………………………………? – Yes, twice.
(drive/ a bus?)………………………………………….? – No,never.
(break/ your leg?)……………………………………..? – Yes, once.
V Mary is 65 years old. She has had an interesting life. What has she done?
have do travel be write meet
all over the world a lot of interesting things
a lot of interesting people many different jobs
married three times ten books
She has had many different jobs.
