
Pindelski_Competitive_Strategies
.pdf
The most important actions are those, without which it is impossible to keep the smooth operation of a business model. For Groupon, the most important action is to maintain and continually improve their sales website, which is the only place that generates the company's income. The Groupon website continues to develop in terms of graphics and content. New cities and new sales channels, as the aforementioned Groupon Travel or Groupon Shopping, are constantly being added. For companies operating in the group buying sector, it is extremely important to show new offers. That's why Groupon is urgently seeking new potential partners with interesting for users industries, because they generate a much larger income than the remaining offers do. Searching and persuading new partners is a key business operation.
Key partners constitute a business model described by the most important company suppliers. In the case of group buying websites, suppliers are the partners, meaning they chose to work together with that website. Any business wishing to cooperate with Groupon.pl is considered important. Unfortunately, some companies operate in industries in which signing a contract misses the point, because the partner's offer would not satisfy the mass taste. There are also a lot of businesses, whose premises do not meet the quality requirements of Groupon. These types of businesses do not belong to the website key partners. On the other hand, there is a large group of companies characterized by good quality and business location. Such partners are key elements of the business model. And the Groupon.pl does everything in order to acquire and maintain as many of such partners as possible. Long-term cooperation is profitable for both parties. Groupon uses various techniques in order to improve relationships with such partners. First of all, there is a special team within the company strictly dedicated to ensuring positive contacts with businesses. This team continuously resolves any problems acquired by the partners. In addition, certain applications have been developed in order to facilitate work with website cooperating companies. This is, among others, the Groupon Partners app, working on the same operating systems as the Groupon Mobile. It allows the partner to avoid the retrieval of printed coupons, writing down the protection codes or sending them to Groupon. Simply, by using this application and your phone's camera, scanned codes are automatically sent to the headquarters and are accounted for. A partner may, at any time, check if vouchers are already accounted for, for how many it has already received the money and how many customer payments they still have to receive. In addition, more recently tested is the
170

application that allows for convenient booking appointments with the partner, without the need for calling the facility directly. Companies are very pleased with that feature, because it can assign part of their responsibilities to Groupon.pl, and minimize the risk of making mistakes in reservations. An organization of big events can also be carried out by using Groupon. In the case of major events, where many people come to redeem a voucher, scanners are delivered to partners making it easier to settle all of the vouchers. Partners attend specially created for them seminars and training, on which they can learn how to make the most out of a marketing campaign in order to improve the performance of their business. What's more, in each of the major cities there are occasional events for commercial teams and partners, who aim to improve relationships with old partners and/or want to establish new business contacts.
Cost Structure of the Groupon.pl Company
The costs include all company expenses related to the use of a specific business model. Because of its model Groupon.pl does not bear large costs. It is not a production company, so there is no cost of production, distribution or material expenses. Groupon is an agent applying a fee for placing an offer on its website. Therefore, the only costs incurred by Groupon are the costs related to salaries, offices, vehicle fleet leasing and website maintenance and development. In addition, the high cost includes mail distribution to seven million users, as well as an intensive Internet advertising campaign. These costs are necessary to attract and maintain new users. Being the intermediary, Groupon doesn't focus on low costs or high-value for the user.
Discussion questions:
1.Describe the key success factors for the industry in which Groupon.pl operates.
2.Evaluate the key success factors for Groupon.pl and present, what should be the focus of strategic actions.
3.Set a value chain for the company and determine what may be its competitive advantage.
Further readings
To be read and study by yourself . You can discuss the papers, materials and conclusions during the next class.
171
1.Pindelski M., Competitive advantage in retail industry through innovative approach to the core competence. How Jeronimo Martins won Polish retail market, International Academic Breckenridge Conference, Clute Institute, Breckenridge, Colorado, USA, 2013
Bibliography
1.Boulton, R.E.S., Libert B.D., Samek S.M., Cracking the Value Code. How Successful Businesses are Creating Wealth in the New Economy, Harper Collins, New York, 2000
2.Brandenburger A., Harborne Stuart S., Value Based Business Strategy, Journal of Economics and Management Strategy, 1996, vol.5
3.Horvath P., Balanced Scorecard, Skuteczne wdrażanie strategii, 7th Controllers Congress Proceedings, Jastrzębia Góra 1999, [ed.] S. Olech, od DROGI do Balanced Scorecard, Controlling i rachunkowość zarządcza, 2000, No. 2
4.Porter M.E., Competitive Advantage. Creating and Sustaining Superior Performance, The Free Press, New York 1985.
5.Barcz M., Błędy w budowaniu strategii firmy, Manager No. 1 (64), January 2003
6.Porter M.E., Competitive Advantage. Creating and Sustaining Superior Performance, The Free Press, New York, 1998
Other sources:
1.Http://biznes.onet.pl/trudne-poczatki-groupona-rzadu,49674,5091343,news- detal
2.http://www.bbwp.pl/artykul/copyfighterzy-zrobia-nawet-lewatywe/
3.http://mfiles.ae.krakow.pl/pl/index.php/Kluczowe_czynniki_sukcesu
4.CapGemini Ernst & Young report, 2010
9.Business models vs. competitive strategies.
Pre-class readings:
Osterwalder Alexander, Pigneur Yves, Businessmodel Generation
Available on: http://www.businessmodelgeneration.com/
172

Task: Prepare a short presentation demonstrating the main thesis, assumptions and
conclusions of the Business Model Generation method.
Additional questions to be answered and/or discussed after pre-class readings:
1.What is a business model ?
2.How is it connected to the strategy ?
3.How does one discover or simply name competitive advantages on the basis of the business model ?
9.1. Business Model
According to Scott Fox, a business model is "the right product or service, which appears in the right place, at the right time, for the right group of customers". Fox also states that "a business model is the key to creating a business that will succeed". 30
30 S. Fox, Internetowi milionerzy czyli jak zdobyć fortunę online, Helion, Gliwice 2008, p.125
173

Further discussions about the concept of a business model should be enriched by an approach presented by T. R. Eisenmann. According to him, "business models differ in nature of services provided to customers and differ in actions taken in order to provide these services. A business model is the hypothesis of how a business intends to make a long term profit: what and to whom it intends to sell, how it will generate revenue, what technologies it will use, and will it co-operate with business partners"31.
H. Chesbrough and. R. Rosenbloom, both took a look at a business model through the prism of roles it plays in a company, like i.e.:
•"defining offer value, which is the value generated for the user by an offer based on appropriate technology;
•identifying the market segment, being the consumers for which the technology is useful;
•defining the company's value chain, necessary in creating offers and their relevant distribution;
•estimating cost and potential profits of offers, including range values and structure value chain;
•describing the company's position within the network connecting suppliers and customers, including the identification of potential partners and competitors;
•competitive strategy formulation, thanks to which an innovative business can gain and maintain advantage over the competitors".32
When trying to understanding the essence of what a business model is, it is worth taking a closer look at Allan Afuah's point of view. According to Afuah, a "business model is a method adopted by a company, that allows it to expand and use resources in order to provide customers with a product and service offer, whose value exceeds the competition's offer and which, at the same time, ensures the company's profitability. Such a model sets out a detailed plan of earning money today, as well as the long term, including factors determining the maintenance of the company's sustainable competitive
31T. R. Eisenmann, Internet Business model: text and cases, McGraw-Hill, 2002, p. XII.
32H. Chesbrough, R. Rosenbloom, The Role of the Business Model in Capturing Value from Innovation:
Evidence from Xerox Corporation’s Technology Spin-Off Companies, Harvard Business School Working Paper 01-002, p. 7. http://www.hbs.edu/research/facpubs/workingpapers/papers2/0001/01002.pdf
174

advantage, which is to achieve better results than the results of the competition over an extended period of time".33
For private company owners, the most important long-term objective is to maximize their business value. A business value can be determined by:
•profits;
•dividends paid out to its shareholders;
•current market position;
•shares value. 34
In accordance with the theories of contemporary companies, the main business objective is to raise its value, and meet the needs of its stakeholders 35 (subjects, which are involved in its operation, including: supplier, employees, local communities), but there is no doubt that a company, which does not benefit the owners, has no raison d'être, and when it is liquidated, it will prevent all the remaining stakeholders from achieving their goals.
A smoothly functioning company must produce added value resulting from the activities, whose results are higher than the expenditures incurred.
Exercise 14
Business model and success factors
The previously quoted Allan Afuah believes that the deciding success factor is the economic efficiency defined by three components:
•the company's Business Model;
•the environment in which the company operates;
•change factors.36
Tasks and discussion questions:
1.What is a company’s success ? How could it be measured ?
2.According to your opinion list company’s success factors and discuss them.
3.How environment may influence firm’s business model ?
Aufah’s determinants of economic efficiency, and a position of a business model within this system are presented in a diagram below.
33A. Afuah, Ch. L. Tucci, Biznes internetowy - strategie i modele, Oficyna Ekonomiczna, Krakow 2003, p. 20.
34Based on C. Suszyński, Teoria przedsiębiorstwa – materiał do wykładu, Warsaw 2005, p. 13.
35http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Stakeholder_theory .
36A. Afuah, Ch. L. Tucci, Op. cit., p. 19.
175

Fig.18 Determinants of economic efficiency
|
|
|
Business Model |
|
|
|
|
|
• Elements and relationships between |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
others |
|
|
|
|
|
|
• Dynamics (time variability) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Change factor |
|
|
|
|
||
• |
Characteristics |
|
|
Results |
||
• |
Causes |
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Surroundings
•Competition surrounding
• Macroeconomics surrounding
Source: A. Afuah, Ch. L. Tucci, Biznes internetowy - strategie i modele, Oficyna Ekonomiczna, Krakow 2003, p. 20
Based on the definitions above, we can create a coherent picture of what a business model actually is. But some questions still remain – for instance: what does it consist of, how does one build it and how does one analyze it?
Afuah proposes how to identify individual stages of a business model development37, starting from a simple observation that all business models operating in companies are to generate a long-term profit.
Achieving profit is a result of taking a series of actions, including to:
1- offer your customers value, which may take the form of either a product or a distinctive quality, or lower price than the competition's;
2- set a segment of customers, since different consumers have different needs; 3 - determine offers range;
37 Cf. A. Afuah, Ch. L. Tucci, ibidem., p. 90.
176

4 - offer the right price;
5 - report sources of revenue for the company, the price of the offer (company still has to decide, what will be the source of its revenue).
Once the plan is ready, the company should proceed with specific actions, as a result of which, offered value will be produced. Whether the activities will end up being successful depends on the skills of a company's employees. After achieving success, an advantage over the competitors products has to be maintained, which helps in achieving a long-term profit, as well as when new players become interested in the market. Finally, the effectiveness of plans depends on how the listed items are implemented, which on one hand is influenced by resource management skills, and on the other hand the reality of assumptions used when creating the business model. Therefore, particular attention must be paid to relationships between different components being consistent, and the entire unit to consider and use the surrounding environment, which completes a business model.
9.2 Construction of a Business Model
A business model is a description of conditions and methods used in an organization's value creation, and the means of its delivery and reaping profits from it38. In general, it is understood as a total concept of an organization's functioning39. Through the analysis of individual aspects of a business model, there are nine components that make up its structure: segment of clients; set of values; the right relationships with customers; distribution, sales and communication channels; key resources; key business partners; key business actions; revenue streams; business cost structure.
Fig.19 Company's business model components
38Osterwalder A., Pigneur Y., Business Model Generation. A Handbook for Visionaries, Game Changers, and Challengers, Published by John Wiley & Sons, Inc., Hoboken, New Jersey, 2010
39Obłój K. Tworzywo skutecznych strategii. Na rynku starych i nowych reguł konkurencji, Polish Economics Publisher, Warsaw, 2002
177
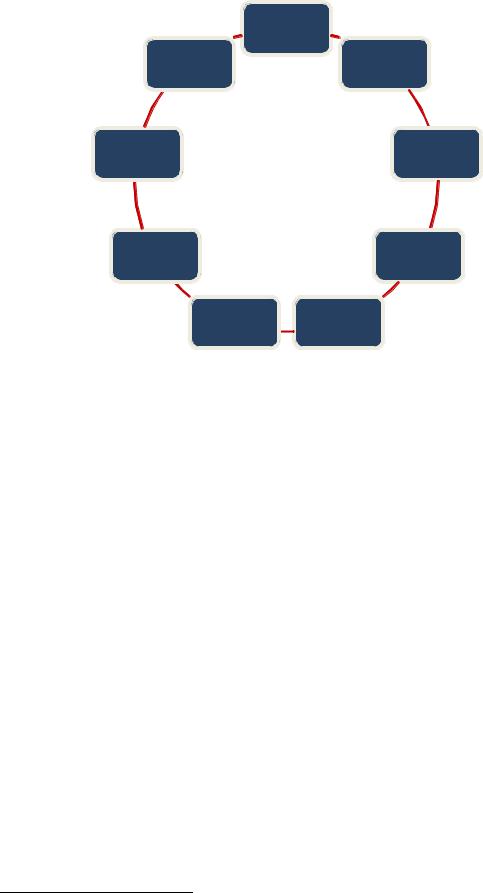
|
Client |
|
Segment |
Cost |
Value |
Structure |
Proposition |
Key |
Channels |
|
Partners |
||
|
Key |
Customer |
Operations |
Relationships |
Key |
Revenue |
Resources |
Streams |
Source: author’s own elaboration based on Osterwalder A., Pigneur Y., Business Model Generation. A Handbook for Visionaries, Game Changers, and Challengers, Published by John Wiley & Sons, Inc., Hoboken, New Jersey, 2010
Alexander Osterwalder and Yves Pigneur proposed a Business Model Canvas40 that can be called: the business model template (graphic template here: http://www.businessmodelgeneration.com/canvas/). It consists of nine blocks representing different aspects of the business operations. The components filled with content and interchangeably connected describe a product, a service or the entire organization and its market proposal. The nine elements are: key partners, key activity, key resources, added value, distribution channels, cost structure, revenue streams, customer segment and customer relationships. A description of individual components should start from the most important one, the customer segment.
Customer segment
According to the authors above, this is a very important, if not the most important element of a business model. It defines customer segments supplied with added value (with a product or a service) created by the company. Clients are the core of each business model, therefore meeting their needs is very important here. Hence the division of segments differing from one another in terms of needs, behaviour and a number of other
40 A. Osterwalder, Y. Pigneur, Business Model Generation: A Handbook for Visionaries, Game Changers, and Challengers, New Jersey 2010.
178
characteristics. From a company point of view, the reasons for determining segments according to the rules of a business model may be:
•Isolated segment requires a businessreasoned, distinctive offer.
•Getting into a segment is possible only through specific distribution channels
•A segment requires specific ways of behaviour and relationship building.
•Each segment has a different, but attractive profitability
•Customers from separate segments prefer different forms of payments.
With this in mind, customers may be grouped together, according to the following segments:
Mass Market. A business model based on such client description does not specify customer target groups. Value proposition, customer relationship or distribution channels focus on a major, potential group of buyers, described by similar needs. An example of this would be Faster Moving Consumer Goods (FMCG), like: home care products, groceries, electronics, etc.
Niche market. In the case of a business in a limited, niche segment, the value proposition, distribution channels and customer relationships are tailored to the specific needs of buyers of the niche market. Some of the examples are: products and services for hobbyists, narrowly-themed TV channel, and themed portals.
Multi-Segmented Market. In certain business models, different segments are distinct, but in general, they may be quite similar to each other. For example, suppliers of carbonated beverages distinguish their wholesalers by their size (large, medium or small) which simultaneously is segmenting its customers. These segments are similar, but yet very different in certain characteristic needs for each of the groups. It has an impact on the remaining elements of such a business model, meaning on the value proposition, distribution channels, customer relationships and the revenue structure.
Diversified Market. By isolating diversified segments, a company provides products and services only to several selected target groups with different needs. The Israeli “Hapoalim Bank” is known as the largest online bookstore in the world. Using its experience in the field of running a massive Internet web server, Amazon.com began selling services, called "Cloud Computing". This is how virtual servers and data storages started to be available to Internet based businesses. It offers personal or business accounts, capital investment support, and the experience Amazon has in the banking industry it uses by investing in start-ups.
179
