
- •1. The Scope and Method of Economics
- •1.1. Scope of Economics
- •1.1.1. Microeconomics
- •1.1.2. Macroeconomics
- •1.2. Analytic Tools and Methods of Economics
- •1.2.1. A Key Assumption: Rational Self-Interest
- •1.2.2. Opportunity Cost
- •1.2.3. Marginal Analysis & Sunk Cost
- •1.2.4. Positive vs. Normative
- •1.2.5. 4 Steps to Reach a Conclusion
- •1.3. From economic Theories to economic Policy
- •1.3.1. The Building of Theories and Models
- •1.3.2. Economic Policy and 4 Criteria for Judging
1.2.4. Positive vs. Normative
The questions economics asks and attempts to answer fall into two categories. Positive economics is an assertion about economic reality that can be supported or rejected by reference to the facts. It is used to understand the behavior and operation of economic systems, rather than passing judgments on them. Normative economics reflects opinions and values, judging whether the outcomes are good or bad. Simply speaking, positive economics deal with what is while normative economics is concerned with what should be.
Not
so normative as arts nor so positive as science
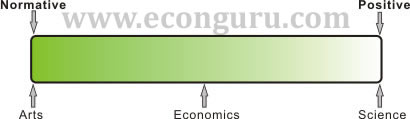
The peculiarity of economics derives itself from these two kinds of statements, normative statements and positive statements, distinguishing economic discipline from both art and science that are either normative or positive. Economics, on the other hand, is not so normative as art nor so positive as science. In fact, many economists confront one another on a number of economic topics such as what the proper role of government should be.
1.2.5. 4 Steps to Reach a Conclusion
Theories or models are formal conclusions achieved or discovered through scientific procedures. In economic analysis and research though, it is not so "scientific". As in physical experiments, variables and factors can be controlled and manipulated very precisely, enabling you to anticipate almost everything. Economists, nevertheless, do research and perform experiments in a much more complex and unpredictable situation, trying to achieve conclusions primarily by observation. They are unable to control known variables in ways they want them to, not to mention those possibly missed out, scrambling the data or simply misleading them. What physicists discover can be formulated exactly in mathematics as they are in reality, and always correct; whereas things an economist discovers do not always hold true and some of them arouse dispute.
Ways an economic conclusion and a physical one differ |
||
|
Physics |
Economics |
ENVIRONMENT |
Fully controlled |
Slightly controlled |
PRIMARY STRATEGY |
Math. induction & deduction |
Observation |
CORRECTNESS |
Always true |
Not at times |
UNANIMITY |
Yes |
Not at times |
Anyway, to study economists problems, economists employ a process of theoretical investigation called the scientific method comprised of 4 steps:
Identify and define the question as well as relevant variable.
Make assumptions, that is the prerequisites or condition for the theory to apply.
Formulate a hypothesis, that is how variables relate to and affect one another.
Validation of the hypothesis, testing the predictions against actual evidence.
If the answer to step 4 is negative, then either the hypothesis is incorrect or the previous two steps do not go smoothly; otherwise, hypothesis passes the validity test and a theory or model is confirmed.
