
- •«Волгоградский государственный медицинский университет»
- •Кафедра иностранных языков с курсом латинского языка
- •Методические указания
- •I семестр Занятие 1(продолжительность-3ч.)
- •Занятие 2(продолжительность-3ч.)
- •Занятие 3(продолжительность-3ч.)
- •Занятие 4(продолжительность-3ч.)
- •Занятие5(продолжительность-3ч.)
- •Занятие 6(продолжительность-3ч.)
- •Занятие 7(продолжительность-3ч.)
- •Раздел2.Основной курс
- •Занятие 8(продолжительность-3ч)
- •Занятие 9 (продолжительность-3ч)
- •Занятие 10 (продолжительность-3ч)
- •Занятие 11 (продолжительность-3ч)
- •Используйте приведенные ниже клише для построения обобщенных высказываний:
- •Занятие 12 (продолжительность-3ч)
- •Занятие 13(продолжительность-3ч.) Итоговая контрольная работа по теме «Биология как наука. Формы организации жизни на Земле. Биологическое разнообразие» Занятие 14 (продолжительность-3ч)
- •Занятие 15 (продолжительность-3ч)
- •Занятие 16 (продолжительность-3ч)
- •Занятие 17 (продолжительность-3ч)
- •Занятие 18 (продолжительность-3ч)
- •Сравните Present Simple Active & Present Continuous Active
- •Занятие 2(продолжительность-2ч.)
- •Занятие 3(продолжительность-2ч.)
- •Занятие 4(продолжительность-2ч.)
- •Занятие 5(продолжительность-2ч.)
- •Занятие 6(продолжительность-2ч.)
- •Занятие 9(продолжительность-2ч.)
- •Занятие 10(продолжительность-2ч.)
- •4) Работа над грамматическим материалом:
- •Занятие 11(продолжительность-2ч.)
- •Занятие 12(продолжительность-2ч.)
- •Занятие 13(продолжительность-2ч.) Итоговая контрольная работа по теме «Микробиология как наука. Вирусология и иммунология» Занятие 14(продолжительность-2ч.)
- •Занятие 15(продолжительность-2ч.)
- •Занятие 16(продолжительность-2ч.)
- •Занятие 17(продолжительность-2ч.)
- •Занятие 18(продолжительность-2ч.)
- •Занятие 19(продолжительность-2ч.) Итоговая контрольная работа по теме «Физика. Основные законы физики. Физика в медицине»
Занятие 13(продолжительность-3ч.) Итоговая контрольная работа по теме «Биология как наука. Формы организации жизни на Земле. Биологическое разнообразие» Занятие 14 (продолжительность-3ч)
Тема: Физиология систем и органов. Основные физиологические процессы в организме человека.
Цель: развитие навыков чтения и повседневного общения, а также формирование и развитие компетенций:
-ОК-1-способность к обобщению, анализу, восприятию информации, постановке цели и выбору путей ее достижения, владение культурой мышления;
-ОК-2-способность логически верно, аргументировано и ясно строить устную и письменную речь, создавать тексты профессионального назначения;
ПК-13- способность использовать один из иностранных языков в общении и профессиональной деятельности на уровне, не ниже разговорного.
Задачи:
-Повторить временные формы страдательного залога–времена группы Simple (Indefinite);
-Тренировать навык изучающего чтения для перевода специальных текстов по теме «Физиология»;
-Освоить терминологию по теме «Физиология систем и органов».
Этапы занятия: 1) Речевая разминка:
Ответьте на вопросы:
What does physiology study?
What do we call a specialist in physiology?
What organ systems are there in the human body?
How do they function?
What is the main function of the heart/lungs/kidneys/liver/spleen/stomach/gallbladder?
What is oxygen required for?
How is oxygen carried throughout the body?
How many blood circulations are there in the human body?
Расскажите о циркуляции крови в организме человека. Используйте схему циркуляции крови:
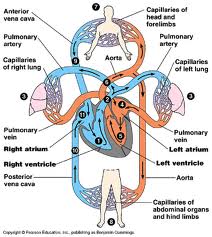
The venous blood from the systemic and portal circulation is brought to the right atrium of the heart. From the right atrium the blood passes into the right ventricle. During the ventricular systole the blood is pumped into the pulmonary artery. From the pulmonary artery the venous blood enters the pulmonary circulation. Through the pulmonary artery the blood is brought to the lungs where it discharges out carbon dioxide and takes in oxygen. The oxygenated blood from the venous part of the pulmonary capillary system passes into the veins and venules. After passing the four pulmonary veins the arterial blood is brought to the left atrium. From the left atrium the blood passes into the left ventricle. During the contraction of the left ventricle the arterial blood is pumped into the aorta. After that the blood is carried through the arteries to all parts of the body.
2) Изучающее чтение «Structure and functions of the
human body»:
Задание1. Выучите следующие слова и словосочетания: inner - внутренний, hollow - полый, chamber - камера, contraction - сокращение, to pump – нагнетать, накачивать, wave - волна, corpuscle [‘kopəsl] – клетка крови, corpuscular element – форменный элемент, platelet – тромбоцит, пластинка, numerous - многочисленный, colouring substance (hemoglobin) [himə’globin] – красящее вещество (гемоглобин), to take part in – принимать участие в, carbohydrate - углевод, exchange - обмен, carbon dioxide – углекислый газ, alveolus-alveoli - альвеола, to transfer - переносить, to breathe in/out – вдыхать/выдыхать, to extend - расширяться, dilated – расширенный/увеличенный, capacity - емкость, stimulus – stimuli – стимул/импульс, to summarize – суммировать/обобщать, motor cortex – двигательный отдел коры головного мозга, feeding substance – питательное вещество
The cardiovascular system consists of the heart, vessels and blood. The heart is an inner hollow muscular organ placed within the chest and included in the pericardium. The heart consists of two chambers divided by the septum. Each of the chambers has two connected parts: the atrium and the ventricle. There are three groups of vessels – arteries, veins and capillaries. The contractions of the heart pump the blood through the arteries to all the parts of the body. Each wave of heart contraction and a period of rest following it compose a cardiac cycle. Blood is a fluid tissue which is composed of plasma and the corpuscular elements - red corpuscles or erythrocytes, white corpuscles or leucocytes and blood platelets or thrombocytes. The erythrocytes are the most numerous cellular elements. They contain red colouring substance or hemoglobin.
The lungs are the main organs of the respiratory system located in the lateral cavities of the chest. The lungs are separated from each other by the mediastinum. They are covered with the pleura. The right lung consists of 3 lobes and the left one consists of two lobes. The lungs take part in the production of physiologically active substances, in the regulation of blood coagulation, in the metabolism of proteins, fats and carbohydrates. The exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide takes place in the alveoli of the lungs. Hemoglobin transfers oxygen in the blood to all tissues and organs of our body. When one breathes in, the volume of the chest increases and the lungs extend. The pressure in the lungs becomes less and the atmospheric air enters the lungs. When one breathes out, the volume of the chest decreases and the lungs contract. The pressure in the lungs becomes higher and the air goes out of the lungs.
The digestive system is formed by a musculomembraneous canal which consists of the mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, and large intestine. The stomach is a dilated portion of the alimentary canal. It is in the upper part of the abdomen under the diaphragm. It has a capacity of from 2 to 4 litres. The liver is the largest gland of the alimentary tract. The small intestine is composed of the duodenum, jejunum and ileum. The large intestine is divided into caecum, colon and rectum. The useful constituents of food are absorbed by the small intestine, while the useless move into the large intestine
The brain is the main organ of the nervous system. It is the center for regulating and coordinating body activities. The brain consists of about 12 billion cells. Each cell is connected to the other by nerve fibres. A constant flow of stimuli comes into the brain through the spinal cord. When all the received stimuli have been summarized and analyzed the brain sends orders to different parts of the human body. The motor cortex controls many body movements. The hypothalamus controls such functions as blood pressure. To provide a proper work of the brain the nervous cells must be well supplied with oxygen and feeding substances. And for this purpose any human being must have regular complete rest, i.e. (id est = that is) sleep. When one sleeps the vital activity of the nervous system is restored. So sleep is of a great protective significance to the human being.
Задание2. Найдите английские эквиваленты для следующих выражений из текста: орган, расположенный в грудной клетке, камеры разделенные перегородкой, по артериям ко всем частям тела, период отдыха, расположенный в боковых полостях грудной клетки, состоять из долей, выработка физиологически активных веществ, обмен белков, жиров, углеводов, в альвеолах легких, объем грудной клетки увеличивается/уменьшается, воздух выходит из легких, железы пищеварительного тракта, под диафрагмой, полезные компоненты пищи, соединяться посредством нервных волокон, полученные стимулы, отправлять приказы, для обеспечения надлежащей работы, для этой цели, жизненная активность восстанавливается
Задание3.Найдите в тексте примеры употребления глаголов в Present/Past/Future Simple Passive. Распределите все глаголы в тексте на те, которые употребляются в страдательном залоге и те, которые не употребляются. Например,
Употр-ся в страд.залоге |
Не употреб-ся в страд.залоге |
are separated from |
consist of |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Задание4. Дополните вводные предложения аннотации таким образом, чтобы они выражали содержание каждого абзаца в обобщенном виде:
1) The cardiovascular system consists of ….
The cardiovascular system also includes ….
Blood which circulates through the body is …
2) The lungs are the organs which ….
The lungs play a role in …
When a person breathes in, … . When a person breathes out, … .
3) The digestive system consists of …
The glands of the alimentary tract are …
4) The brain is the main organ of …
Stimuli come into the brain … from … .
In its turn, the brain sends signals ….
The human brain needs regular supply of …
Задание5. В соответствии с содержанием текста выберите правильные ответы на вопросы:
1) What type of organ is the heart?
2) What chambers is the heart divided into?
3) What do contractions of the heart result in?
4) What are the constituent elements of the blood?
5) What is the structure of the lungs?
6) How is blood transferred to the tissues and organs of the body?
7) What is the stomach?
8) What parts is the large intestine divided into?
9) What parts is the small intestine divided into?
10) What does the brain consist of?
11) What happens to the stimuli which come into the brain?
12) Why is it necessary to have regular rest?
3) Информативное чтение «Lungs.Physiology of the lungs»:
There are two lungs which are located in the chest. They are separated from each other by the mediastinum. The lungs are covered by the pleura. They are conical in shape and each lung has the base, apex, two borders and three surfaces. In the adult the weight of the lungs is about 1.350 g. The right lung is heavier than the left one, because it consists of three lobes and the left one is composed of two lobes.
The structure of the lung consists of an external serous coat, the visceral layer of the pleura, subserous elastic tissue and the parenchyma.
The physiology of the lungs is associated with their structure. There are over 700, 000, 000 alveoli ['əlviolai] in the lungs. The lungs have many capillaries with the total surface of about 80 sq. m. This particular structure of the lungs enables the exchange of gases between the alveolar air and the blood. Elastic fibers of the connective tissue which form the walls of the alveoli alveolar passages enable the lungs to dilate.
When one breathes normally not all the alveoli and capillaries of the lungs are opened. When respiration becomes deep, the number of opened alveoli and capillaries increases. The regulation of the vital capacity of the lungs is important for the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide which takes place in the lungs. In the adult the vital capacity of the lungs is about 3-4 litres. When the depth of respiration increases the vital capacity may be 6 litres and even more. The lungs take part in the production of physiologically active substances, in the regulation of blood coagulation, in the metabolism of proteins, fats and carbohydrates.
Задание1. Соотнесите начало предложения и его окончание:
1. The lungs are covered |
a. the weight of the lungs is about 1.350 g. |
2. The physiology of the lungs |
b. the number of opened alveoli and capillaries increases. |
3. Elastic fibers in the walls of the alveoli |
c. is about 3-4 litres. |
4. When respiration becomes deep, |
d. with the total surface of about 80 sq. m. |
5. In the adult, |
e. from each other by the mediastinum. |
6. The right lung is |
f. enable the lungs to dilate. |
7. In the adult the vital capacity of the lungs |
g. heavier than the left one. |
8. The lungs have many capillaries |
h. the vital capacity may be 6 litres and even more. |
9. The lungs are separated |
i. is associated with their structure. |
10. When the depth of respiration increases |
j. by the pleura. |
Задание2. Задайте вопросы к выделенным словам:
1. The primary function of the respiratory system is to obtain oxygen by body's cells & eliminate carbon dioxide that cells produce. 2. The exchange of gases (O2 & CO2) between the alveoli & the blood occurs by simple diffusion. 3. Breathing is an active process requiring the contraction of skeletal muscles. 4. The primary muscles of respiration include the external intercostal muscles and the diaphragm. 5. The diaphragm is a sheet of muscle located between the thoracic & abdominal cavities. 6. As the external intercostal muscles & diaphragm contract, the lungs expand. 7. During expiration, the respiration muscles relax & lung volume decreases.
Задание3. Соотнесите русские слова и английские эквиваленты:
1. углекислый газ |
A. external serous layer |
2. границы |
B. carbon dioxide |
3. паренхима |
C. mediastinum |
4. наружный серозный слой |
D. vital capacity of the lungs |
5. жизненная емкость легких |
E. total surface |
6. средостение |
F. apex |
7. верхушка |
G. parenchyma |
8. общая поверхность |
H. borders |
Задание4. Дополните вводные предложения аннотации таким образом, чтобы они выражали содержание каждого абзаца в обобщенном виде:
А) The left and right lungs are located …
Each lung has …
The right lung is …
The lung proper consists of …
Б) The lungs have many capillaries which …
The walls of the alveoli are made up of elastic fibers which …
В) When a person breathes normally, …
When the respiration becomes deep, …
The vital capacity of the lungs is … , but it tends to increase …
Задание5. Переведите на английский язык, используя лексику из текста:
1. Легкие – это одни из самых больших органов в организме человека. 2. Легкие покрыты тонким слоем (layer) ткани, который называется плевра. 3. Легкие имеют розовый (pink) цвет. 4. В легких имеется более 600 миллионов альвеол. 5. Когда альвеолы заполняются (fill up with) воздухом, легкие расширяются (dilate). 6. Альвеолы способствуют тому (allow), что кислород из воздуха поступает (pass into)в кровь. 7. Все клетки человеческого организма нуждаются в кислороде. 8. Воздух, который мы выдыхаем, содержит углекислый газ и продукты метаболизма (waste products).
