
- •Theoretical mechanics unit 1
- •1. Learn the notions and their definitions.
- •2. Read, translate and fulfill the tasks.
- •6. Complete the sentences.
- •1. Learn the notions and their definitions.
- •2. Read the text to find illustrations of the notions in the title.
- •Vocabulary
- •Match the titles to the parts of the text:
- •What statements are true or false:
- •Choose the right statement:
- •5. Fill in the gaps.
- •6. Complete the sentences.
- •7. Group the synonyms.
- •1. Learn the notions and their definitions.
- •2. Analyze the principal notions of the text. Statics. Strenth of Materials
- •Vocabulary
- •Match the titles to the parts of the text:
- •What statements are true or false:
- •4. Choose the right statement:
- •5. Fill in the gaps.
- •6. Complete the sentences.
- •7. Group the synonyms.
- •1. Learn the notions and their definitions.
- •2. Read and sum up the text simplifying and compressing the difficult sentences.
- •Vocabulary
- •Match the titles to the parts of the text:
- •3.What statements are true or false:
- •4. Choose the right statement:
- •5. Fill in the gaps.
- •6. Complete the sentences.
- •7. Group the synonyms.
- •The theory of machines and mechanisms
- •1. Learn the notions and their definitions.
- •2. Look through the text for the problems described. Examplify them using your experience. Translate and retell the text.
- •Vocabulary
- •Match the titles to the parts of the text:
- •What statements are true or false:
- •4. Choose the right statement:
- •5. Fill in the gaps.
- •6. Complete the sentences.
- •7. Group the synonyms.
- •1. Find in the text the names of fasteners, their description and classification. Read and translate the text. Kinds of Fasteners
- •Vocabulary
- •Match the titles to the parts of the text:
- •What statements are true or false:
- •4. Choose the right statement:
- •5. Fill in the gaps.
- •6. Complete the sentences.
- •7. Group the synonyms.
- •Power-transmission equipment
- •1. Learn the notions and their definitions.
- •1. Read and translate the following text. Define the words –connectors between the title, text, paragraphs and sentences.
- •Vocabulary
- •1.Match the titles to the parts of the text:
- •What statements are true or false:
- •4. Choose the right statement:
- •5. Fill in the gaps.
- •6. Complete the sentences.
- •7. Group the synonyms.
- •1. Learn the notions and their definitions.
- •2. Read the text and give titles to paragrahps. Translate the text. Types of Gears
- •Vocabulary
- •Match the titles to the parts of the text:
- •Match the notions to their definitions:
- •What statements are true or false:
- •4. Choose the right statement:
- •5. Fill in the gaps.
- •6. Complete the sentences.
- •7. Group the synonyms.
- •1. Learn the notions and their definitions.
- •2. Read, translate and retell the text.
- •Vocabulary
- •Match the titles to the parts of the text:
- •What statements are true or false:
- •4. Choose the right statement:
- •5. Fill in the gaps.
- •6. Complete the sentences.
- •7. Group the synonyms.
- •Food industry equipment Unit 10
- •1. Read, translate and retell the text.
- •Vocabulary
- •Match the titles to the parts of the text:
- •Match the notions to their definitions:
- •3). What statements are true or false:
- •4. Choose the right statement:
- •5. Fill in the gaps.
- •6. Complete the sentences.
- •7. Group the antonyms.
- •Vocabulary
- •Match the notions to their definitions:
- •2).Match the titles to the parts of the text:
- •3.What statements are true or false:
- •4. Choose the right statement:
- •5. Fill in the gaps.
- •1. The centrifugal pumps have the disadvantages: that their output is effected by changes in pressure on the delivery side and they are not suitable for (1) liquids.
- •6. Complete the sentences.
- •7. Group the synonyms.
- •Unit 12
- •1. Learn the notions and their definitions.
- •1. Read, translate and retell the text.
- •Industrial Heat-Exchange Equipment Heat-Exchangers. Principles of Unit Operations
- •Vocabulary
- •Match the titles to the parts of the text:
- •What statements are true or false:
- •6) The simplest type of heat exchanger is the double-pipe heat exchanger as the basis for others.
- •4. Choose the right statement:
- •5. Fill in the gaps.
- •6. Complete the sentences.
- •7. Group the synonyms.
- •Metals unit 13
- •1. Learn the notions and their definitions.
- •2. Read the text. Find the difference between metals and metalloids. Translate the text.
- •Match the titles to the parts of the text:
- •6. Complete the sentences.
- •7. A. Group the synonyms.
- •Match the titles to the parts of the text:
- •Match the notions to their definitions:
- •3.What statements are true or false:
- •2). Parts may not be freely interchanged or substituted in assembly or repair, without hand-fitting.
- •4. Choose the right statement:
- •1). Precision of operation makes it possible to interchange or substitute parts in assembly or repair, without … .
- •6. Complete the sentences.
- •7. Group the synonyms.
- •Electricity unit 15
- •1. Learn the notions and their definitions.
- •Polarity concept of negative and positive.
- •2. Read, translate and retell the text. Electric Current
- •Vocabulary
- •1.Match the titles to the parts of the text:
- •3.What statements are true or false:
- •4). Choose the right statement:
- •5. Fill in the gaps.
- •Group the synonyms.
- •1. Read and translate the text, paying attention to the specific patent expressions. Describe the drawings.
- •1Match the titles to the parts of the text:
- •2. Match the notions to their definitions:
- •3.What statements are true or false:
- •2). The pipe joint or coupling is also suitable for use with metal pipes.
- •3). If composed of suitable material the sealing ring will be contracted into good sealing engagement with the pipe.
- •4. Choose the right statement:
- •6. Complete the sentences.
- •Додаток 1
- •Verbs of motion and doing Tense Forms. Active Voice
- •Passive Voice
- •Infinitive Forms
- •Infinitive Functions
- •Complex Subject with the Infinitive
- •Complex Object with the Infinitive
- •Participle Forms
- •Додаток 2
- •Список літератури
2. Read the text and give titles to paragrahps. Translate the text. Types of Gears
A). This is a gear. It is a set of toothed wheels working together in a machine. The gears may be different types: adjusting gear, bevel gear, cone friction gear, clutch gear, feed gear.
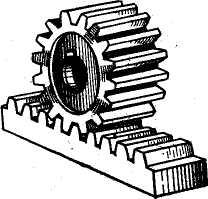
Fig. 23. Rack and pinion
Gears are used in machines to transmit motion and power by means of positive, contact between toothed wheels. Gears are a form of wheel-and-axle. Gears may be classified according to their shaft (axle) relationship. Three such types are parallel, intersecting, and skewed shafts. Spur and helical gears are commonly used with parallel shafts, bevel gears with intersecting shafts, and helical and worm gears with skewed shafts. One of the most common examples of gearing in a machine is the transmission of an automobile. Gears are a vital part of such household machines as the hand-held drill, the electric saw, the hedge-clipper, and the snowblower. Gears are also classified according to the shape oftheir teeth.The major types are spur, helical, bevel, hypoid, and worm and wheel gears
B). Spur Gears. The form of spur gear teeth resembles a mathematical curve – usually the involute, sometimes the cycloid. Only a portion of the tooth follows the involute form because the lower part of the tooth (flank) must provide adequate clearance. In ordinary spur gears, the teeth are cut parallel to the working shaft. This means that there is no side thrust on the shaft. It also means that only a limited number of teeth can be in meshing contact at a given time. One special configuration of spur gears is called a planetary gear train (see illustration). It has been used in automobiles and propeller-driven aircraft.
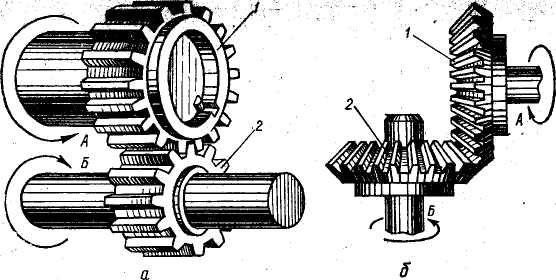
Fig. 24. a.spur gears engaging b. spiral bevel gears engaging
C). Helical Gears. Helical gears are usually used for large power transmission. Such gears are cut in the form of helices and thus lie at an angle to the shaft. Because gearing cut at an angle causes a side thrust on the shaft, it is customary to cut such gears double, so that each series of teeth offsets the side thrust of the other.
Bevel Gears. The driving pinion and ring gear are spiral bevel gears –that is, each gear tooth follows the curve of a spiral. The idler and side gears have straight teeth. Bevel gears are frequently used to drive vertical pumps or process machinery with horizontal drivers.
D). Worm and Wheel Gears is another type of gearing used for nonintersecting shafts or extensions of shafts and make use of worm and wheel gear. The driving gear is a rotating, spiral (worm) that meshes with the teeth of the wheel. Large speed reductions are possible with this arrangement. Gear teeth of a cycloidal profile engage in a rolling action which minimizes friction; however, pinion and gear shafts of cycloidal gears must be very accurately aligned and spaced.
E). Planetary gears consist of three sets of gears, a pinion (sun gear) meshing with two or more planet gears which in turn rotate within a stationary internal gear, that is forming part of the housing. The planet gears are connected to one shaft and the sun gear to the other shaft. Planetary-gear systems are compact, achieve a large reduction in a limited space, and result in input and output shafts in the same center line.
