
- •Theoretical mechanics unit 1
- •1. Learn the notions and their definitions.
- •2. Read, translate and fulfill the tasks.
- •6. Complete the sentences.
- •1. Learn the notions and their definitions.
- •2. Read the text to find illustrations of the notions in the title.
- •Vocabulary
- •Match the titles to the parts of the text:
- •What statements are true or false:
- •Choose the right statement:
- •5. Fill in the gaps.
- •6. Complete the sentences.
- •7. Group the synonyms.
- •1. Learn the notions and their definitions.
- •2. Analyze the principal notions of the text. Statics. Strenth of Materials
- •Vocabulary
- •Match the titles to the parts of the text:
- •What statements are true or false:
- •4. Choose the right statement:
- •5. Fill in the gaps.
- •6. Complete the sentences.
- •7. Group the synonyms.
- •1. Learn the notions and their definitions.
- •2. Read and sum up the text simplifying and compressing the difficult sentences.
- •Vocabulary
- •Match the titles to the parts of the text:
- •3.What statements are true or false:
- •4. Choose the right statement:
- •5. Fill in the gaps.
- •6. Complete the sentences.
- •7. Group the synonyms.
- •The theory of machines and mechanisms
- •1. Learn the notions and their definitions.
- •2. Look through the text for the problems described. Examplify them using your experience. Translate and retell the text.
- •Vocabulary
- •Match the titles to the parts of the text:
- •What statements are true or false:
- •4. Choose the right statement:
- •5. Fill in the gaps.
- •6. Complete the sentences.
- •7. Group the synonyms.
- •1. Find in the text the names of fasteners, their description and classification. Read and translate the text. Kinds of Fasteners
- •Vocabulary
- •Match the titles to the parts of the text:
- •What statements are true or false:
- •4. Choose the right statement:
- •5. Fill in the gaps.
- •6. Complete the sentences.
- •7. Group the synonyms.
- •Power-transmission equipment
- •1. Learn the notions and their definitions.
- •1. Read and translate the following text. Define the words –connectors between the title, text, paragraphs and sentences.
- •Vocabulary
- •1.Match the titles to the parts of the text:
- •What statements are true or false:
- •4. Choose the right statement:
- •5. Fill in the gaps.
- •6. Complete the sentences.
- •7. Group the synonyms.
- •1. Learn the notions and their definitions.
- •2. Read the text and give titles to paragrahps. Translate the text. Types of Gears
- •Vocabulary
- •Match the titles to the parts of the text:
- •Match the notions to their definitions:
- •What statements are true or false:
- •4. Choose the right statement:
- •5. Fill in the gaps.
- •6. Complete the sentences.
- •7. Group the synonyms.
- •1. Learn the notions and their definitions.
- •2. Read, translate and retell the text.
- •Vocabulary
- •Match the titles to the parts of the text:
- •What statements are true or false:
- •4. Choose the right statement:
- •5. Fill in the gaps.
- •6. Complete the sentences.
- •7. Group the synonyms.
- •Food industry equipment Unit 10
- •1. Read, translate and retell the text.
- •Vocabulary
- •Match the titles to the parts of the text:
- •Match the notions to their definitions:
- •3). What statements are true or false:
- •4. Choose the right statement:
- •5. Fill in the gaps.
- •6. Complete the sentences.
- •7. Group the antonyms.
- •Vocabulary
- •Match the notions to their definitions:
- •2).Match the titles to the parts of the text:
- •3.What statements are true or false:
- •4. Choose the right statement:
- •5. Fill in the gaps.
- •1. The centrifugal pumps have the disadvantages: that their output is effected by changes in pressure on the delivery side and they are not suitable for (1) liquids.
- •6. Complete the sentences.
- •7. Group the synonyms.
- •Unit 12
- •1. Learn the notions and their definitions.
- •1. Read, translate and retell the text.
- •Industrial Heat-Exchange Equipment Heat-Exchangers. Principles of Unit Operations
- •Vocabulary
- •Match the titles to the parts of the text:
- •What statements are true or false:
- •6) The simplest type of heat exchanger is the double-pipe heat exchanger as the basis for others.
- •4. Choose the right statement:
- •5. Fill in the gaps.
- •6. Complete the sentences.
- •7. Group the synonyms.
- •Metals unit 13
- •1. Learn the notions and their definitions.
- •2. Read the text. Find the difference between metals and metalloids. Translate the text.
- •Match the titles to the parts of the text:
- •6. Complete the sentences.
- •7. A. Group the synonyms.
- •Match the titles to the parts of the text:
- •Match the notions to their definitions:
- •3.What statements are true or false:
- •2). Parts may not be freely interchanged or substituted in assembly or repair, without hand-fitting.
- •4. Choose the right statement:
- •1). Precision of operation makes it possible to interchange or substitute parts in assembly or repair, without … .
- •6. Complete the sentences.
- •7. Group the synonyms.
- •Electricity unit 15
- •1. Learn the notions and their definitions.
- •Polarity concept of negative and positive.
- •2. Read, translate and retell the text. Electric Current
- •Vocabulary
- •1.Match the titles to the parts of the text:
- •3.What statements are true or false:
- •4). Choose the right statement:
- •5. Fill in the gaps.
- •Group the synonyms.
- •1. Read and translate the text, paying attention to the specific patent expressions. Describe the drawings.
- •1Match the titles to the parts of the text:
- •2. Match the notions to their definitions:
- •3.What statements are true or false:
- •2). The pipe joint or coupling is also suitable for use with metal pipes.
- •3). If composed of suitable material the sealing ring will be contracted into good sealing engagement with the pipe.
- •4. Choose the right statement:
- •6. Complete the sentences.
- •Додаток 1
- •Verbs of motion and doing Tense Forms. Active Voice
- •Passive Voice
- •Infinitive Forms
- •Infinitive Functions
- •Complex Subject with the Infinitive
- •Complex Object with the Infinitive
- •Participle Forms
- •Додаток 2
- •Список літератури
6. Complete the sentences.
Depending оn the 1) ____ of the joint, and the conditions of 2)____ , nuts are selected differing in form (hexagonal, round, etc.), in thickness (normal, thin, thick). In various 3)____ joints, nuts can take external 4) ____ load which is compressive or tensile. The latter nuts are known as 5)____ nuts and they belong to the special 6)____. Washers 7)____ the jointed members against 8) ____ during tightening.
d)expanding, c)purpose, f)assembly, g)design, b)tension, e)protect, h)damage, a)threaded.
7. Group the synonyms.
1) turn, 2)fasten, 3)cutting, 5) transfer, 4)construct, 6) build, 7)use, 8)utilize, 10)convert, 13)revolve, 14)transform, 15)join, 11) create, 20) rotate, 16) thread, 17)attach, 9) purpose, 19)unite, 12)aim, 18)change.
Power-transmission equipment
UNIT 7
1. Learn the notions and their definitions.
Mechanism A component of a machine that transmits or changes motion.
Coupling A machine elements used to join one shaft to another, permanent or semipermanent connections.
Clutch A mechanism permitting easy and quick connection and disconnection of two shafts.
Key a machine part composed of one detail insert into another, used to transmit torque between a shaft and a machine part assembled on it.
Cam A rotating or sliding piece of machinery that acts as part of pair to impart or receive motion.
Follower The other part of a cam mechanism, usually a rod and shaft that receives and transmits motion from the cam.
Ratchet A mechanism that works with a pawl. The ratchet is a bar or wheel with inclined teeth; the pawl is usually a rod that can drop between the teeth to permit motion in only one direction.
Text 1
1. Read and translate the following text. Define the words –connectors between the title, text, paragraphs and sentences.
Couplings
A). Couplings are machine elements used to join one shaft to another, which are needed because of specialized operations of the machine – for example, installation or servicing. The coupling of an electric motor driving a water pump or a gear box may transmit power while preventing an overload, compensate for misalignments of machinery, and minimize vibrations. Couplings normally form permanent or semipermanent connections between shafts, while clutches are associated with rapid engagement.

Fig. 14. Gear and dental flexible coupling.
B)
Solid
couplings
consist
of rigid flanges on each shaft, bolted
solidly together to form a continuous stiff shaft. Their use is
favored when it is desired that the connected machines
act as a single unit (for example, the rotor of
a motor or generator may be used as the flywheel of a reciprocating
engine or compressor) or to reduce over-all length
(such as an overhanging blower) or to eliminate bearings
(by coupling components together such as a gear
pinion to a turbine). Shaft misalignment can result
between the two shafts, increases bearing loads, and produces
a frictional power loss. It is
this
frictional power
that imposes a limitation on the
allowable
misalignment
of high-speed

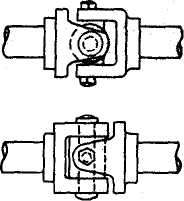
Fig. 15. Solid couplings.
shafts, because the friction heat increases faster with speed than the heat-dissipation ability.
Couplings for high-speed and / or high-power machinery are almost exclusively of the gear (or dental) type. Torque is transmitted by two coupling halves bolted together, which have at each end an internal gear that meshes with gear teeth machined on the periphery of the shaft flanges. Under running conditions, misalignment, errors in tooth spacing, etc., will cause movement between the mating gear teeth, requiring that lubricating oil or grease be used to prevent damage by fretting.
C) Disconnectable Couplings. When it is necessary to disconnect or connect machines while in operation a jaw-type coupling can be used provided it is operated only when the two shafts are running at the same speed. Friction clutches allow the shafts to be engaged while revolving at different speeds, and overrunning clutches will disengage automatically when the speed of the driven unit exceeds that of the driver. Overrunning clutches may be of a jaw type or may use oval pins between an inner and an outer raceway which jam when the torque is in one direction and roll out of engagement for reversed torques. These devices can be used to prevent reverse rotation.

Fig. 16. Rubber flexible coupling..
D) Flexible couplings can be designed to compensate for shaft misalignment or to modify the torsional flexibility of shafts to reduce the effect of torque variations. Torsional flexibility is obtained by using rubber bushings between the bolts and the flanges or, for jaw-type clutches, by use of rubber inserts or rubber bushings between the flange and the shaft. Still other designs use straps to transmit the torque. Couplings that are designed for misalignment use straps, knuckle joints, wobble plates, or some other mechanism that allows a sliding action between meshing parts.
E) Hydraulic coupling. The hydraulic coupling consists of two open-faced vaned impellers placed face to face and enclosed in a housing containing oil. The rotation of an impeller connected to the driver creates a vortex. The output impeller, connected to the driven machine, obtains its power by slowing down the vortex. The shafts are coupled by filling the case with oil and are disconnected by draining.
F) An electric coupling consists of a metal ring connected to the driver shaft, which surrounds an electromagnet mounted on the output shaft. Shafts are coupled by energizing the magnet and disconnected by demagnetizing the field.
Variable speed is obtained by regulating the current to the electromagnet and slip losses are dissipated with air or water circulation.
Note. open-faced vaned impeller – відкрита гідропередача.
