
- •Introduction An economy driven by competition
- •The u.S. Economy Today
- •Vocabulary
- •Exercises
- •The challenges of this century
- •Vocabulary
- •Basic ingredients of the u.S. Economy
- •Vocabulary
- •Exercises
- •A mixed economy: the u.S. System
- •Vocabulary
- •Exercises
- •Government’s role in the u. S. Economy
- •Direct services
- •Regulation and control
- •Stabilization and growth
- •Direct assistance
- •Vocabulary
- •Exercises
- •The passive use of –able.
- •Fluctuations in economic activity the business cycle
- •The great depression
- •Vocabulary
- •Exercises
- •Form adjectives from these nouns:
- •Form verbs from these adjectives:
- •Form nouns from these verb-adjective pairs:
- •6 From small business to the corporation the sole proprietor
- •The business partnership
- •Franchising and chain stores
- •Large corporations: advantages and disadvantages
- •How corporations raise capital
- •The threat of monopoly
- •Vocabulary
- •Exercises
- •7 Stocks, commodities and markets
- •The importance of dividends
- •The stock exchanges
- •Over-the-counter stocks
- •Buying stock on margin
- •Commodities futures
- •Market dynamics
- •Vocabulary
- •Exercises
- •8 Monetary and fiscal policy
- •Money in the u.S. Economy
- •The u.S. Money supply
- •The federal reserve system
- •Fiscal policy
- •Vocabulary
- •Exercises
- •9 Taxation
- •The power to tax
- •Current federal taxes
- •Taxing for nonrevenue purposes
- •Nontax revenue and borrowing
- •Vocabulary
- •Exercises
- •656099, Г. Барнаул, пр-т Ленина, 46
The passive use of –able.
EXAMPLE The difficulty can be avoided.
The difficulty is avoidable.
The commodity can be marketed.
The plan can be tested.
The flow of work can be measured.
The relationship can be defined.
The product can be obtained.
Exercise 4. Give suitable opposites for these words
EXAMPLE capitalism : communism
minority |
maximum |
theoretical |
positive |
public |
collective |
solid |
simplify |
longterm |
Exercise 5. Translate.
Военные ведомства оказывают мощное влияние на Президента.
Повышение государственных расходов на выплату пенсий и пособий по безработице несомненно приведет к увеличению темпов инфляции.
Решение о строительстве нового шоссе между провинцией Квебек (Канада) и штатом Техас (США) послужит интересам нации в целом.
Благосостояние народа зависит от количества денежной массы в обращении.
После того, как был запрещен выброс вредных веществ в реку, компания была вынуждена установить новые очистные сооружения, что привело к повышению цен на продукцию.
Антимонопольное законодательство не разрешает производителям-монополистам бесконтрольно повышать цены на товары первой необходимости.
Введение новых тарифов на ввоз подержанных машин призвано уменьшить количество аварийных ситуаций на дорогах страны.
Экономический спад привел к резкому обнищанию населения.
Забастовочный комитет потребовал увеличения заработной платы и выполнения программ по социальному страхованию.
Пособия малообеспеченным семьям предоставлялись в ограниченном объёме.
Fluctuations in economic activity the business cycle
Economic activity has been subject to considerable variation ever since records have been available. Periods of rapid expansion have been followed by stagnation and depression; rising prices, which have many times produced inflation, have been succeeded by falling prices; full employment by unemployment; rising wages by falling wages; and expanding output by declining output. These fluctuations have come to be associated in the public mind as the “business cycle”. What precisely is meant by this phrase? For a long time all succeeding business fluctuations were treated by observers as if they actually represented the same sequence of events as all their predecessors. It was noted that some were stronger than others, and that some depressions were more disastrous than others. In the nineteenth century cycles were characterized by widespread monetary and banking instability and crises were accompanied by mass sales of securities in short periods of market “panics” or by run of depositors on banks in “banking crises”.
Nowadays economists refer to a business cycle as a type of fluctuations found in the aggregate economic activity of a nation that organized its work mainly in business enterprises. A business cycle is identified as a sequence of five phases:
Contraction (a slowdown in the pace of economic activity);
Trough (when the economy hits bottom, usually in a recession, the lower turning point of a business cycle);
Expansion (a speedup in the pace of economic activity);
Peak (the upper turning of a business cycle);
Revival (economic recovery) (See picture 1).
P
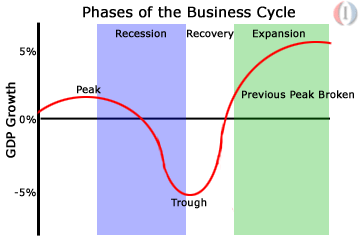
A recession occurs if a contraction is severe enough. A deep trough is called a slump or a depression.
This sequence of changes is recurrent but not periodic. The peaks and troughs of business cycles are referred to as “turning points”.
In other words, the business cycle is the periodic but irregular up-and-down movements in economic activity, measured by fluctuations in real GDP and other macroeconomic variables such as employment, real personal income, industrial production and retail sales.
The business cycle is affected by all the forces of supply and demand. However, it is most dependent on the availability of capital, which is dependent upon interest rates. Too much capital will turn a healthy expansion into a peak, at which point greed will bid up the price of assets, often causing inflation. At this point, a stock market correction may indicate that assets are overvalued, creating fear and a contraction. The Federal Reserve lowers interest rates to spur the economy into expansion during a trough. It raises rates during an expansion to avoid too much of a peak.
A trough usually is accompanied by a recession and a bear market, while an expansion is usually signaled by a bull market and inflation.
Recessions and business cycles are thought to be a normal part of living in a world of inexact balances between supply and demand. What turns a normal recession or 'ordinary' business cycle into an actual depression is a subject of debate and concern. The even larger question is whether it is largely a failure on the part of free markets or largely a failure on the part of government efforts to regulate interest rates, curtail widespread bank failures, and control the money supply.
