
- •Однокомпонентные системы.
- •Правило определения путей кристаллизации двухкомпонентных систем с ликвацией и полиморфными превращениями.
- •Правило определения пути кристаллизации двухкомпонентной системы с образованием твердых растворов.
- •Диаграмма состояния двухкомпонентных систем с образованием твердых растворов
- •Применение правила рычага в двухкомпонентных системах.
- •Треугольник концентраций
- •2.Точки составов химических соединений.
- •3.Пограничные кривые и поля первичной кристаллизации.
- •Тема: Применеие правила рычага в трехкомпонентной системе. Системы MgO-Al2o3- SiO2, k2o - Al2o3- SiO2, Na2o - CaO- SiO2, Li2o - Al2o3- SiO2
Треугольник концентраций
Вершинам треугольника АВС соответствует стопроцентное содержание того компонента, обозначение которого стоит у данного угла треугольника, а два других угла соответствуют нулевому содержанию этого компонента.
2.Точки составов химических соединений.
Находятся в углах треугольника концентраций АВС. Точки составов двойных бинарных соединений, образуемых двумя какими-либо компонентами системы располагаются на сторонах треугольника концентраций. Точки составов тройных соединений, образуемых тремя компонентами системы находятся внутри треугольника концентраций (А1В1С1)

3.Пограничные кривые и поля первичной кристаллизации.
Все поле треугольника концентрации разделяется пограничными кривыми – ab, ef fc, cg, cd, gd на ряд участков называемых полями первичной кристаллизации (k-n-e-b-a-k), (b-e-f-c-d-b), (d-c-g-d).
4.Тройные точки – это три сходящиеся пограничные кривые на диаграммах состояния образуют тройные точки bef, в которых если кристаллизация не закончена в равновесии находится 4 фазы – это жидкость состава этой точки и три кристаллических соединения, поля кристаллизации которых находятся в этой точке.
В тройной точке «b» в равновесии жидкой фазы находится кристаллы АВ, АС, А1В1С1 в равновесии жидкой фазы с находятся кристаллы АВ , АС , А1В1С1.
5. Соединительные прямые и элементарные треугольники. Соединительные прямые – это прямые линии на трехкомпонентных диаграммах состояния, соединяющие точки составов индивидуальных химических соединений , имеющие сложные поля первичной кристаллизации. Например, АВ - А1В1С1 ; А1В1С1 – АС .
6. Бинодальные кривые – если в одну из частных двойных систем А-С составляющих трехкомпонентную систему имеется область ликвации, примыкающей к стороне АС треугольника, ограниченной линией Рm,Pl называется бинодальной кривой.
7. Кривые полиморфных превращений – при постоянной температуре совпадает с изотермой соответствующей температуре полиморфного превращения. Например: компонент В имеет две полиморфные модификации В’ B’’ с температурным превращением 1500 С, то кривая полиморфного превращения будет совпадать на трехкомпонентной диаграмме состояния с линией изотермы qS соответствующей 1500С.
Lecture № 24 ФХС.
Theme: Трехкомпонентные of system. Elements of a structure of the diagrams of a condition трехкомпонентных of systems.
In трехкомпонентных systems of independent parameters are temperature and concentration of two components. At нонвариантном a condition of system, when it is impossible to change temperature and concentration of components, when F=0 the maximal number of phases will be equal 4. In the condensed condition when р=1 a maximum quantity Fmax=3+1-1=3.
In a basis of methods of the graphic image of threefold systems lays равносторонний a triangle. On which parties postpone temperatures, as the corners are answered by(with) pure(clean) components And, In, From concentration 100 %, the quantity(amount) of ordinates will be 3. ordinates correspond(meet) to temperature плавления tA, tB, tC of pure(clean) components And, In and С.
The lateral surfaces represent the diagram двухкомпонентных of systems with эвтектикой Е1 Е2 Е3.
Elements of a structure of the diagrams of a condition
Triangle of concentration изотермы, points of structures of chemical connections, boundary curve, field primary кристаллизации, threefold points connecting direct, бинодальные of curve, curve polymorphic transformations.
1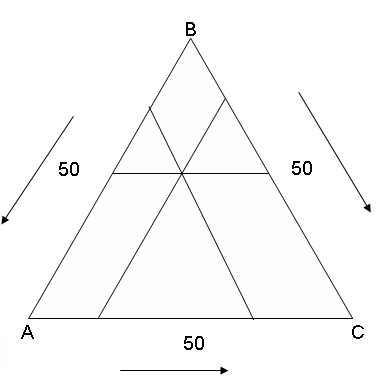 .
Triangle of concentration
.
Triangle of concentration
To tops of a triangle АВС there corresponds(meets) the absolute contents of that component, which designation costs(stands) at the given corner of a triangle, and other two corners correspond(meet) to the zero contents of this component.
2. Point of structures of chemical connections.
A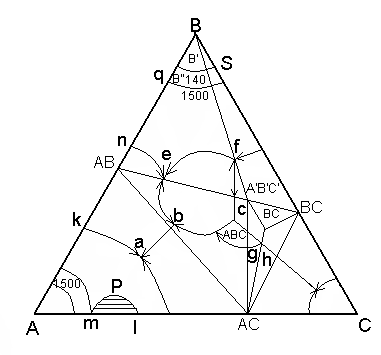 re
in corners of a triangle of concentration АВС.
The points of structures of double binary connections formed by two
any components of system settle down on the parties of a triangle of
concentration. The points of structures of threefold connections
formed by three components of system are inside a triangle of
concentration (А1В1С1)
re
in corners of a triangle of concentration АВС.
The points of structures of double binary connections formed by two
any components of system settle down on the parties of a triangle of
concentration. The points of structures of threefold connections
formed by three components of system are inside a triangle of
concentration (А1В1С1)
3. Boundary curves and fields primary кристаллизации.
All field of a triangle of concentration is divided(shared) by boundary curves - ab, ef fc, cg, cd, gd on a number(line) of sites named by fields primary кристаллизации (k-n-e-b-a-k), (b-e-f-c-d-b), (d-c-g-d).
4. The threefold points are three converging boundary curves on the diagrams of a condition form threefold points bef, in which if кристаллизация is not completed in balance there are 4 phases is a liquid of structure of this point and three crystal connections, the fields кристаллизации which are in this point.
In a threefold point "b" in balance of a liquid phase is crystals АВ, АС, А1В1С1 in balance of a liquid phase with are crystals АВ, АС, А1В1С1.
5. Connecting direct and elementary triangles. Connecting direct are direct lines on трехкомпонентных the diagrams of a condition connecting points of structures of individual chemical connections having complex(difficult) fields primary кристаллизации. For example, АВ - А1В1С1; А1В1С1 - АС.
6. Бинодальные curves - if in one of private(individual) double systems А-С of components трехкомпонентную system there is an area ликвации, contiguous to the party АС of a triangle limited line Рm, Pl is called бинодальной by a curve.
7. Curves of polymorphic transformations - at constant temperature coincides with изотермой to appropriate temperature of polymorphic transformation. For example: the component In has two polymorphic updatings In 'B' with temperature transformation 1500 With, a curve of polymorphic transformation will coincide on трехкомпонентной to the diagram of a condition with a line изотермы qS appropriate 1500С.
Lecture № 25 ФХС. Theme: The basic types of the diagram of condition of treecomponent systems and rule of job with them. Definition of the contents of components on the triangle of concentration in systems of binding materials.
As it was already marked, the diagrams of a condition allow first of all to define way crystallization and way melting, and for the same structure graphically these ways are identical, but are opposite on a direction and sequence of phase transformations. Therefore at construction of a way melting on three-component the diagrams of a condition often it happens expedient to define a way crystallization of the appropriate structure before its complete hardening in a final point crystallization, and then, beginning from this point to do the same way in the opposite direction, meaning, that the phase transformations, occurring in equilibrium conditions, at cooling (way crystallization) are opposite on the character to transformations occurring at heating (a way melting). For example, if at cooling occurs crystallization any of connection, at heating occurs melting of its crystals. If at cooling there is an allocation of any crystals for the bill interaction between allou and before the dropped out firm phase, at heating, on the contrary, there is decomposition these crystalls and etc.
Rules of job with three-component by the diagrams of a condition on separate types of these diagrams in their common expression are considered below. The specified rules are considered in that sequence, which usually should adhere at definition of ways of phase changes.

Definition of the contents of components on a triangle of concentration in systems of binding materials.
For definition of the contents any of a component, for example A (the fig. 1), in three-component allou (or total contents of components in firm phases), answering to the given figurative point М, through this point is necessary to lead a straight line ab, parallel opposite (in relation to top of a triangle with %100 contents of this component, i.e. А) party ВС of a triangle of concentration. This straight line cuts on two other parties АВ and АС of a triangle equal pieces (аВ and bС), which characterize the contents of a component A (in this case 30 %).
Precisely as for definition of the contents of components B and C are spent the appropriate straight lines parallel the parties АС (a straight line cd) and АВ (a straight line ef), contents of components B and C will be defined(determined) accordingly by pieces сА (or dC) and еА (or fB) (in this case 50 % B and 20 % С).
From a fig. 1 it is easy to be convinced, that the definition of the contents of components can be made easier on any one party of a triangle of concentration. For this purpose from the given point М to any one party of a triangle, for example АС, the pieces Me and Mb parallel two other parties of a triangle are spent therefore the first party АС will be broken on three pieces appropriate to the contents of all three components - the contents A will define a piece bС - 30 %, C - piece еА- 20 % and B - piece bе- 50 %.
Лекция № 26 ФХС .
Тема: Определение температуры начала кристаллизации расплавав системе вяжущих материалов (или температуры конца плавления твердой смеси)
Т емпература
начала кристаллизации расплавов (или
конца плавления твердой смеси) будет
температура соответствовать той изотерме
на какую попадает точка состава этого
расплава. На рисунке тип трехкомпонентной
диаграммы состояния системы с эвтектикой
без двойных или тройных химических
соединений и твердых растворов.
Температура начала кристаллизации
состава а будет при температуре 1400С
(при этой температуре закончится полное
расплавление твердой смеси этого
состава).
емпература
начала кристаллизации расплавов (или
конца плавления твердой смеси) будет
температура соответствовать той изотерме
на какую попадает точка состава этого
расплава. На рисунке тип трехкомпонентной
диаграммы состояния системы с эвтектикой
без двойных или тройных химических
соединений и твердых растворов.
Температура начала кристаллизации
состава а будет при температуре 1400С
(при этой температуре закончится полное
расплавление твердой смеси этого
состава).
Lecture № 26 ФХС.
Theme: definition of temperature of a beginning кристаллизации расплавав to system of knitting materials (or temperature of the end плавления of a firm mix)
Definition the temperature of beginning crystallization of allou (or temperature of the end melting a firm mix)
In temperature began crystallization of allou (or end melting of a firm mix) there will be a temperature appropriate by that isoterm, on which the point of structure it allou gets.
In a fig. the type threecomponent of the diagram of a condition of system with eutetic without double or threefold chemical connections and firm solutions is submitted. In temperature began crystallization of structure and there will be a temperature 14000C, as the point and is on isoterm with this temperature (at same temperature will be finished complete melting of a firm mix of this structure).
I f
the point of structure gets between two isoterms, that, accepting
conditionally, that temperature between them changes on line of
dependence (that strictly creating not always correctly),
interpolation find temperature appropriate to the given point of
structure.
f
the point of structure gets between two isoterms, that, accepting
conditionally, that temperature between them changes on line of
dependence (that strictly creating not always correctly),
interpolation find temperature appropriate to the given point of
structure.
The definition of structure primary crystallized from melt of a firm phase
Is primary dropping out at crystallization by a phase there will be crystals of that connection, in a field primary crystallization which the point of structure initial melt lays.
In a fig.1 is represented the type of three-component diagram of a condition with binary chemical connection АС melting congruous. From melt of structure а1 by first at appropriate temperature (in this case 1300 °С) the crystals of connection АС will drop out, as the point of this structure lays in a field primary crystallization of this connection.
If the point of structure initial melt (for example, а2) gets on congruous boundary curve (for example, Е1е3), at appropriate temperature (1400 °С) simultaneously will begin crystallization of two connections A and АС, the fields primary crystallization which are divided by this curve. If the point of structure initial melt gets on incongruous boundary curve, the way of crystallization from it at once will leave and will begin to drop out crystals of one connection, in which field after that the point of structure of a liquid phase gets.
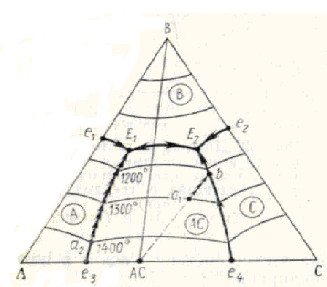
Figure 1- The diagrams of a condition of three-component system with double (binary) chemical connection AC congruous melting
Definition of final phases and final point of crystallization on the diagrams of a condition
At the given structure initial melt the diagram of a condition allows even without construction of a way of crystallization to define structure of final crystal phases after end of crystallization of melt. On final phases it is possible to define on the diagram a final point of crystallization, which characterizes temperature, at which comes to an end of crystallization and structure of a liquid phase at last moment of crystallization. At job with the diagrams of a condition it is recommended to do it before construction of a way of crystallization, that allows limiting this way initial and final points and by that to avoid mistakes at definition of a sequence of phase changes. The structure of final crystal phases after end of crystallization three-component of melt is defined by a rule of an elementary triangle.
Final products of crystallization are those three connections, the points of which structures lay in tops of an elementary triangle, inside which there is a point of structure initial melt. A final point of crystallization three-component melt is that threefold point, in which the fields of primary crystallization of final phases of crystallization converge.
For example, the diagram of three-component system with binary connection АС, melting incongruous (fig. 2), contains two elementary triangles A-B-AC and АС-В-С. For all three-component melts, the points of which structures get in an elementary triangle A-B-AC, final phases of crystallization according to the stated rule will be connections A, B and АС, forming this elementary triangle, and final point of crystallization - point of double lowering G, in which the fields of primary crystallization of these connections converge. Precisely as all melts, the points of which structures get in an elementary triangle АС-В-С, finish to crystallize in eutectic Е with allocation of connections АС, B and C as final phases of crystallization.

Figure 2- The diagrams of a condition of three-component system with double (binary) chemical connection AC incongruous melting
It is necessary to specify, that at job with the diagrams of a condition there can be so-called special cases, at which some general rules are not always applicable. It, for example, concerns to definition of final phases of crystallization, when the point of initial melt gets on a connecting straight line or precisely corresponds to a point of structure any of connection in the given system. If the point of initial structure gets on a connecting straight line (for example, a point a, fig. 2), final phases of crystallization will be those two connections (B and АС), the points of which structures are connected by this connecting straight line (in similar cases initial structure it is necessary to consider as belonging private to two-component system formed by these connections). If the point of structure of initial melt precisely corresponds to structure of any connection, a final product of crystallization will be one phase - crystals of this connection.
Definition of a primary way of change of structure liquid phase after beginning of crystallization
At crystallization from melt of one firm phase the structure of a liquid phase (melt) changes (i. e. the way of crystallization passes) from a point of structure initial melt on continuation of the straight line which has been carried out through a point of structure of crystallizes connection and a point of structure of initial melt in the party of downturn of temperature.
For initial melt a1 (see fig. 1) the structure of a liquid phase at crystallization of connection АС changes (i.е. the way of crystallization passes) on continuation of a straight line АC- a1 connecting point АС and a1, i.е. till a straight line a1b in the party shown by arrows. If the point of structure of initial melt (for example, a2) gets on congruous boundary curve, the change of structure of a liquid phase (way of crystallization) at simultaneous crystallization of two firm phases (in this case A and АС) will occur in the party of downturn of temperature on this curve. If the point of structure of initial melt gets on incongruous boundary curve, the way of crystallization from it will leave and in this case works described corrected definitions of a primary way of change of structure of a liquid phase, i.e. the way of crystallization passes on continuation of a straight line connecting a point of structure of crystallizes phase and a point of structure of initial melt.
Definition of way of crystallization at polymorphic transformations
The way of crystallization at presence in system of polymorphic transformations does not change the direction and is defined by general rules. At crossing isotherm appropriate temperature of polymorphic transformation, there is a transition (at constant temperature) one polymorphic modification of crystal substance in another.
In a fig. 3 the type of the three-component diagram of a condition with threefold chemical connection (ABC) is submitted melting congruous (on it the cases of polymorphic transformations and immiscible liquids) are represented. The component B in system A-B-C has three polymorphic forms designated B', B" and B'". At cooling of melt of structure а1 the crystals of modification B' will drop out at temperature t1, appropriate temperature of polymorphic transformation B'↔В", these crystals will proceed in updating B" between temperatures t1 and t2 from melt the crystals of modification B" will be allocated which at temperature t2 will proceed in modification B'".

Figure 3- The diagrams of a condition of three-component system with threefold chemical connection ABC congruous melting and immiscible liquids
The definition of structure primary crystallized from melt of a firm phase
Is primary dropping out at crystallization by a phase there will be crystals of that connection, in a field primary crystallization which the point of structure initial melt lays.
In a fig.1 is represented the type of three-component diagram of a condition with binary chemical connection АС melting congruous. From melt of structure а1 by first at appropriate temperature (in this case 1300 °С) the crystals of connection АС will drop out, as the point of this structure lays in a field primary crystallization of this connection.
If the point of structure initial melt (for example, а2) gets on congruous boundary curve (for example, Е1е3), at appropriate temperature (1400 °С) simultaneously will begin crystallization of two connections A and АС, the fields primary crystallization which are divided by this curve. If the point of structure initial melt gets on incongruous boundary curve, the way of crystallization from it at once will leave and will begin to drop out crystals of one connection, in which field after that the point of structure of a liquid phase gets.
Figure 1- The diagrams of a condition of three-component system with double (binary) chemical connection AC congruous melting
Definition of final phases and final point of crystallization on the diagrams of a condition
At the given structure initial melt the diagram of a condition allows even without construction of a way of crystallization to define structure of final crystal phases after end of crystallization of melt. On final phases it is possible to define on the diagram a final point of crystallization, which characterizes temperature, at which comes to an end of crystallization and structure of a liquid phase at last moment of crystallization. At job with the diagrams of a condition it is recommended to do it before construction of a way of crystallization, that allows limiting this way initial and final points and by that to avoid mistakes at definition of a sequence of phase changes. The structure of final crystal phases after end of crystallization three-component of melt is defined by a rule of an elementary triangle.
Final products of crystallization are those three connections, the points of which structures lay in tops of an elementary triangle, inside which there is a point of structure initial melt. A final point of crystallization three-component melt is that threefold point, in which the fields of primary crystallization of final phases of crystallization converge.
For example, the diagram of three-component system with binary connection АС, melting incongruous (fig. 2), contains two elementary triangles A-B-AC and АС-В-С. For all three-component melts, the points of which structures get in an elementary triangle A-B-AC, final phases of crystallization according to the stated rule will be connections A, B and АС, forming this elementary triangle, and final point of crystallization - point of double lowering G, in which the fields of primary crystallization of these connections converge. Precisely as all melts, the points of which structures get in an elementary triangle АС-В-С, finish to crystallize in eutectic Е with allocation of connections АС, B and C as final phases of crystallization.
Figure 2- The diagrams of a condition of three-component system with double (binary) chemical connection AC incongruous melting
It is necessary to specify, that at job with the diagrams of a condition there can be so-called special cases, at which some general rules are not always applicable. It, for example, concerns to definition of final phases of crystallization, when the point of initial melt gets on a connecting straight line or precisely corresponds to a point of structure any of connection in the given system. If the point of initial structure gets on a connecting straight line (for example, a point a, fig. 2), final phases of crystallization will be those two connections (B and АС), the points of which structures are connected by this connecting straight line (in similar cases initial structure it is necessary to consider as belonging private to two-component system formed by these connections). If the point of structure of initial melt precisely corresponds to structure of any connection, a final product of crystallization will be one phase - crystals of this connection.
Definition of a primary way of change of structure liquid phase after beginning of crystallization
At crystallization from melt of one firm phase the structure of a liquid phase (melt) changes (i. e. the way of crystallization passes) from a point of structure initial melt on continuation of the straight line which has been carried out through a point of structure of crystallizes connection and a point of structure of initial melt in the party of downturn of temperature.
For initial melt a1 (see fig. 1) the structure of a liquid phase at crystallization of connection АС changes (i.е. the way of crystallization passes) on continuation of a straight line АC- a1 connecting point АС and a1, i.е. till a straight line a1b in the party shown by arrows. If the point of structure of initial melt (for example, a2) gets on congruous boundary curve, the change of structure of a liquid phase (way of crystallization) at simultaneous crystallization of two firm phases (in this case A and АС) will occur in the party of downturn of temperature on this curve. If the point of structure of initial melt gets on incongruous boundary curve, the way of crystallization from it will leave and in this case works described corrected definitions of a primary way of change of structure of a liquid phase, i.e. the way of crystallization passes on continuation of a straight line connecting a point of structure of crystallizes phase and a point of structure of initial melt.
Definition of way of crystallization at polymorphic transformations
The way of crystallization at presence in system of polymorphic transformations does not change the direction and is defined by general rules. At crossing isotherm appropriate temperature of polymorphic transformation, there is a transition (at constant temperature) one polymorphic modification of crystal substance in another.
In a fig. 3 the type of the three-component diagram of a condition with threefold chemical connection (ABC) is submitted melting congruous (on it the cases of polymorphic transformations and immiscible liquids) are represented. The component B in system A-B-C has three polymorphic forms designated B', B" and B'". At cooling of melt of structure а1 the crystals of modification B' will drop out at temperature t1, appropriate temperature of polymorphic transformation B'↔В", these crystals will proceed in updating B" between temperatures t1 and t2 from melt the crystals of modification B" will be allocated which at temperature t2 will proceed in modification B'".
Figure 3- The diagrams of a condition of three-component system with threefold chemical connection ABC congruous melting and immiscible liquids
Лекция № 28 ФХС
Тема: Определение первичного пути изменения состава жидкой фазы после начала кристаллизации. Определение пути кристаллизации при полиморфных превращениях.
При кристаллизации из расплава одной твердой фазы состав жидкой фазы (расплава) изменится, то есть путь кристаллизации проходит от точки состава исходного расплава по продолжению прямой проведенной через точку состава кристаллизующий соединения и точки состава исходного расплава в сторону понижения температуры. Для исходного расплава а1 состав жидкой фазы при кристаллизации соединения АС изменяется по продолжению прямой АС-а1. Если точка состава исходного расплава а2 попадает на конгруэнтную пограничную кривую, то изменение состава жидкой фазы (путь кристаллизации) при одновременной кристаллизации двух твердых фаз А и АС будет происходить в сторону понижения температуры по этой кривой.
Определение пути кристаллизации при полиморфных превращениях.
Путь кристаллизации при наличии в системе полиморфных превращений не изменяет своего направления. При пересечении изотермы, соответствующей температурного превращения происходит переход (при постоянной температуре) одной полиморфной модификации кристаллического вещества в другую.
Определение пути кристаллизации при ликвации.
К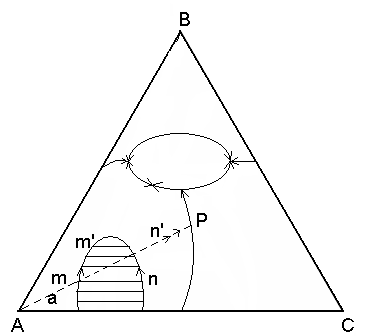 ристаллизация
расплава а начинается с выделением
кристаллов А. Состав жидкой фазы при
этом изменится по продолжению прямой
Аа. Точка m
– это однородный расплав – расслаивается
на две несмешивающиеся жидкости. Состав
первой соответствует точка m,
а второй n.
При дальнейшей кристаллизации компонента
А состав первой жидкости будет изменяться
по левой ветви бинадальной кривой от
точки m
до m’,
а второй жидкости по правой ветви от n
до n’.
ристаллизация
расплава а начинается с выделением
кристаллов А. Состав жидкой фазы при
этом изменится по продолжению прямой
Аа. Точка m
– это однородный расплав – расслаивается
на две несмешивающиеся жидкости. Состав
первой соответствует точка m,
а второй n.
При дальнейшей кристаллизации компонента
А состав первой жидкости будет изменяться
по левой ветви бинадальной кривой от
точки m
до m’,
а второй жидкости по правой ветви от n
до n’.
Definition of a primary way of change of structure liquid phase after beginning of crystallization
At crystallization from melt of one firm phase the structure of a liquid phase (melt) changes (i. e. the way of crystallization passes) from a point of structure initial melt on continuation of the straight line which has been carried out through a point of structure of crystallizes connection and a point of structure of initial melt in the party of downturn of temperature.
For initial melt a1 (see fig. 1) the structure of a liquid phase at crystallization of connection АС changes (i.е. the way of crystallization passes) on continuation of a straight line АC- a1 connecting point АС and a1, i.е. till a straight line a1b in the party shown by arrows. If the point of structure of initial melt (for example, a2) gets on congruous boundary curve, the change of structure of a liquid phase (way of crystallization) at simultaneous crystallization of two firm phases (in this case A and АС) will occur in the party of downturn of temperature on this curve. If the point of structure of initial melt gets on incongruous boundary curve, the way of crystallization from it will leave and in this case works described corrected definitions of a primary way of change of structure of a liquid phase, i.e. the way of crystallization passes on continuation of a straight line connecting a point of structure of crystallizes phase and a point of structure of initial melt.
Definition of way of crystallization at polymorphic transformations
The way of crystallization at presence in system of polymorphic transformations does not change the direction and is defined by general rules. At crossing isotherm appropriate temperature of polymorphic transformation, there is a transition (at constant temperature) one polymorphic modification of crystal substance in another.
In a fig. 3 the type of the three-component diagram of a condition with threefold chemical connection (ABC) is submitted melting congruous (on it the cases of polymorphic transformations and immiscible liquids) are represented. The component B in system A-B-C has three polymorphic forms designated B', B" and B'". At cooling of melt of structure а1 the crystals of modification B' will drop out at temperature t1, appropriate temperature of polymorphic transformation B'↔В", these crystals will proceed in updating B" between temperatures t1 and t2 from melt the crystals of modification B" will be allocated which at temperature t2 will proceed in modification B'".
Figure 3- The diagrams of a condition of three-component system with threefold chemical connection ABC congruous melting and immiscible liquids
Лекция № 29 ФХС
Тема: Определение пути кристаллизации при ликвации. Определение характера пограничных кривых.
Определение пути кристаллизации при ликвации.
К ристаллизация расплава а начинается с выделением кристаллов А. Состав жидкой фазы при этом изменится по продолжению прямой Аа. Точка m – это однородный расплав – расслаивается на две несмешивающиеся жидкости. Состав первой соответствует точка m, а второй n. При дальнейшей кристаллизации компонента А состав первой жидкости будет изменяться по левой ветви бинадальной кривой от точки m до m’, а второй жидкости по правой ветви от n до n’.
К ристаллизация расплава а начинается с выделением кристаллов А. Состав жидкой фазы при этом изменится по продолжению прямой Аа. Точка m – это однородный расплав – расслаивается на две несмешивающиеся жидкости. Состав первой соответствует точка m, а второй n. При дальнейшей кристаллизации компонента А состав первой жидкости будет изменяться по левой ветви бинадальной кривой от точки m до m’, а второй жидкости по правой ветви от n до n’.
Определение характера пограничных кривых.
Для определения характера кривой (конгруэнтное или инконгруэнтное) на каком – либо ее участке необходимо в точках, ограничивающих этот участок, провести касательные в этой кривой. Если эти касательные пересекают соответствующую соединительную прямую, соединяющая точки состава твердой фазы, находящуюся в равновесии вдоль пограничной кривой, то она будет на данной участке конгруэнтное, а если не пересекает то инконтруэнтое.
Диаграммы состояния трехкомпонентной системы с эвтектикой. Двойные системы, плавящуюся с разложением в тройной системе.
Э та
диаграмма без химических соединений
с одной тройной эвтектикой. Процесс
кристаллизации при охлаждении состава
m
в точке а будет происходить следующим
образом: понижение температуры расплава
соответствуют участок Аа, когда
температура расплава станет равной
температуре первыми начнут выделяться
кристаллы вещества А. По мере дальнейшего
охлаждения расплава будет обедняться
компонентом А и, следовательно, обогащаться
компонентами В и С. Состав расплава
будет изменяться по линии ас, являющимся
продолжением Аа. Линия ас называется
путем кристаллизации. При достижении
температуры соответствующий точке с,
расплав на столько обогатится компонентом
С, что этот компонент начнет выделяться
в виде эвтектике вместе с веществом А.
Путь кристаллизации пойдет по линии
двойной эвтектике Е1Е
от точки с до тройной эвтектике Е. В
точке Е наряду с а и с будет выделяться
и третий компонент В до окончательного
застывания всего состава кристаллов
АС и В при температуре равной tE
в точке Е останется постоянной. По
окончании процесса кристаллизации
застывшая система из кристаллов А, В и
С продолжает охлаждаться до температуры
окружающего пространства.
та
диаграмма без химических соединений
с одной тройной эвтектикой. Процесс
кристаллизации при охлаждении состава
m
в точке а будет происходить следующим
образом: понижение температуры расплава
соответствуют участок Аа, когда
температура расплава станет равной
температуре первыми начнут выделяться
кристаллы вещества А. По мере дальнейшего
охлаждения расплава будет обедняться
компонентом А и, следовательно, обогащаться
компонентами В и С. Состав расплава
будет изменяться по линии ас, являющимся
продолжением Аа. Линия ас называется
путем кристаллизации. При достижении
температуры соответствующий точке с,
расплав на столько обогатится компонентом
С, что этот компонент начнет выделяться
в виде эвтектике вместе с веществом А.
Путь кристаллизации пойдет по линии
двойной эвтектике Е1Е
от точки с до тройной эвтектике Е. В
точке Е наряду с а и с будет выделяться
и третий компонент В до окончательного
застывания всего состава кристаллов
АС и В при температуре равной tE
в точке Е останется постоянной. По
окончании процесса кристаллизации
застывшая система из кристаллов А, В и
С продолжает охлаждаться до температуры
окружающего пространства.
Пользуясь правило рычага в любой точке пути кристаллизации на диаграмме состояния трехкомпонентной системы можно определить содержание жидкой фазы. Для пути кристаллизации с характерной точкой состава с содержанием жидкой фазы определиться соотношением:
С%
=
![]()
Диаграммы состояния трехкомпонентной систем с двойными химическими соединениями, плавящуюся конгруэнтно.
Е сли
три компонента АВС образуют двойное
химическое соединение AmBn,
то на диаграмме состояния появляется
дополнительное поле кристаллизации
этого соединения. Для нахождения
конечной точки кристаллизации и
определения вида выделяющихся кристаллов
проводится соединительная линия СAmBn.
Эта линия делит треугольник АВС на два
треугольника. Тройная эвтектика всегда
располагается внутри фазового или
элементарного треугольника в вершинах
которого помещены фазы кристаллов в
этой эвтектике. Точка 1 находится в поле
кристаллизации компонента А. Так как
точка 1 находится в треугольнике АСAmBn,
то кристаллизации заканчивается в точке
Е5 .
сли
три компонента АВС образуют двойное
химическое соединение AmBn,
то на диаграмме состояния появляется
дополнительное поле кристаллизации
этого соединения. Для нахождения
конечной точки кристаллизации и
определения вида выделяющихся кристаллов
проводится соединительная линия СAmBn.
Эта линия делит треугольник АВС на два
треугольника. Тройная эвтектика всегда
располагается внутри фазового или
элементарного треугольника в вершинах
которого помещены фазы кристаллов в
этой эвтектике. Точка 1 находится в поле
кристаллизации компонента А. Так как
точка 1 находится в треугольнике АСAmBn,
то кристаллизации заканчивается в точке
Е5 .
Соединим вершину А с точкой 1 пунктирной линией и продолжаем ее до линии двойной эвтектики. Отрезок А-1 означает понижение температуры расплава. Кристаллы компонента А начинаются только в точке1. НА участке 1-к продолжается выделение кристаллов А и происходит обогащение расплава веществом AmBn. При достижении температуры соответствующей точке к концентрация расплава на столько обогатится компонентами AmBn, что начнет выделяться в виде эвтектики вместе с веществом А, и путь кристаллизации пойдет по линии двойной эвтектики Е2Е5 . На участке к – Е5 происходит увеличение кристаллов А и AmBn. Окончательно расплав застывает в точке Е5 с выделением кроме А и AmBn еще и кристаллов С. Таким образом состав кристаллов определяется только составом соединений, лежащих в вершинах элементарного треугольника, где находится фигуративная точка.
Диаграммы состояния трехкомпонентной систем с двойными химическими соединениями, плавящуюся инконгруэнтно.
 Точка
1 находится вне поля кристаллизации
этого соединения и соединительная линия
не пересекает линии резорбции
(растворения). Каждый элемент треугольника
должен располагать своей трехлучевой
звездой в которой заканчивается
кристаллизация. Для треугольника АСAmBn
такой трехлучевой звездой будет Pn.
Для треугольника AmBnСВ
- Е4 .
Поэтому все составы расположенные в
треугольнике АСAmBn
заканчивают кристаллизоваться в точке
Pn,
а все составы треугольника AmBnСВ
– в точке Е4.
Линию UP
называют линией резорбции, эта линия
является характерной на всем протяжении
и на ней происходит растворение ранее
выделившихся кристаллов А из всех
составов которые расположены в поле
компонента А. Одновременно с резорбцией
кристалла А происходит образование
кристаллов AmBn.
Точка Pn
не является эвтектической и втоже время
служит конечным пунктом кристаллов
составов треугольника АС AmBn
и называется точкой двойного подъема
Точка
1 находится вне поля кристаллизации
этого соединения и соединительная линия
не пересекает линии резорбции
(растворения). Каждый элемент треугольника
должен располагать своей трехлучевой
звездой в которой заканчивается
кристаллизация. Для треугольника АСAmBn
такой трехлучевой звездой будет Pn.
Для треугольника AmBnСВ
- Е4 .
Поэтому все составы расположенные в
треугольнике АСAmBn
заканчивают кристаллизоваться в точке
Pn,
а все составы треугольника AmBnСВ
– в точке Е4.
Линию UP
называют линией резорбции, эта линия
является характерной на всем протяжении
и на ней происходит растворение ранее
выделившихся кристаллов А из всех
составов которые расположены в поле
компонента А. Одновременно с резорбцией
кристалла А происходит образование
кристаллов AmBn.
Точка Pn
не является эвтектической и втоже время
служит конечным пунктом кристаллов
составов треугольника АС AmBn
и называется точкой двойного подъема
Lecture № 29 Theme:
Definition of the way of crystallization at immiscibles liquid. Definition of character of boundary curves. Definition of character of process occurring at change of temperature along boundary curves. Definition of direction of fall of temperature on boundary curves (rule of the temperature maximum).
 Boundary
curves and fields primary crysallization.
Boundary
curves and fields primary crysallization.
All field of a triangle of concentration is divided by boundary curves (for example, ah, be, ef, dg and etc, fig. 2) on line of sites named as fields primary crystallization (for example, field k-n-е-b-а-k, b-е-f-с-d-b, d-с-g-d and etc).
To each chemical connection in the given system there corresponds the certain field primary crystallization (in figures an accessory of fields primary crystallization to those or other connections is designated by the formula, taken in a circle, this connection). After beginning crystallization within the limits of any field primary crystallization in balance there are two phases - liquid and crystals of that connection, which possesses this field. For example, the field d-с-g-d in a fig. 2 is a field primary crystallization of connection ABC and, hence, in it a field in balance with a liquid there are crystals of this connection. The system means by a rule of phases within the limits of fields primary crystallization due-variants. If crystallization is not completed, all points of fields primary crystallization show structure of a liquid phase (alloy), taking place in balance with firm phase - crystals of connection, which belongs this field primary crystallization (if crystallization is completed, point place primary crystallization characterize total chemical structure of firm phases).

Fig. 3. The mutual arrangement points of structures and fields primary crystallization for connections, melting cogrous (а), uncogrous (b, c) and decomposed in firm condition (b)
The arrangement on the diagram of a condition of a point of structure of the given connection and its field primary crystallization determines character of process occurring at heating of this connection:
1) if the point of structure of double or threefold connection lays in an own field primary crystallization, this connection melting without decomposition, i.e. cogrous (for example, connection АС and ABC, fig. 3, а);
2) if the point of structure of double connection lays outside of a field by its primary crystallization, and the field adjoins to the party of a triangle, on which the point of structure of this connection, it melting with decomposition, i.e. uncogrous (for example, connection АС, fig. 3, b);
3) if the point of structure of double connection lays outside of a field by its primary crystallization, and last is located inside a triangle of concentration, not adjoining to the party of a triangle, on which the point of structure of this double connection lays, it at heating is decomposed in firm condition (for example, connection ВС, fig. 3, b);
4) if the point of structure of threefold connection lays outside of a field by its primary crystallization, this connection melting with decomposition, i.e. uncogrous (for example, connection ABC, fig. 3, b).
On boundary curves, each of which divides two fields primary crystallization, in balance there are three phases - liquid and crystals of two connections, which fields divides this curve (for example, on a boundary curve ab in a fig. 2 in balance with a liquid there are crystals of connections АВ and АС). The system by a rule of phases in this case is mono-variants. All points of boundary curves in process crystallization show structure of a liquid phase which is taking place in balance with crystals of the appropriate connections. Boundary curves the arrows usually underline direction of fall of temperature. Depending on character of process occurring in system at change of temperature along boundary curves, they are divided on cogrous and uncogrous. On cogrous of boundary curves there is a physical process crystallization (at downturn of temperature) or melting (at increase of temperature). Uncogrous curves as against cogrous are curves, on which there is a chemical reaction accompanying with disappearance one and occurrence of other phases in system. Cogrous and uncogrous boundary curves differ also by that the way crystallization from first never goes, and from second can (though and not necessarily) leave, having left uncogrous curve.
Лекция № 30 ФХС
