
- •Brian Carl Morgan, Doctor of Philosophy, 2006
- •1. Introduction
- •Introduction
- •Passive Techniques
- •Active Techniques
- •Thesis Objectives and Structure
- •Chapter 2: gray-scale technology
- •Introduction
- •Gray-scale Background
- •Theoretical Background
- •Optical Mask Constraints
- •Standard Lithography Process
- •Design and Lithography Advancements
- •Minimum Feature Limitations
- •2.3.3. Double Exposures
- •Pattern Transfer
- •Deep Reactive Ion Etching (drie)
- •Selectivity Characterizations
- •Technology Collaborations
- •Phase Fresnel Lens (nasa)
- •2.5.2.1. Compensated Aspect Ratio Dependent Etching (carde)
- •Conclusion
- •Chapter 3: elect rostatic comb-drives using goay-scale technology
- •Introduction
- •Electrostatic Actuation Fundamentals
- •Tailored Comb-finger Design and Simulation
- •Analytical Displacement Simulations (2-d)
- •Finite Element Analysis (3-d)
- •Instability Considerations
- •Reduced Height Suspensions
- •Fabrication
- •Comb-drive Testing
- •Reduced Height Comb-fingers
- •Conclusion
- •Introduction
- •Tunable mems Resonator Operation
- •1. Introduction 1
- •1.1. Introduction 1
- •2.1. Introduction 11
- •3.1. Introduction 36
- •4.1. Introduction 51
- •Gray-scale Electrostatic Springs
- •Testing and Characterization
- •Conclusion
- •Introduction
- •Device Concept
- •Figure 5.5: Calculated coupling as two co-axial single-mode fibers are separated longitudinally.
- •Figure 5.6: Alignment schematic for a bent fiber cantilever coupling to a fixed output fiber.
- •Alignment Wedges
- •Fabrication
- •Assembly
- •Actuation Concept Demonstration
- •Introduction
- •Experimental Setup
- •Static Testing
- •Table 6.3: Measured fiber locations for discrete actuation voltages. These 4 points form the corners of a diamond shaped alignment area.
- •Channel a (va2)
- •1. Introduction 1
- •1.1. Introduction 1
- •2.1. Introduction 11
- •3.1. Introduction 36
- •4.1. Introduction 51
- •Horizontal displacement
- •Voltage Squared (v2)
- •Auto-alignment Algorithms
- •Figure 6.16: Simplified hill-climbing algorithm block diagram.
- •Automated Fiber Alignment Results
- •Settling Time, Coarse Threshold Power (%Peak)
- •Testing Summary and Discussion
- •Conclusion
- •Summary of Accomplishments
- •Future Work
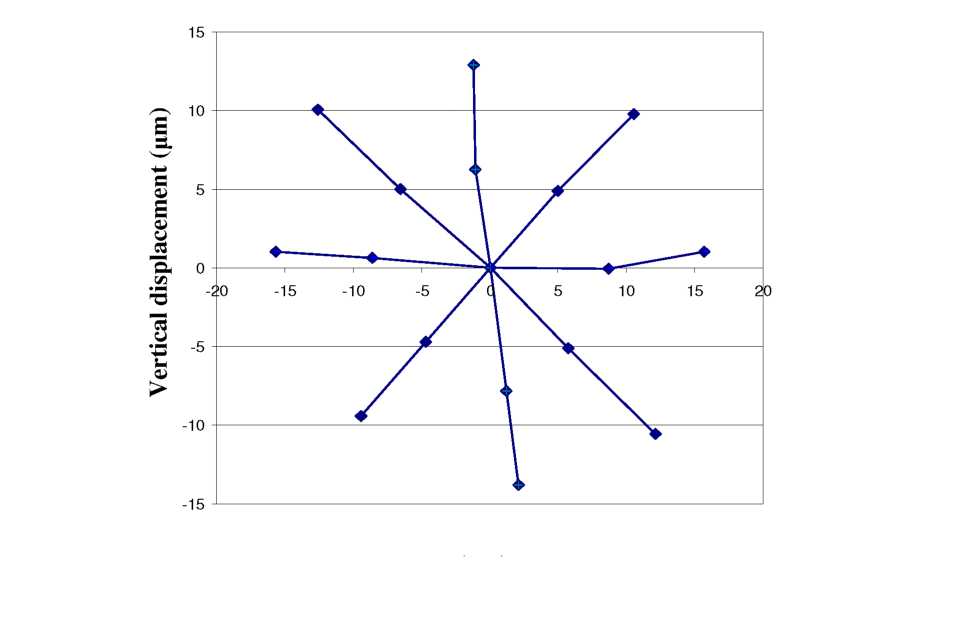
Figure
6.9: Primary axes of movements show trajectories along ~45°,
demonstrating that Cartesian control of fiber is possible.Horizontal displacement
 As
a brief demonstration that the Cartesian control principle produces
similar results starting from an arbitrary point (not the center), a
module was created in LabVIEW to automatically create successive
fiber movements at the behest of an operator. The LabVIEW module
(shown in Figure 6.10) allows the user to define a starting location
and then press buttons to determine the direction and magnitude of
the next fiber movement. While buttons only exist for every 45° in
the figure, arbitrary angles can also be manually entered with
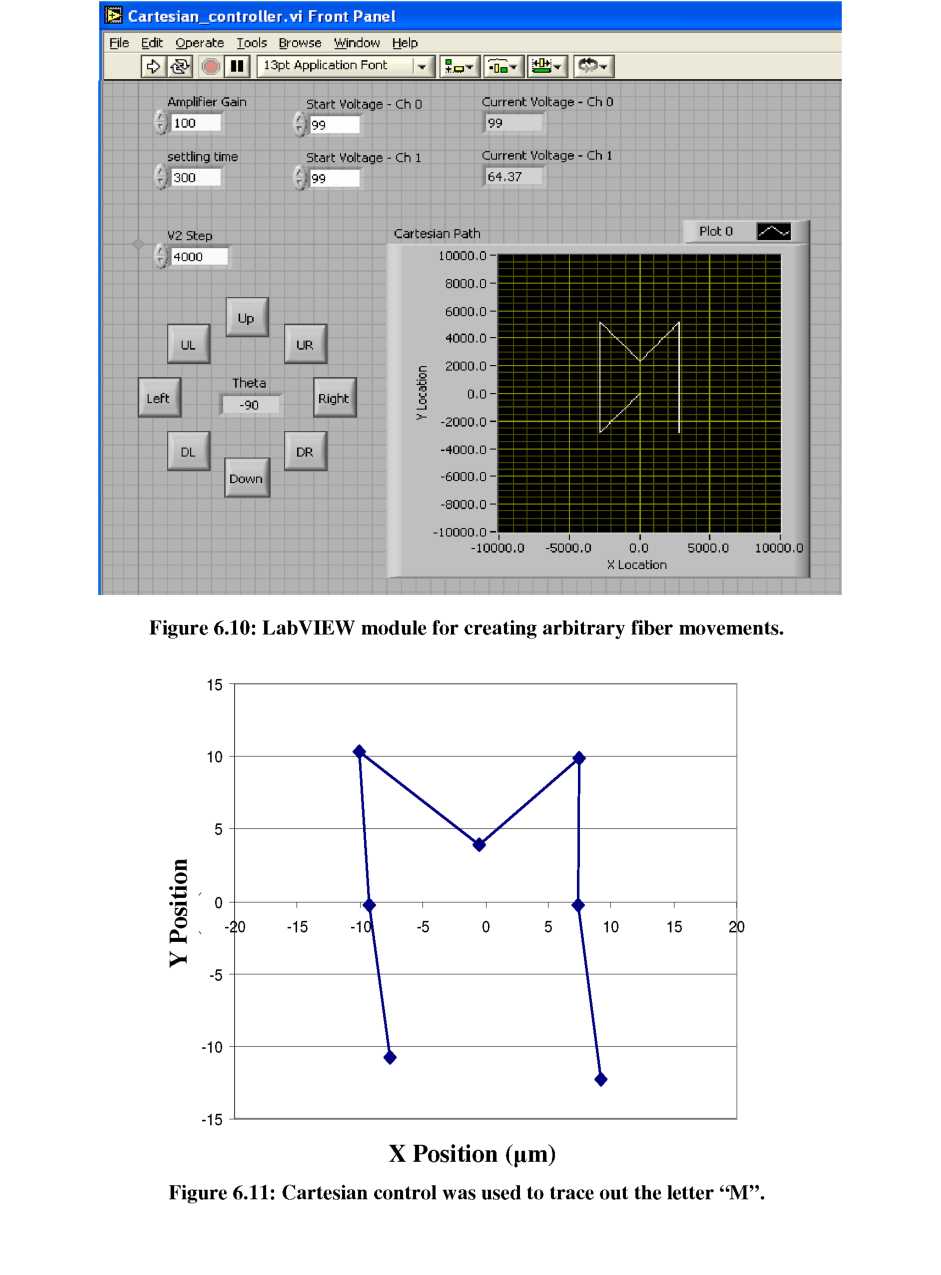
slight changes to the program. To demonstrate this operability, the
letter “M” was traced out with the fiber tip using sequential
movements and facet scans to measure fiber location (see Figure
6.11). Both vertical and angled trajectories across the diamond
alignment area were necessary to create the desired shape. Once
again slight non-linear motion was observed.
As
a brief demonstration that the Cartesian control principle produces
similar results starting from an arbitrary point (not the center), a
module was created in LabVIEW to automatically create successive
fiber movements at the behest of an operator. The LabVIEW module
(shown in Figure 6.10) allows the user to define a starting location
and then press buttons to determine the direction and magnitude of
the next fiber movement. While buttons only exist for every 45° in
the figure, arbitrary angles can also be manually entered with
slight changes to the program. To demonstrate this operability, the
letter “M” was traced out with the fiber tip using sequential
movements and facet scans to measure fiber location (see Figure
6.11). Both vertical and angled trajectories across the diamond
alignment area were necessary to create the desired shape. Once
again slight non-linear motion was observed.
The 45° trajectories and “M” tests have clearly demonstrated that Cartesian control of the fiber tip location can be achieved using simplified geometrical transforms to control the coupled motion of two alignment wedges. Improvements in wedge morphology and angle are expected to improve the symmetry of fiber movement.
Hysteresis Evaluation
Another important quasi-static characteristic to investigate is hysteresis of the
