
- •2. Concept of elasticity: notion, types, methods of calculation
- •Methods of elasticity calculation:
- •Income elasticity of Demand
- •3. Market mechanism: demand, supply, prices
- •4. Consumer’s behavior: the cardinal utility theory
- •5. Consumer’s behavior: the ordinal utility theory
- •Indifference curve(ic) and its properties.
- •Indifference curve, its shape and mrs
- •6 Income and substitution effects of a price change: Slutski and Hicks approaches
- •Income& substitution effects.
- •7 Production function & scale effects
- •8. Comparative analysis of profit maximization under perfect competition and under pure monopoly
- •I Perfect Competition
- •II Monopoly
- •III Profit Maximization in the short-run
- •9. Models of oligopoly
- •10. Alternative theories of the firm.
- •1) Traditional profit maximizing Theory
- •2) Managerial Theory
- •3) Growth Theory
- •2. Economies of scale
- •4) Behavioral Theories
- •11. Producer’s equilibrium in the inputs market
- •12. Price determination in the monopsonic labour market
- •13. Market failures and the economic role of the government
- •Indirect:
- •14. Distribution and redistribution of income and wealth
- •1. Inequality in income and wealth distribution
- •15: Social equilibrium. The Edgeworth box. Pareto efficiency
- •1. Subject, matter and methodology of economics
III Profit Maximization in the short-run
Perfect Competition
P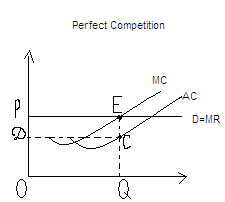 >AC
(AC=OD or QC) P is high enough to cover average costs AC and to bring
some profit. AP=AR-AC=>P-AC; TP=AP*Q= DPEC;
>AC
(AC=OD or QC) P is high enough to cover average costs AC and to bring
some profit. AP=AR-AC=>P-AC; TP=AP*Q= DPEC;
TP= TR (OPEQ) – TC (ODCQ) = TP (DPEC)
Monopoly
A C<P;
AC (OD or QC); TP=AP*Q=PFCD
C<P;
AC (OD or QC); TP=AP*Q=PFCD
TP= TR- TC;
TR=P*Q= OPFQ
TC= AC*Q=ODCQ
TP= OPFQ- ODCQ= PFCQ
9. Models of oligopoly
1. Abstract model of oligopoly
2. Oligopoly models
3. Nash equilibrium.
Criteria:
1. Few firms in an industry or many firms most of them small and few big and they dominate on the market.
3. Barriers to enter are very strict.
4. The product can be either homogeneous or differentiated.
5. Firms influence the price.
6. Demand curve is sloping down.

Perfect Monopolistic Oligopoly Monopoly
Competition Competition
7. Firms are interdependent. They depend upon one another. They behave according expectation about rivals.
Models:
 Cartel
Cartel
When firms collude they behave like monopoly. They agree mutual output and price.
Cartel appeared in the beginning of xx century. Government would forbid cartels. But internationally they exist. Demand should be inelastic, participants should play according the rule, there is very big incentive to cheat.
Tacit collusion
Because cartel are forbidden they do so because they know well one another.
Price leadership
One firm sets the price and others take it. The leader skims the slaves and other also gain profit.
Barometric firm
Sometimes to become price leader the firm mustn't be the biggest it may be prestigious firm. And other firms take the prices.
Rules of thumb
It helps to firm coordinate behavior without meeting. When AC increases by 10% every producer know how to change price.
Price-benchmarks
When Christmas sales occur every producer knows how to change the price.
Non-collusion model
Kinked demand curve model
Assumptions
There is certain market price
If a firm increases the price the rivals won't do the same.
If a firm decreases the price the rivals will do the same. In the result slops of demand curves will be different.

P
MC3 MC1
MC2
Pe N
MR1
A
B D2 D1
0 Q
Qe M+MR2 In vertical section AB change doesn’t-t effect level of price.
Demand curve will be kinked.
In oligopoly price competition isn't effective it gains 0 results.
Prices are relatively stable.
Game theory
Gamers can only play according to the rule. And in each case there are some penalties and praises.
Prisoners dilemma
|
B chooses to: |
||
Not confess |
Confess |
||
A chooses to: |
Not confess |
A: 1 year B: 1 year |
A: 10 years B: free |
Confess |
A: free B:10 years |
A: 5 year B: 5 year |
|
Maximax strategy is an optimistic approach, when the person expect the rival will do the best possible thing. The best will be chosen.
To confess is dominant strategy.
Nash analyzed it.
Nash equilibrium
Cournot model
French economist. He worked out the theories called duopoly.
1 firm in the market and it produces everything. New firm appears - it should reduce the price. First firm takes situation as given. New firm produces bigger amount and reduce prices and old takes price until they will be in equilibrium they will do so.
Q=q1+q2 q1=q2
C=0 MC=0
P=a-bQ P=a-b(q1+q2)
TR1=PQ1=(a-b(q1+q2)q1 => MR1=a-bq2-2bq1=0
TR2=PQ2=(a-b(q1+q2)q2 => MR2=a-bq1-2bq2=0
MR=MC
q1=(a-bq2)/2b
q2=(a-bq1)/2b – reaction function
q*=q1=q2=a/3b
Q=2a/3b P=a/3
.

q1
PCE
Cournot equilibrium
a/3b
ME
a/3b q1
2) firms are of the same size and their output is equal.
In the case of duopoly firms produce more than in monopoly but less than in PC.
If cost is introduced in the formulas we get:
Q=2(a-c)/3b
P=(Q+2c)/a
Stackellberg model is quantity leadership model.
