
- •Table of content
- •Introduction
- •Introduction to theoretical Background
- •1.2. Forex
- •1.2.1 Defining of Forex
- •1.2.2 History of Forex
- •1.2.3 Forex market participants
- •1.2.4 Daily turnover in Forex market
- •1.2.5 Types of exchange rate
- •Managed float regime
- •4). Free float regime
- •1.3.6 Factors, that effect to foreign exchange
- •1.3.7 Foreign exchange transactions
- •Forward transaction
- •Options
- •Futures
- •1.3 Risk management
- •1.3.1 The history of the theory of risk management
- •1.3.2 Defining of risk management
- •1.3.3 Foreign exchange risk
- •1.3.4 Types of foreign exchange risk
- •1.3.8 Foreign Exchange Risk Management
- •1.3.9 Stages and methods Foreign Exchange Risk Management
- •1.3. 10 Methods to reduce the foreign exchange risk
- •1.3.11 Methods of insurance from foreign currency risks
- •1. Балабанов и.Т. «Риск-менеджмент» – Москва.: Финансы и статистика, 1997.
- •1. Жуков е.Ф. «Банки и банковские операции» – Москва.: юнити, 1997.
- •1.3.12 Problems of foreign exchange risk management
1.3.4 Types of foreign exchange risk
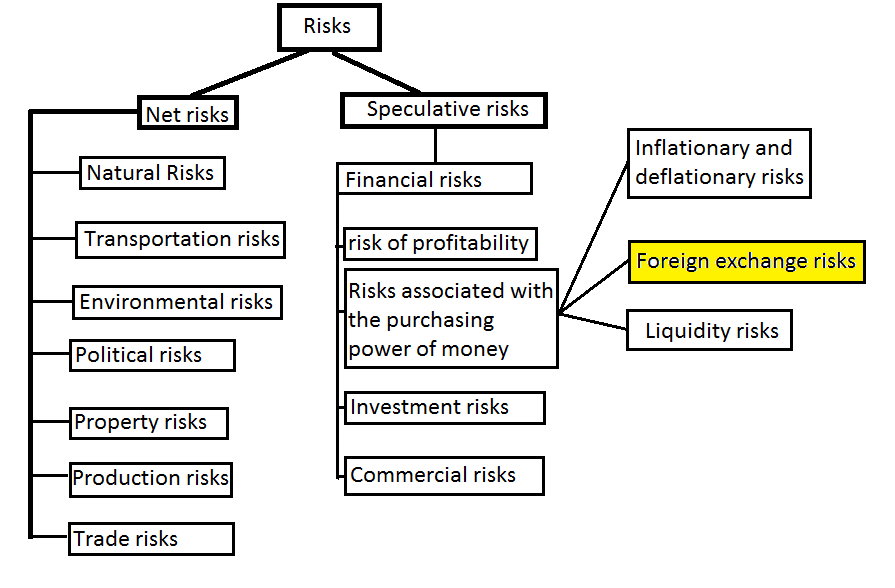
Figure 1. Risk classification according to their functional orientation
Foreign exchange risk includes several major subtypes:
Translational foreign exchange risks arising from the consolidation of the accounts of foreign subsidiaries to the financial accounts of the parent companies of multinational corporations. This risk is of an accounting nature, and driven by the need considering the assets and liabilities of the company in various foreign currencies. It represents a balance effect, but little or no exchange rate risk reflects the transaction. So from an economic point of view, closer attention should be paid operational foreign exchange risk, because it reflects the impact of exchange rate changes on the future the payment flow, that is, on the future profitability of the firm;
Operational foreign exchange risk - arises in during such business operations, the specific stipulates which make a payment or receipt of funds in foreign currency did not at the time of the transaction, and after a while. This risk may reduce the real amount of revenue over the initial estimates;
Economic currency risk - the likelihood of reducing revenue or profit opportunity due to changes in exchange rates. This type of foreign exchange risk for the company consists in the fact the cost of its assets and liabilities may change as a large as well as in the lower side due to future changes in the exchange rate.
Economic foreign exchange risk has long-term nature and due to the fact the firm produces expenses in one currency, but receives to the other, as a result of any change in exchange rates may affect the financial position of the company. There are two subspecies of economic foreign exchange risk:
Direct economic risk - reducing profits for future operations;
Indirect economic risk - the loss of a certain part of the price competition compared to foreign producers (especially dangerous for firms from countries with weak national currency).
Hidden risks.
There are operational, translational and economic risks, which at first glance is not obvious. For example, a supplier in the domestic market can use imported inputs, and the company uses the services of the supplier, indirectly exposed to operational risk, as the increase in the cost of supplier costs as a result of the depreciation of the national currency would cause this supplier to raise prices. Another example would be the situation with the importer to whom the invoice is issued in the national currency, and which finds that prices change from foreign supplier in accordance with the changes of the exchange rate in order to ensure price stability in the currency of the supplier.
Hidden operating or translational risks may arise in the case of foreign subsidiaries are exposed to their own risks. Suppose that the U.S. subsidiary of the British company exports its products to Australia. For a U.S. subsidiary of a risk of loss from changes in the Australian dollar, and it may suffer losses as a result of adverse changes in the Australian dollar relative to U.S. dollar. Such losses would undermine the profitability of the branch. There is indirect operational risk, as revenue gains from subsidiary will be reduced. The parent company also faces translation risk, if the reduction of branch profits will be reflected in the valuation of the assets of the branch in the balance sheet of the parent company
Банковское дело: Учебник для вузов / Под ред. О.В. Лаврушиной .- М.: Дело, 2004
Международные валютно-кредитные и финансовые отношения: Учебник / Под ред. Л.Н. Красавиной. – М.: Финансы и статистика, 2005
Международный менеджмент: Учебник / Под ред. Пивоварова С.И. .- М., 2004
