
- •Marketing Communication Model.
- •The Concept of Integrated Marketing Communications
- •Channels of Distribution. Criteria for channel’s selection.
- •Trade Intermediaries, their role in the marketing channels strategy.
- •5. Personal Selling, its role in the marketing communications
- •6. Process of Advertising Campaign Planning
- •7. Direct Marketing Methods
- •8. Observation method in marketing research
- •9. Experiments in Marketing Research
- •10. Qualitative marketing research, its types and goals
- •11. Quantitative marketing research. Comparative analysis of surveys methods
- •12. The sequence and content of Marketing Planning Stages
- •13. The technique of swot analysis, its implementation
- •14. Marketing budget and control in marketing planning
- •15. The surveys in marketing research. Types and Use
- •16. Questionnaire development. Types of Questions and questions sequence.
- •17. Development and implementation of focus-groups. Peculiarities of qualitative data analysis and interpretation
- •18. Sampling in marketing research. Types of samples procedures. Sample size estimation.
- •19. Panel’s research. Evaluation of market share of products on the basic of panels research results
- •20. Marketing Information System (main blocks). Its importance for the organization
- •21. The Logic of marketing research process
- •22. Factors, influencing consumer behavior. Model “Stimulus – Reaction”
- •23. Couplend’s classification of products.
- •24. Kotler’s Multi-attribute model of Product
- •25. The goals and main tools of Advertising and pr- campaigns. Methods of Advertising campaigns effectiveness evaluation
- •26. Relationship marketing. Consumer loyalty development. Partner relationships
- •27. Branding policy. Methods of Brand equity estimations
- •28. Main stages of New Product Development. Methods of laboratory and natural experiments for product testing
- •29. Marketing strategy and tactics. Linking corporate and functional strategies.
- •30. Marketing mix. The contents and priorities in marketing tools selections
- •31. Marketing pricing policy. Demand-oriented, costs-oriented, competitive-oriented pricing strategies
- •32. Profit and value equations and their role in marketing pricing policy
- •33. Market segmentation. Criteria of target segment selection. Market positioning.
- •34. Demand: level and structure. Methods of demand evaluation.
- •35. Methods of attitudes measurement. Osgud scale, Likert scale.
- •36. Product Life cycle (plc). Different marketing aims and tools on the different stages of plc
- •37. The process of Consumer Purchase decision. Cognitive dissonance, and Marketing strategy for its minimization
- •38. Marketing matrix (bcg, Ansof’s, Porter’s competitive matrix)
- •39. Personal selling. Methods of personal selling effectiveness evaluation
- •40. Sales promotions. Target audience. Main tools of sales promotions. Pro and cons of Sales promotions
- •Pr and their role in the overall marketing strategy.
- •Organization of marketing function within management structure. Marketing specialists job descriptions.
- •International marketing. Main peculiarities of marketing strategies on the international markets
- •Scanning of the international marketing environment
- •Entry modes in the international marketing, comparative analysis
- •Adaptation vs. Standardization strategies for international firms
- •Peculiarities of b2b marketing. Specifics of markets, products and main participants.
- •Peculiarities of marketing of services.
- •Peculiarities of electronic commerce and e-marketing
- •The role of marketing in the financial institutions
- •Information and computer systems and programs and their role in marketing analysis
- •Marketing audit. Main stages and goals
- •Pull and push strategies in marketing channels development.
- •Description of flows in different marketing flows
- •Theory of conflicts in marketing channels.
- •New marketing paradigms and the future of the marketing tools
- •Main indicators of marketing channels effectiveness
- •Market capacity and market share equations.
27. Branding policy. Methods of Brand equity estimations
Branding is a decision in which an organization uses a name, phrase, design, symbol or combination of these to identify its products and distinguish them from those of competitors. A brand name is any word, design, shape, sound, color or combination of these used to distinguish a seller’s goods. A trade name is a commercial legal name under which a company does business. A trademark identifies that a firm has legally registered its brand name or trade name so the firm has its exclusive use thereby preventing others from using it. Brand equity is the added value a given brand name gives to a product beyond the functional benefits provided. Brand equity gives a competitive advantage.
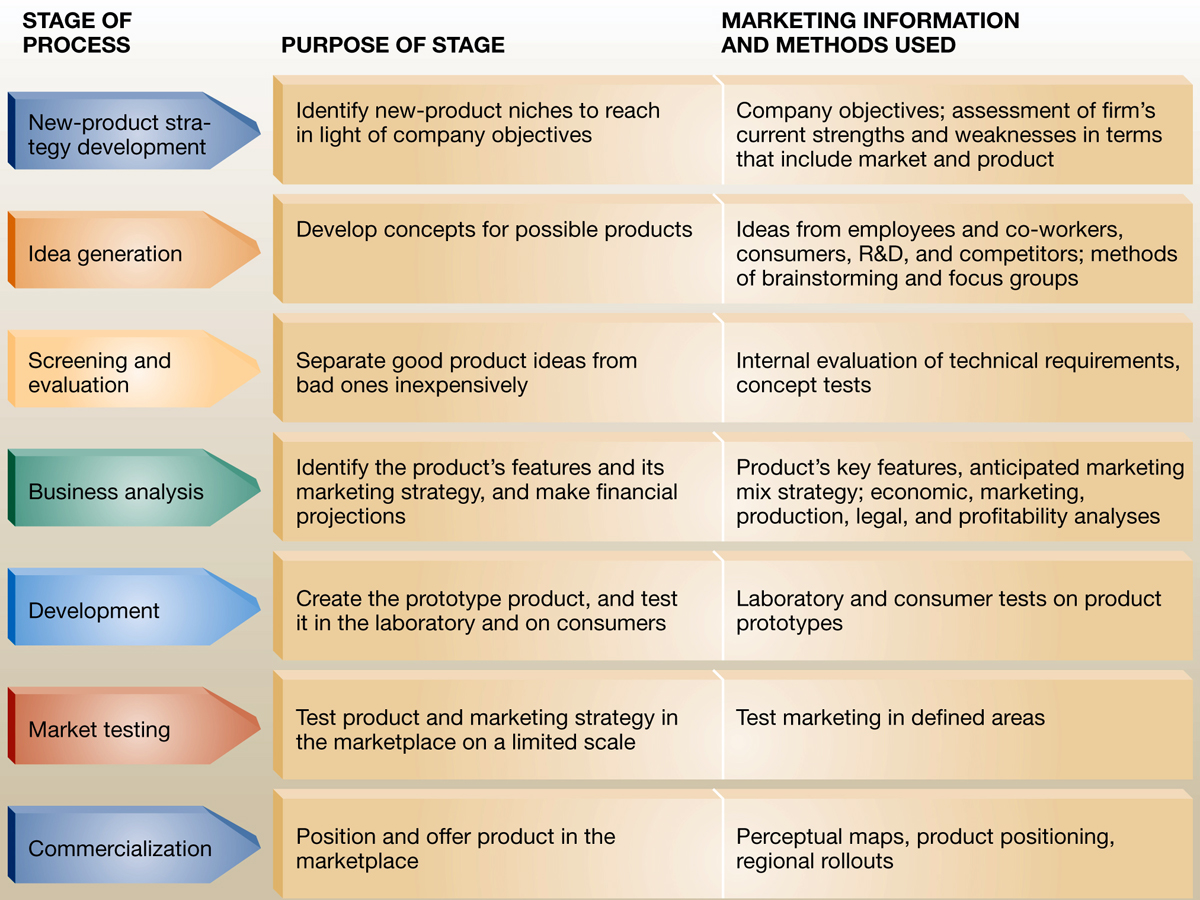
28. Main stages of New Product Development. Methods of laboratory and natural experiments for product testing
new product development (NPD) is the term used to describe the complete process of bringing a new product or service to market. There are two parallel paths involved in the NPD process: one involves the idea generation, product design and detail engineering; the other involves market research and marketing analysis. Companies typically see new product development as the first stage in generating and commercializing new products within the overall strategic process of product life cycle management used to maintain or grow their market share.
Testing techniques:
Monadic - The monadic test simulates real life
Sequential Monadic - Sequential monadic designs are often used to reduce costs. In this design, each respondent evaluates two products
Protomonadic - The protomonadic design begins as a monadic test, followed by a paired-comparison
Paired-Comparison Test - Paired-comparison designs
Repeated Pairs - Each respondent participates in a paired-comparison taste test, followed by a second paired-comparison test
Triangle Test - Each participant is presented with three products and asked to taste all three and choose the one that is different from the other two.
Sensory Research
Ingredient Screening
29. Marketing strategy and tactics. Linking corporate and functional strategies.
A marketing strategy is the means by which a marketing goal is to be achieved, usually characterized by a specific target market and a marketing program to reach it.
Marketing tactics are detailed day-to-day operational decisions essential to the overall success of marketing strategies.
The corporate level is where top management directs overall strategy for entire organization. Each business unit of the company has marketing and other specialized activities (e. g. finance, R&D, HR) at the functional level, which is where groups of specialists create value for the organization.
30. Marketing mix. The contents and priorities in marketing tools selections
Elements of the marketing mix are often referred to as 'the four Ps':
Product - A tangible object or an intangible service that is mass produced or manufactured on a large scale with a specific volume of units. Intangible products are service based like the tourism industry & the hotel industry or codes-based products like cellphone load and credits. Typical examples of a mass produced tangible object are the motor car and the disposable razor. A less obvious but ubiquitous mass produced service is a computer operating system. Packaging also needs to be taken into consideration.
Price – The price is the amount a customer pays for the product. It is determined by a number of factors including market share, competition, material costs, product identity and the customer's perceived value of the product. The business may increase or decrease the price of product if other stores have the same product.
Place – Place represents the location where a product can be purchased. It is often referred to as the distribution channel. It can include any physical store as well as virtual stores on the Internet.
Promotion represents all of the communications that a marketer may use in the marketplace. Promotion has four distinct elements: advertising, public relations, word of mouth and point of sale. A certain amount of crossover occurs when promotion uses the four principal elements together, which is common in film promotion. Advertising covers any communication that is paid for, from cinema commercials, radio and Internet adverts through print media and billboards. Public relations are where the communication is not directly paid for and includes press releases, sponsorship deals, exhibitions, conferences, seminars or trade fairs and events. Word of mouth is any apparently informal communication about the product by ordinary individuals, satisfied customers or people specifically engaged to create word of mouth momentum. Sales staff often plays an important role in word of mouth and Public Relations (see Product above).
