
- •Marketing Communication Model.
- •The Concept of Integrated Marketing Communications
- •Channels of Distribution. Criteria for channel’s selection.
- •Trade Intermediaries, their role in the marketing channels strategy.
- •5. Personal Selling, its role in the marketing communications
- •6. Process of Advertising Campaign Planning
- •7. Direct Marketing Methods
- •8. Observation method in marketing research
- •9. Experiments in Marketing Research
- •10. Qualitative marketing research, its types and goals
- •11. Quantitative marketing research. Comparative analysis of surveys methods
- •12. The sequence and content of Marketing Planning Stages
- •13. The technique of swot analysis, its implementation
- •14. Marketing budget and control in marketing planning
- •15. The surveys in marketing research. Types and Use
- •16. Questionnaire development. Types of Questions and questions sequence.
- •17. Development and implementation of focus-groups. Peculiarities of qualitative data analysis and interpretation
- •18. Sampling in marketing research. Types of samples procedures. Sample size estimation.
- •19. Panel’s research. Evaluation of market share of products on the basic of panels research results
- •20. Marketing Information System (main blocks). Its importance for the organization
- •21. The Logic of marketing research process
- •22. Factors, influencing consumer behavior. Model “Stimulus – Reaction”
- •23. Couplend’s classification of products.
- •24. Kotler’s Multi-attribute model of Product
- •25. The goals and main tools of Advertising and pr- campaigns. Methods of Advertising campaigns effectiveness evaluation
- •26. Relationship marketing. Consumer loyalty development. Partner relationships
- •27. Branding policy. Methods of Brand equity estimations
- •28. Main stages of New Product Development. Methods of laboratory and natural experiments for product testing
- •29. Marketing strategy and tactics. Linking corporate and functional strategies.
- •30. Marketing mix. The contents and priorities in marketing tools selections
- •31. Marketing pricing policy. Demand-oriented, costs-oriented, competitive-oriented pricing strategies
- •32. Profit and value equations and their role in marketing pricing policy
- •33. Market segmentation. Criteria of target segment selection. Market positioning.
- •34. Demand: level and structure. Methods of demand evaluation.
- •35. Methods of attitudes measurement. Osgud scale, Likert scale.
- •36. Product Life cycle (plc). Different marketing aims and tools on the different stages of plc
- •37. The process of Consumer Purchase decision. Cognitive dissonance, and Marketing strategy for its minimization
- •38. Marketing matrix (bcg, Ansof’s, Porter’s competitive matrix)
- •39. Personal selling. Methods of personal selling effectiveness evaluation
- •40. Sales promotions. Target audience. Main tools of sales promotions. Pro and cons of Sales promotions
- •Pr and their role in the overall marketing strategy.
- •Organization of marketing function within management structure. Marketing specialists job descriptions.
- •International marketing. Main peculiarities of marketing strategies on the international markets
- •Scanning of the international marketing environment
- •Entry modes in the international marketing, comparative analysis
- •Adaptation vs. Standardization strategies for international firms
- •Peculiarities of b2b marketing. Specifics of markets, products and main participants.
- •Peculiarities of marketing of services.
- •Peculiarities of electronic commerce and e-marketing
- •The role of marketing in the financial institutions
- •Information and computer systems and programs and their role in marketing analysis
- •Marketing audit. Main stages and goals
- •Pull and push strategies in marketing channels development.
- •Description of flows in different marketing flows
- •Theory of conflicts in marketing channels.
- •New marketing paradigms and the future of the marketing tools
- •Main indicators of marketing channels effectiveness
- •Market capacity and market share equations.
Information and computer systems and programs and their role in marketing analysis
Marketing information system (MIS): consists of people, equipment, and procedures to gather, sort, analyze, evaluate, and distribute needed, timely, and accurate information to marketing decision makers.
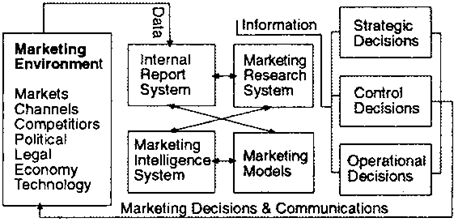
Marketing decision support system (MDSS). Information system that links sales and marketing managers with relevant databases. It is defines as a coordinated collection of data, systems, tools, and techniques with supporting software and hardware which an organization gathers and interprets the relevant information from business and environment and turns it into a basis for marketing action.
Market analysis for product software consists of a number of techniques that allow an organization to collect and disseminate information from their external environment of software products for use in determining their market strategy and actions.
Marketing audit. Main stages and goals
Marketing audit is a comprehensive, systematic, independent, and periodic examination of a company’s or business unit’s marketing environment, objectives, strategies, and activities, with a view to determining problem areas and opportunities and recommending a plan of action to improve the company’s marketing performance.
A marketing audit starts with agreement between the company officer(s) and the marketing auditor(s) on the audit’s objectives and time frame, and a detailed plan of who is to be asked what questions. The cardinal rule for marketing auditors is: Don’t rely solely on company managers for data and opinions.
The marketing audit examines six major components of the company’s marketing situation. Components:
Part I. Marketing Environment Audit
Macroenvironment
Demographic
Economic
Environmental
Technological
Political
Cultural
Task environment
Markets
Customers
Competitors
Distribution and Dealers
Suppliers
Facilitators and Marketing Firms
Publics
Part II. Marketing Strategy Audit
Business Mission
Marketing Objectives and Goals
Strategy
Part III. Marketing Organization Audit
Formal Structure
Functional Efficiency
Interface Efficiency
Part IV. Marketing Systems Audit
Marketing Information System
Marketing Planning System
Marketing Control System
New-Product Development System
Part V. Marketing Productivity Audit
Profitability Analysis
Cost-Effectiveness Analysis
Part VI. Marketing Function Audits
Products
Price
Distribution
Marketing Communications
Sales Force
Pull and push strategies in marketing channels development.
Marketing channels = sets of interdependent organizations involved in the process of making a product or service available for use or consumption. Marketing channel performs the work of moving goods from producers to consumers – achieve goods available to target markets.
Push Marketing creates a situation within the retail environment where the manufacturer and the retailer work together to promote one specific product model or entire product line. This may involve setting up distribution channels and persuading middle men and retailers to stock the product. Example: "Taking the product to the customer“ 1)Trade show promotions to encourage retailer demand 2)Negotiation with retailers to stock your product 3)Efficient supply chain allowing retailers an efficient supply 4)Point of sale displays
Pull Marketing creates a situation in which consumers knowingly request a branded product and "pull" it through the distribution channel. A pull strategy requires a highly visible brand which can be developed through mass media advertising or similar tactics. Example: "Getting the customer to come to you” 1)Advertising and mass media promotion 2)Word of mouth referrals 3)Customer relationship management 4)Sales promotions and discounts
