
- •Marketing Communication Model.
- •The Concept of Integrated Marketing Communications
- •Channels of Distribution. Criteria for channel’s selection.
- •Trade Intermediaries, their role in the marketing channels strategy.
- •5. Personal Selling, its role in the marketing communications
- •6. Process of Advertising Campaign Planning
- •7. Direct Marketing Methods
- •8. Observation method in marketing research
- •9. Experiments in Marketing Research
- •10. Qualitative marketing research, its types and goals
- •11. Quantitative marketing research. Comparative analysis of surveys methods
- •12. The sequence and content of Marketing Planning Stages
- •13. The technique of swot analysis, its implementation
- •14. Marketing budget and control in marketing planning
- •15. The surveys in marketing research. Types and Use
- •16. Questionnaire development. Types of Questions and questions sequence.
- •17. Development and implementation of focus-groups. Peculiarities of qualitative data analysis and interpretation
- •18. Sampling in marketing research. Types of samples procedures. Sample size estimation.
- •19. Panel’s research. Evaluation of market share of products on the basic of panels research results
- •20. Marketing Information System (main blocks). Its importance for the organization
- •21. The Logic of marketing research process
- •22. Factors, influencing consumer behavior. Model “Stimulus – Reaction”
- •23. Couplend’s classification of products.
- •24. Kotler’s Multi-attribute model of Product
- •25. The goals and main tools of Advertising and pr- campaigns. Methods of Advertising campaigns effectiveness evaluation
- •26. Relationship marketing. Consumer loyalty development. Partner relationships
- •27. Branding policy. Methods of Brand equity estimations
- •28. Main stages of New Product Development. Methods of laboratory and natural experiments for product testing
- •29. Marketing strategy and tactics. Linking corporate and functional strategies.
- •30. Marketing mix. The contents and priorities in marketing tools selections
- •31. Marketing pricing policy. Demand-oriented, costs-oriented, competitive-oriented pricing strategies
- •32. Profit and value equations and their role in marketing pricing policy
- •33. Market segmentation. Criteria of target segment selection. Market positioning.
- •34. Demand: level and structure. Methods of demand evaluation.
- •35. Methods of attitudes measurement. Osgud scale, Likert scale.
- •36. Product Life cycle (plc). Different marketing aims and tools on the different stages of plc
- •37. The process of Consumer Purchase decision. Cognitive dissonance, and Marketing strategy for its minimization
- •38. Marketing matrix (bcg, Ansof’s, Porter’s competitive matrix)
- •39. Personal selling. Methods of personal selling effectiveness evaluation
- •40. Sales promotions. Target audience. Main tools of sales promotions. Pro and cons of Sales promotions
- •Pr and their role in the overall marketing strategy.
- •Organization of marketing function within management structure. Marketing specialists job descriptions.
- •International marketing. Main peculiarities of marketing strategies on the international markets
- •Scanning of the international marketing environment
- •Entry modes in the international marketing, comparative analysis
- •Adaptation vs. Standardization strategies for international firms
- •Peculiarities of b2b marketing. Specifics of markets, products and main participants.
- •Peculiarities of marketing of services.
- •Peculiarities of electronic commerce and e-marketing
- •The role of marketing in the financial institutions
- •Information and computer systems and programs and their role in marketing analysis
- •Marketing audit. Main stages and goals
- •Pull and push strategies in marketing channels development.
- •Description of flows in different marketing flows
- •Theory of conflicts in marketing channels.
- •New marketing paradigms and the future of the marketing tools
- •Main indicators of marketing channels effectiveness
- •Market capacity and market share equations.
МАРКЕТИНГ
Marketing Communication Model.
S
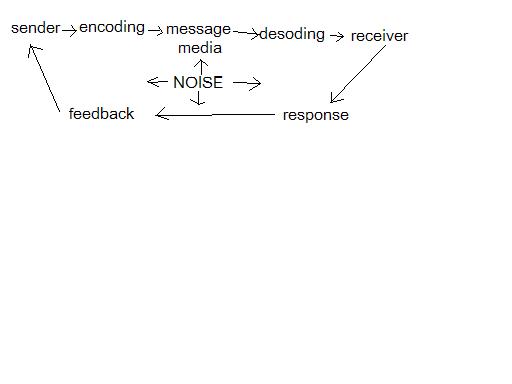 imple
communications models show a sender sending a message to a receiver
who receives and understands it. Real life is less simple - many
messages are misunderstood, fail to arrive or, are simply ignored. It
is essential to ensure the accuracy and relevance of any message,
clever encoding, and reducing 'noise'.
imple
communications models show a sender sending a message to a receiver
who receives and understands it. Real life is less simple - many
messages are misunderstood, fail to arrive or, are simply ignored. It
is essential to ensure the accuracy and relevance of any message,
clever encoding, and reducing 'noise'.
The Concept of Integrated Marketing Communications
Integrated Marketing Communications is a strategic business process used to plan, develop, execute and evaluate coordinated, measurable persuasive brand communication programs over time with consumers, customers, prospects, and other targeted, relevant external and internal audiences.
Promotion Mix: Combination of one or more of the communication tools used to inform, persuade, or remind prospective buyers
1. Advertising
2. Sales promotion
3. Events and experiences
4. Public relations and publicity
5. Direct marketing
6. Interactive marketing
7. Word-of-mouth marketing
8. Personal selling
Channels of Distribution. Criteria for channel’s selection.
1) Direct channel 2) indirect channel
Distribution channels may not be restricted to physical products alone.
Factors influencing channel selection:
Target market coverage – intensive/exclusive/selective distribution
Profitability
Satisfying buyers requirements
Which channel and intermediaries will: (1) provide the best coverage of the target market? (2) best satisfy the buying requirements of the target market? and (3) be the most profitable?
Trade Intermediaries, their role in the marketing channels strategy.
A marketing channel consists of individuals and firms involved in the process of making a product or service available.

Intermediaries perform functions and activities:
transactional (buying, selling, risk taking)
logistical (assorting, storing, sorting, transporting)
facilitating (financing, grading, marketing info and research)
5. Personal Selling, its role in the marketing communications
Personal selling is one of the oldest forms of promotion. It involves the use of a sales force to support a push strategy (encouraging intermediaries to buy the product) or a pull strategy (where the role of the sales force may be limited to supporting retailers and providing after-sales service). Roles: (1) Prospecting - trying to find new customers
(2) Communicating - with existing and potential customers about the product range
(3) Selling - contact with the customer, answering questions and trying to close the sale
(4) Servicing - providing support and service to the customer in the period up to delivery and also post-sale
(5) Information gathering - obtaining information about the market to feedback into the marketing planning process
(6) Allocating - in times of product shortage, the sales force may have the power to decide how available stocks are allocated Advantages:
• face-to-face activity; high degree of personal attention
• sales message can be customised to meet the needs
• respond directly and promptly to customer questions and concerns
• demonstrate the product
• build good long-term relationships
