
- •29. Calculate multiplication of two binary numbers 1011 X 101 110111
- •36. What will be the algebraic function for the following graphic sym
- •87. What’s a Boolean equation?
- •88. What’s the Inverter?
- •89. What is a hardwired program?
- •90. How is the Efficiency of Cache memory characterized (estimated)?
- •91. On what (phenomenon) is the write mechanism of a magnetic disk based?
- •92. How are data organized on a magnetic disk?
- •93. How does the user determine the signed and unsigned binary numbers?
- •96. Which of the numbers: (01111)2, (011110)2, (0011)2 are even, and which are odd?
- •97. What’s the difference between decimal and binary counting?
- •98. Is counting in binary different from counting in any other number system?
- •100. Which of the listed below parameters are used for estimation performance of internal (primary) memory?
- •101. Which of the listed below parameters are used for estimation performance of external (secondary) memory?
- •102. Is Processor (cpu) controlled by any hardware or software?
- •103. What’s a software?
- •104. What’s a hardware?
- •136. What will be the number of sides of Koch Snowflake after n iterations?
- •137. Provided that the side of the first equilateral triangle is s for Koch Snowfalke, Length of each side after n iteration is:
- •138. In floating-point arithmetic, addition and subtraction are more complex than multiplication and division. What are basic phase(s) of the algorithm for addition and subtraction?
- •151. What does the or gate require in order to get a high output?
- •152. A gate with a single input and a single output, and it is used to complement, or invert, a digital signal.
- •153. What’s the operation of nand gate?
- •154. What’s the operation of nor gate?
- •161. Calculate subtraction of two binary numbers 101101-100111 110
1. The main devices (nodes) of computer interconnected by __________ with parallel wires.
A. Bus
B. Processor
C. Videocard
D. CPU
E. Disk
2. ___________ is a device or a complex of devices, which is intended for mechanization or automating of data processing, and which is constructed on the base of electronic elements (transistors, logic circuits, magnet elements and so on).
A. Computer System
B. CPU
C. Graphical processor
D. Keyboard
E. RAM
3. ____________ is a specification of its interfaces, which determines data processing and includes: methods of data coding, system of instructions, principles of software-hardware interaction. It is also determined as a set of information, which is necessary and sufficient for programming in the machinery code.
A. Architecture of the Computer Science
B. Architecture of the Computer Devices
C. Architecture of the Computerized Data
D. Architecture of the Computerized Information
E. Architecture of the Computer
4. _________ is a device, which serves as a central commutator for data transfer among data channels, CPU and the main memory. It may be considered as a dispatcher (manager) of access to the main memory by CPU and data channels (it provides independence for work as for the channels, so CPU).
A. Multiplexor
B. Resistor
C. Transistor
D. Processor
E. Trigger
5. ____________ is an electronic device on the base of semiconductor crystal, which has got three or more electrodes; it intended for amplification, generation or transformation electric oscillations.
A. Multiplexor
B. Resistor
C. Transistor
D. Processor
E. Trigger
6. ___________ is an area of internal (high-speed) memory for temporary storing data.
A. RAM
B. Register
C. ROM
D. Multiplexor
E. Processor
7. Which device reads in instructions and data, writes out data after processing, and uses control signals to control the overall operation of the system. It also receives interrupt signals?
A. CPU
B. RAM
C. Bus
D. Fan
E. Multiplexor
8. ___________ is a set of electric pathways and service electronic devices (framing), providing exchange of data among computer units and devices.
A. Bus
B. CPU
C. Charge
D. Connection
E. Multiplexor
9. The operational units and their interconnections that realize the architecture of the computer system is the ___________
A. organization of the computer system
B. architecture of the computer system
C. organization of any system
D. architecture of any system
E. none of the statements
10. The algorithm used for filling the interior of a polygon is called
A. Flood fill algorithm
B. Boundary fill algorithm
C. Scan line polygon fill algorithm
D. Koch’s curve algorithm
E. Polygon fill algorithm
11. Which of the following decimal numbers has an exact representation in binary notation?
A. 0.1
B. 0.2
C. 0.3
D. 0.4
E. 0.5
12. Asan writes down a number between 1 and 1,000. Alma must identify that number by asking "yes/no" questions to Asan. Alma knows that Asan always tells the truth. If Alma uses an optimal strategy, then she will determine the answer at the end of exactly how many questions in the worst case?
A. 1000
B. 999
C. 32
D. 10
E. 2
13. To which logical operator does the following truth table belong?<br/>

A. AND
B. OR
C. NAND
D. NOT
E. XOR
14. To which logical operator does the following scheme belong?<br/>

A. AND
B. OR
C. NAND
D. NOT
E. XOR
15. To which logical operator does the following truth table belong?<br/>
A. AND
B. OR
C. NAND
D. NOT
E. XOR
16. To which logical operator does the following truth table belong?<br/>
A. AND
B. OR
C. NAND
D. NOT
E. XOR
17. To which logical operator does the following scheme belong?<br/>

A. AND
B. OR
C. NAND
D. NOT
E. XOR
18. To which logical operator does the following scheme belong?<br/>
A. AND
B. OR
C. NAND
D. NOT
E. XOR
19. Convert (705)<sub>10</sub> to binary 1011000001
20. Convert (705)<sub>10</sub> to octal 1301
21. Convert (705)<sub>10</sub> to hexadecimal 2C1
22. Convert (205)<sub>10</sub> to binary 11001101
23. Convert (205)<sub>10</sub> to octal 1005
24. Convert (205)<sub>10</sub> to hexadecimal CD
25. Convert from base-5 to decimal (4021.2)<sub>5</sub> 511.4
26. Convert from hexadecimal to decimal (B65F)<sub>16</sub> 46687
27. Calculate addition of two binary numbers 101101 + 100111 1010100
28. Calculate subtraction of two binary numbers 101101 + 100111
29. Calculate multiplication of two binary numbers 1011 X 101 110111
30. Convert from binary system to decimal (1010.011)<sub>2</sub> 5,375
31. Convert from octal to decimal (630.4)<sub>8</sub> 408,5
32. Convert from decimal to binary (0.6875)<sub>10</sub> 0,1011
33. What will be the Boolean equation for the following scheme? <br/>
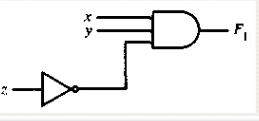
A. F1 = xyz’
B. F1 = x + y + z’
C. F1 = xyz
D. F1 = xy + z’
E. F1= x + yz’
34. What will be the Boolean equation for the following scheme?<br/>
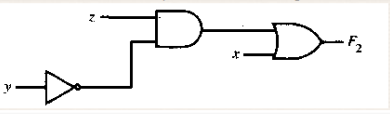
A. F2 = x + y’z
B. F2 = x + yz
C. F2 = xy’z
D. F2 = xyz
E. F2 = xy’ + y’z
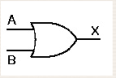
35. What will be the algebraic function for the following graphic symbol?<br/>

A. X = AB
B. X = A + B
C. X = A – B
D. X = (A – B)’
E. All of the statements
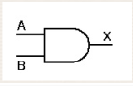
36. What will be the algebraic function for the following graphic sym
bol?<br/>
A. X = A + B
B. X = AB
C. X = A – B
D. X = A’B
E. None of the statements
37. What will be the algebraic function for the following graphic symbol?<br/>
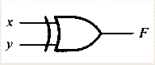
A. F = xy’ + x’y
B. F = xy + x’y’
C. F = x + y’
D. F = y’ + x
E. None of the statements
38. A device or a complex of devices, which is intended for mechanization or automating of data processing, and which is constructed on the base of electronic elements (transistors, logic circuits, magnet elements and so on).
A. Computer
B. Data processing device
C. Converter
D. Printer
E. DBMS machines
39. To which algorithm does the production rule belongs F → F – F ++ F – F<br/>Where, F means "draw forward", + means "turn right 60°", and − means "turn left 60°"
A. Koch Snowflake
B. Koch Island
C. Flood Fill
D. Maze
E. None of the above
40. To which algorithm does the production rule belongs F → F – F +F+ F – F<br/>Where, F means "draw forward", + means "turn right 90°", and − means "turn left 90°"
A. Koch Snowflake
B. Koch Island
C. Flood Fill
D. Maze
E. None of the above
41. Which of the following is(are) internal memory of the system (computer)?
A. CPU register
B. Main memory
C. Cache
D. All of the statements
42. In which of the following gates, the output is 1, if and only if at least one input is 1?
A. NOR
B. AND
C. OR
D. NAND
E. XOR
43. Odd parity of word can be conveniently tested by
A. OR gate
B. AND gate
C. NOR gate
D. XOR gate
E. XNOR gate
44. Which one of the following logic expression is incorrect?
A. 1 XOR 0 = 1
B. 1 XOR 1 XOR 0 = 1
C. 1 XOR 1 XOR 1 = 1
D. 1 XOR 1 = 0
E. 0 XOR 0 = 0
45. Techniques that automatically move program and data blocks into a physical main memory when they are required for execution are called
A. Virtual memory techniques
B. Virtual address techniques
C. Logical address techniques
D. Memory Management Unit
E. None of the statements
46. The binary addresses that the processor issues for either instructions or data are called
A. Virtual address
B. Physical address
C. Instruction address
D. Data address
E. All of the statements
47. ______ translates virtual address into physical address.
A. Processor
B. Memory Management Unit
C. Address translator
D. Main memory
E. Translation Lookaside Buffer
48. Transfer of data between the disk and the main memory is performed using the _______.
A. Memory Management Unit
B. Virtual address translation
C. Cache mechanism
D. Main memory transfer
E. Direct Memory Access
49. In a virtual storage system, a fixed-length block that has a virtual address and that is transferred as a unit between real storage and auxiliary storage.
A. Physical address
B. Virtual address
C. Page
D. Instruction
E. Byte
50. Virtual address generated by processor is interpreted as ____________ followed by an __________.
A. Offset, Virtual page number
B. Page frame, offset
C. Offset, page frame
D. Virtual page number, offset
E. None of the statements
51. What is the specification of offset of virtual address generated by processor?
A. The location of a particular byte (or word) within a page.
B. The information about the main memory location of each page.
C. The current status of the page.
D. The starting address of the page table.
E. All of the statements
52. Information about the main memory location of each page is kept in a ______.
A. Virtual page number
B. Page frame
C. Page table
D. Offset of virtual address generated by processor
E. Page table base register
53. An area in the main memory that can hold one page is called a _______.
A. Page table
B. Page frame
C. Offset of virtual address generated by processor
D. Virtual page number
E. Virtual page frame
54. The starting address of the page table is kept in a ___________.
A. Page table
B. Offset of virtual address generated by processor
C. Virtual page number
D. Page frame
E. Page table base register
55. What is the TLB (translation lookaside buffer)?
A. A small cache that is incorporated into the MMU for storing a copy of a small portion of the page table can be accommodated within the MMU.
B. A small cache that is incorporated into the Cache for storing a copy of a small portion of the page table can be accommodated within the Cache.
C. A unit translates virtual address into physical address.
D. Techniques that automatically move program and data blocks into a physical main memory when they are required for execution
E. None of the statements
56. A special buffer storage, smaller and faster than main storage, that is used to hold a copy of instructions and data in main storage that are likely to be needed next by the processor and that have been obtained automatically from main storage.
A. Main memory
B. Processor
C. MMU
D. Disk storage
E. Cache memory
57. In the pure binary numeration system, either of the digits 0 and 1.
A. Byte
B. Octet
C. Bit
D. Sign
E. Memory
58. The processing performed by a CPU to execute a single instruction.
A. Address translation
B. Processing cycle
C. Instruction cycle
D. Execution cycle
E. CPU cycle
59. A register that is used to hold an instruction for interpretation.
A. Memory address register
B. Memory buffer register
C. Program control
D. Instruction register
E. I/O address register
60. One of the major component types of a computer. It is responsible for the control of one or more external devices (peripherals) and for the exchange of data between those devices and main memory and/or CPU registers.
A. CPU
B. Memory
C. I/O module
D. TLB
E. MMU
61. A register, in a processing unit, that contains the address of the storage location being accessed.
A. Memory address register
B. Memory buffer register
C. I/O address register
D. I/O buffer register
E. Instruction register
62. A register that contains data read from memory or data to be written to memory.
A. Memory address register
B. Memory buffer register
C. I/O address register
D. I/O buffer register
E. Instruction register
63. A code used to represent the operations of a computer.
A. Address
B. Sign
C. Operation code
D. Magnitude
E. None of the statements
64. Which instruction consists of reading an instruction from a location in the memory.
A. Fetch
B. Execute
C. Start
D. Halt
E. Interrupt
65. Which instruction may involve several operations and depends on the nature of the instruction.
A. Execute
B. Fetch
C. Start
D. Halt
E. Interrupt
66. What does processor-memory action do when instruction is loaded into a register?
A. Data may be transferred from processor to memory or from memory to processor.
B. Data may be transferred to or from a peripheral device by transferring between the processor and an I/O module.
C. The processor may perform some arithmetic or logic operation on data.
D. An instruction may specify that the sequence of execution be altered.
E. All of the statements.
67. What does Processor-I/O action do when instruction is loaded into a register?
A. Data may be transferred from processor to memory or from memory to processor.
B. Data may be transferred to or from a peripheral device by transferring between the processor and an I/O module.
C. The processor may perform some arithmetic or logic operation on data.
D. An instruction may specify that the sequence of execution be altered.
E. All of the statements.
68. What does Data processing action do when instruction is loaded into a register?
A. Data may be transferred from processor to memory or from memory to processor.
B. Data may be transferred to or from a peripheral device by transferring between the processor and an I/O module.
C. The processor may perform some arithmetic or logic operation on data.
D. An instruction may specify that the sequence of execution be altered.
E. All of the statements.
69. What does Control action do when instruction is loaded into a register?
A. Data may be transferred from processor to memory or from memory to processor.
B. Data may be transferred to or from a peripheral device by transferring between the processor and an I/O module.
C. The processor may perform some arithmetic or logic operation on data.
D. An instruction may specify that the sequence of execution be altered.
E. All of the statements.
70. Which register specifies a particular I/O device?
A. I/O address register
B. I/O buffer register
C. Memory address register
D. Memory buffer register
E. Instruction register
71. Which register is used for the exchange data between an I/O module and the CPU?
A. I/O address register
B. I/O buffer register
C. Memory address register
D. Memory buffer register
E. Instruction register
72. In Instruction Format if OpCode equals to 0001 which operation should be performed?
A. Load AC from Memory
B. Store AC to Memory
C. Add to AC from Memory
D. Subtract AC from Memory
E. None of the statements
73. In Instruction Format if OpCode equals to 0010 which operation should be performed?
A. Load AC from Memory
B. Store AC to Memory
C. Add to AC from Memory
D. Subtract AC from Memory
E. None of the statements
74. In Instruction Format if OpCode equals to 0101 which operation should be performed?
A. Load AC from Memory
B. Store AC to Memory
C. Add to AC from Memory
D. Subtract AC from Memory
E. None of the statements
75. Why pages should not to be too small?
A. Because the access time of the main memory is much longer than of a magnetic disks.
B. Because the access time of a magnetic disks is much longer than of the main memory.
C. Because the access time of a cache is much longer than of the main memory.
D. Because of the size main memory.
E. Because of the size of cache memory.
76. The _____________ is that part of the computer that actually performs arithmetic and logical operations on data.
A. MMU
B. ALO
C. ALU
D. MMO
E. ALP
77. High-speed memory internal to the CPU. Some of them is user visible; that is, available to the programmer via the machine instruction set. Others are used only by the CPU, for control purposes.
A. Register
B. Read only memory
C. Semiconductor
D. Bus
E. Sequential circuit
78. A shared communications path consisting of one or a collection of lines. In some computer systems, CPU, memory, and I/O components are connected by a common line. Since the lines are shared by all components, only one component at a time can successfully transmit.
A. Bus
B. Path lines
C. Registers
D. Sequential circuit
E. Semiconductor
79. An area in storage used to indicate the order in which instructions are executed, and to hold and indicate the status of the computer system.
A. Random Access Memory (RAM)
B. Programmable Logic Array (PLA)
C. Program Status Word (PSW)
D. Program Counter (PC)
E. Instruction Register (IR)
80. A device that has a number of input lines of which any number may carry signals and a number of output lines of which not more than one may carry a signal, there being a one-to-one correspondence between the outputs and the combinations of input signals.
A. Decoder
B. Encoder
C. Multiplexor
D. Demultiplexor
E. None of the statements
81. A flat circular plate with a magnetizable surface layer, on one or both sides of which data can be stored.
A. Magnetic tape
B. Magnetic plate
C. Magnetic disk
D. Magnetic layer
E. All of the statements
82. A computer-oriented language whose instructions are usually in one-to-one correspondence with computer instructions and that may provide facilities such as the use of macroinstructions. Synonymous with computer-dependent language.
A. Assembly language
B. High level language
C. Programming language
D. Binary language
E. None of the statements
83. Storage used to compensate for a difference in rate of flow of data, or time of occurrence of events, when transferring data from one device to another.
A. Buffer
B. Cache
C. Register
D. Event
E. Chip
84. That part of the CPU that controls CPU operations, including ALU operations, the movement of data within the CPU, and the exchange of data and control signals across external interfaces (e.g., the system bus)
A. Control Unit
B. Arithmetic and Logic Unit
C. Program Counter
D. Instruction Register
E. Memory Address Register
85. A form of I/O in which a special module, called a ____________, controls the exchange of data between main memory and an I/O module.
A. DMA module
B. RAM module
C. BUS module
D. PC module
E. IR module
86. What are logic gates?
A. Logic gates are magnetic devices for building network bridges for forming digital electronic circuitry and have only one output terminal without inputs.
B. Logic gates are silicon wires for building network bridges for forming digital electronic circuitry and have only one output terminal without inputs.
C. Logic gates are the basic building blocks for forming digital electronic circuitry and have only one output terminal and one or more input terminals.
D. Logic gates are coaxial wires of devices for building network bridges for forming digital electronic circuitry and have only one output terminal without inputs.
E. Logic gates are set of flip-flops for building network bridges for forming digital electronic circuitry and have only one output terminal without inputs.
