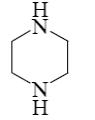
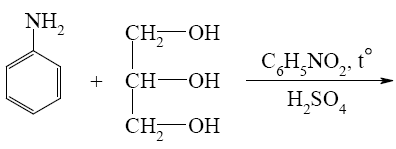
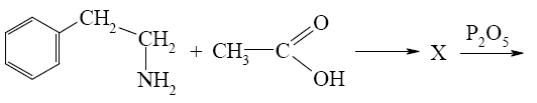
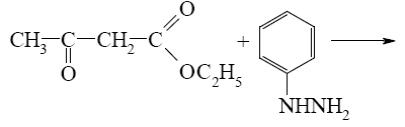
- •Choose the correct range of acidity increase for the following compounds.
- •Formic acid
- •*Formic acid
- •Choose the correct range of acidity increase for the following compounds.
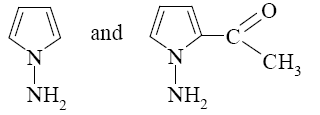
- •What is the identity of the intermediate (a) and the end-product (b) in the
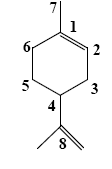
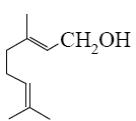
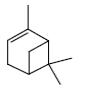
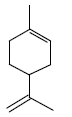
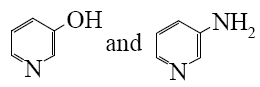
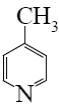
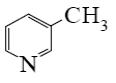
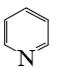
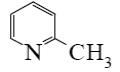
- •To which group of lipids do terpenes belong?
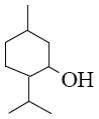
- •Which group of compounds does borneol belong?
- •Which group of compounds does α-pinene belong?
- •What reaction do monosaccharides in the cyclic form?
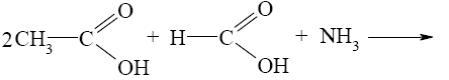
- •Determine what compound will form after the glucose oxidation by Felling reagent:
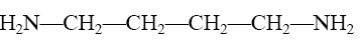
*
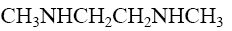
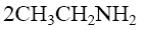
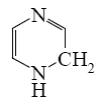
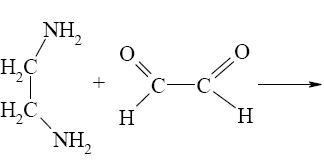
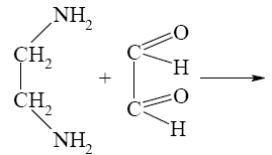
What is the identity of the intermediate (a) and the end-product (b) in the
reaction of ethylenediamine with glyoxal?
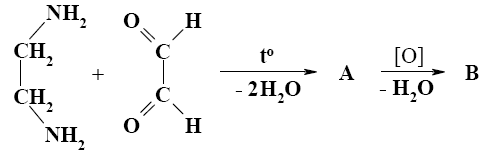
*
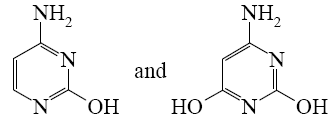
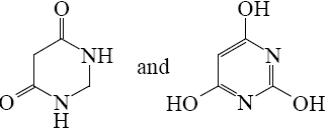
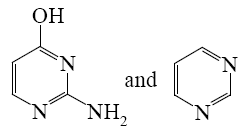
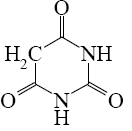
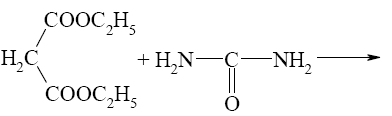
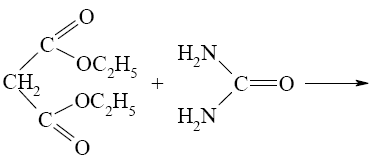
What is the end-product of diethylmalonate condensation with urea?
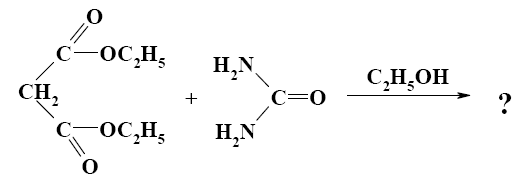
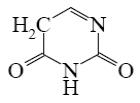
*
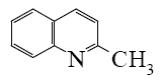
Select the mechanism of the following reaction and the position of isoquinolin it will principally occur?
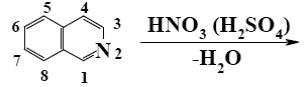
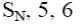
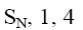
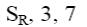
*

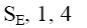
At what positions of quinoline will the following reaction principally occur?
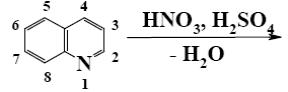
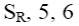
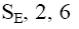
*
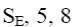
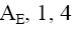
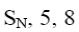
What is the product of indigo Blue oxidation with conc. HNO3?
indoxyl
pyrrole
indole
*isatin
white indigo
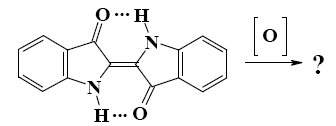
The condensation of which compounds leads to formation of
polyvinylpirrolidone?
furane with ethene
pyrrole with ethylene
pyrrole with acetylene
pyrrolidone with ethylene
*pyrrolidone with acetylene
Which of the following compound can be used as catalyst in the reactions of Yuriev’s cycle?
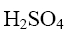
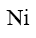
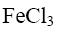
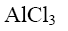
*
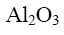
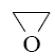
Which of the following compounds will form oxiran when treated with concentrated solution of alkali?
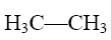
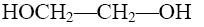
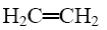
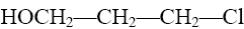
*
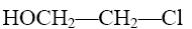
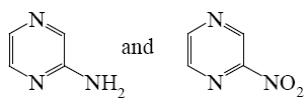
Which group of alkaloids does theophylline belongs to?
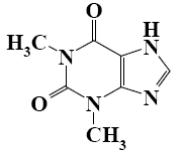
isoquinoline and phenanthroisoquinoline alkaloids
*purine alkaloids
tropane alkaloids
pyridine and piperidine alkaloids
quinoline alkaloids
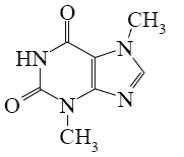
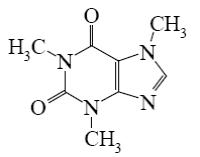
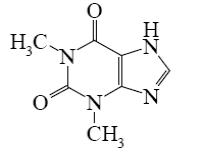
Choose the correct name for theophylline.

5,7- dimethylxanthine
3,5- dimethylxanthine
2,4- dimethylxanthine
4,6- dimethylxanthine
*1,3-dimethylxanthine
Choose the most complete definition of alkaloids.
Alkaloids – naturally occurring (plants) oxygencontaining organic compounds.
Alkaloids – naturally occurring (plants and animals) compounds, which display basic properties.
Alkaloids – heterocyclic compounds with one or more hydroxyl-groups.
Alkaloids – nitrogencontaining organic compounds with glycosidic bonds
*Alkaloids – naturally occurring (plants) nitrogencontaining organic compounds, which display basic properties and high level of biological activity.
Which of the following reagent can be used to confirm the basic properties of
alkaloids?
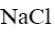
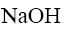
*
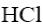
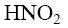
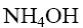
Which of the following reactions result purine?
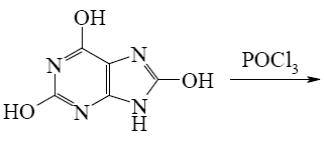
*
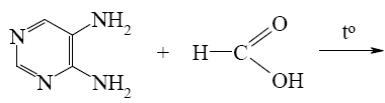
Which is the identity of the intermediate (A) and the end-product (B) in the following scheme?
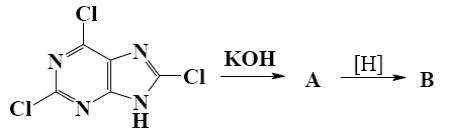
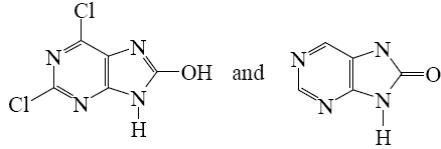
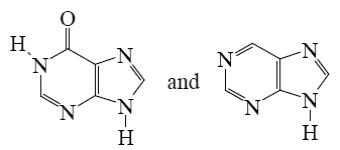
*
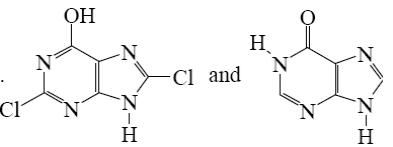
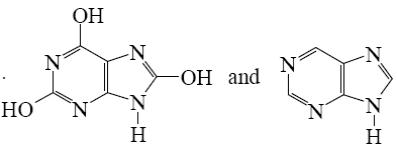
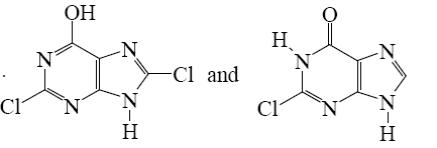
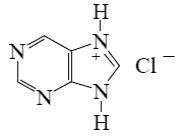
Choose the product of purine reaction with hydrochloric acid?
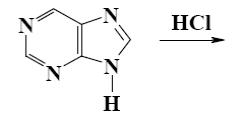
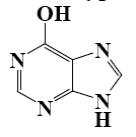
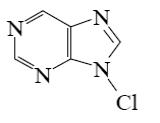
*
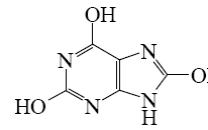
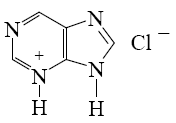
For which purine derivative lactam-lactim tautomerism is possible?
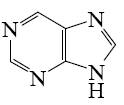
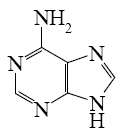
*
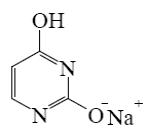
Which salt is formed when uric acid react with alkali?
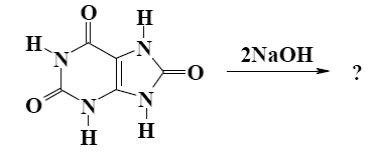
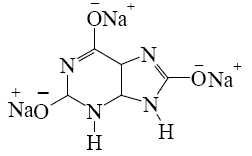
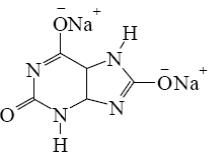
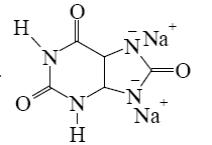
*
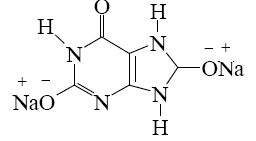

What reaction can be used to identify uric acid?
xanthoprotein test
*murexide test
indophenine test
xanthogenic test
isonitrile test
Choose the product of the following reaction.
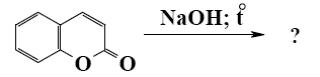
*
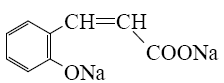
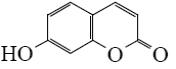
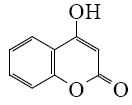
Which of the following reaction result piperidine?
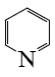
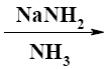


*
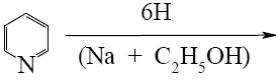
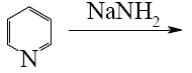
Which end-product is formed when β -picoline (1) first treated with PCl5, and
then with NH3?
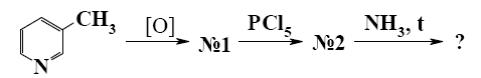
picolinic acid amide
*nicotinamide (vitamin PP)
isonicotinamide
ammonium salt of nicotinic acid
ammonium salt of isonicotinic acid
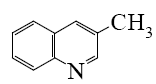
Select the mechanism of the following reaction and the position of quinoline it will principally occur?

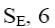
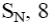
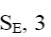
*
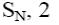
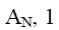
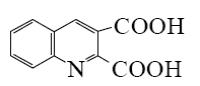
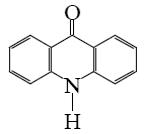
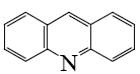
Which is the end-product of acridine oxidation?
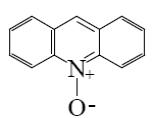
*
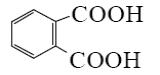
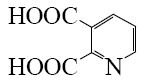
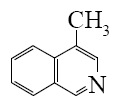
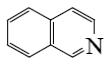
Which is the end-product of isoquinoline oxidation?
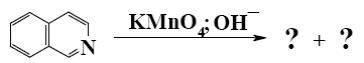
*
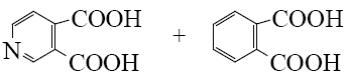
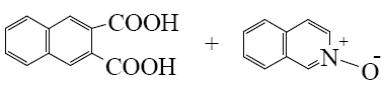
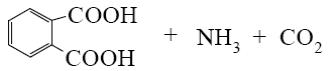
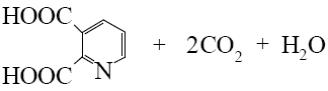
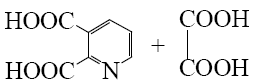
What is the end-product of the following reaction?
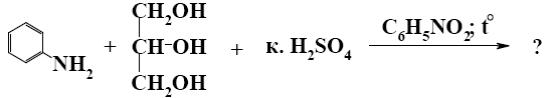
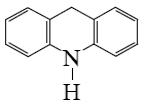
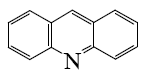
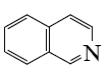
*
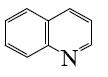
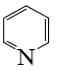
Choose the proper pair of products of the following reaction.
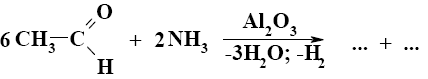
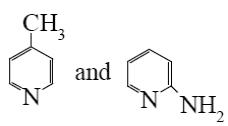
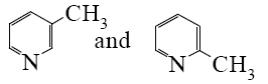
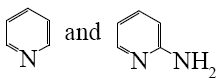
*
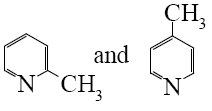
Choose the product of the following reaction.
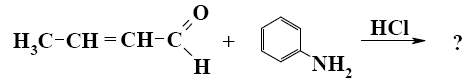
*
Which is the end-product of acrolein condensation?
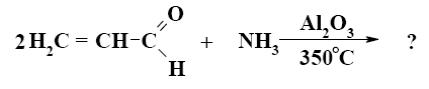
*
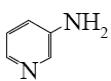
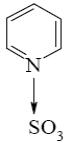
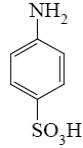
Which of the following compounds can be used for furan sulfonation?
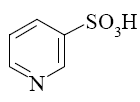
*
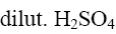
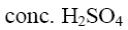
Which is the product of pyrazole reduction with hydrogen according to the
following scheme?
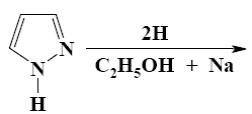
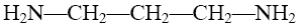
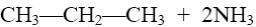
*
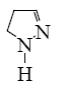
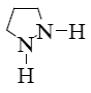
Which is the identity of the end-product (4) in the following scheme?
4-nitrofurfural semicarbazone
3-nitrofurfural
5-nitrofurfural diacetate
5-nitrofurfural
*5-nitrofurfural semicarbazone
Which of the following compounds is indole?
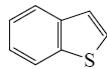
*
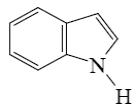
Which reagent can be used to proof the presence of keto-group in isatin
molecule?
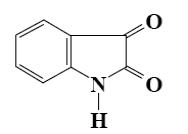
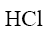

acid fuchsine sulfite
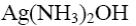
*
What is the product of the following reaction?
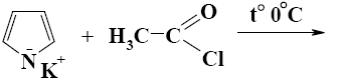
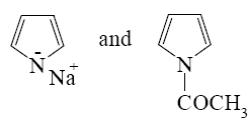
N- methylpyrrole
N- acetylpyrrolium chloride
b-acetylpyrrole
a-acetylpyrrole
*N-acetylpyrrole
Which is the identity of the intermediate (X) and the end-product (Y) in the
following scheme?
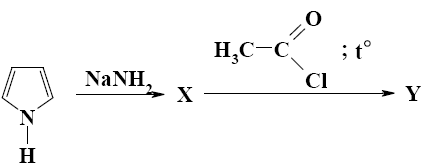
*
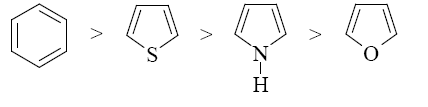
Choose the correct range of SE reactivity decrease for thiophene, furan, benzene, and pyrrole.

*
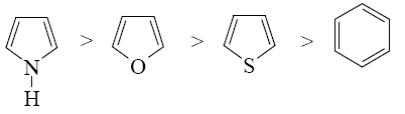
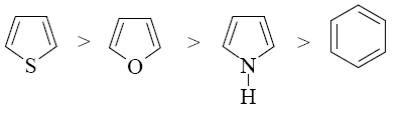
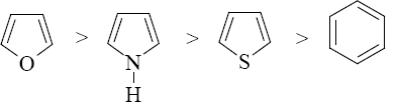
Which of the following heterocycle is acidophobic?
*
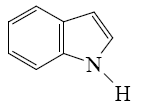
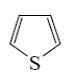
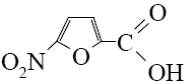
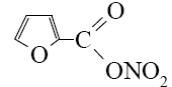
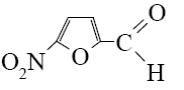
What is the identity of the end-product 2 in the following scheme?
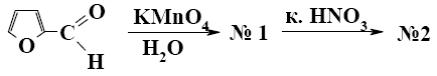
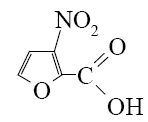
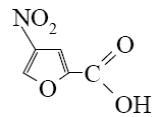
*
Which of the following heterocycle is acidophobic?
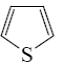
*

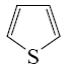
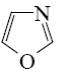
Which reaction is Yuriev’s cycle reaction?
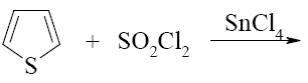
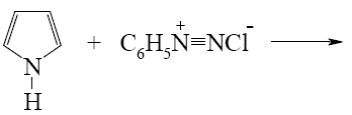
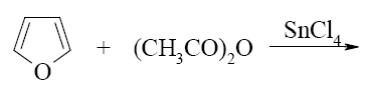
*
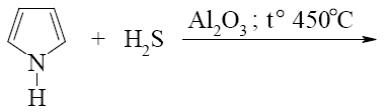
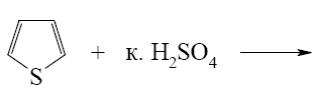
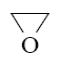
Which of the following heterocycle is aromatic?
*
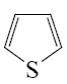
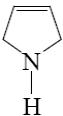
Which type of isomerism is possible for pyrazole and imidazole?
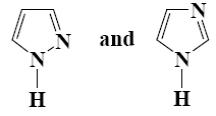
nitro-aci-nitro
*azole
keto-enol
amino-imino
lactam-lactim
Which is the identity of the intermediate (A) and the end-product (B) in the following scheme?
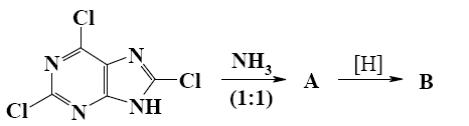
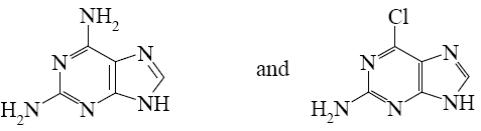
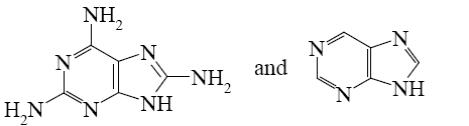
*
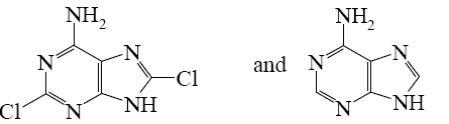
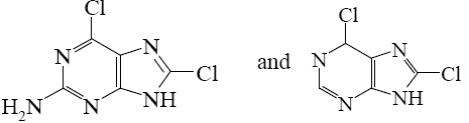
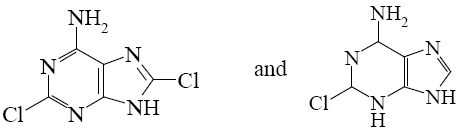
Choose the correct systematic name of purine.
*imidazo[4,5-d] pyrimidine
pyrazolo[4,5-d] pyrimidine
pyridino[4,5-d]pyrimidine
pyrimidino[4,5-d]imidazole
pyridazo[4,5-d]pyrimidine
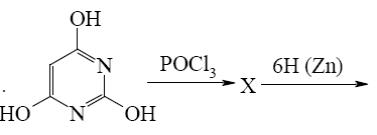
What starting compound is required for barbituric acid synthesis?
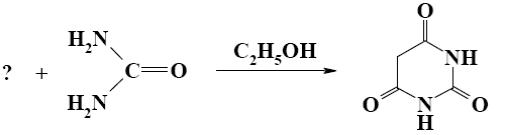
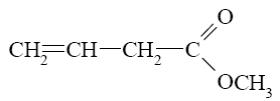
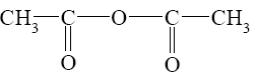
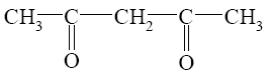
*
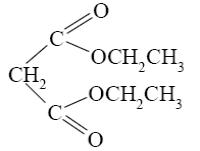
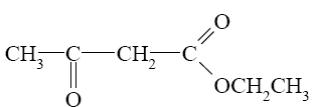
Which of the following reactions lead to pyrimidine formation?
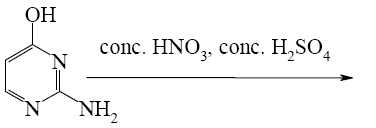
*
Which of the following reaction is impossible?
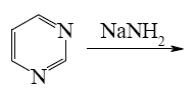
*
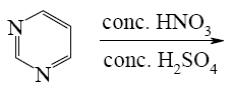
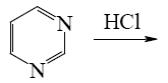
Which of the following reactions lead to pyrazine?
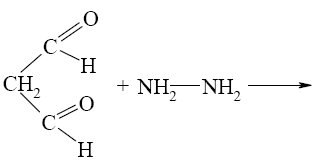
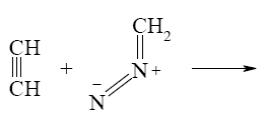
*
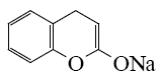
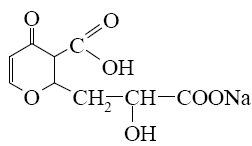
Which of the following reaction lead to coumarin formation?
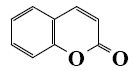
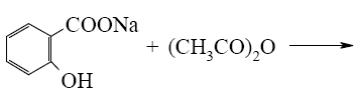
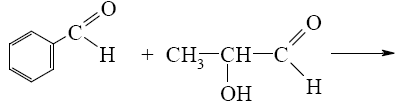
*
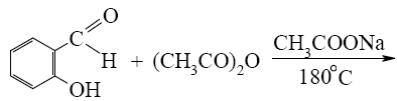
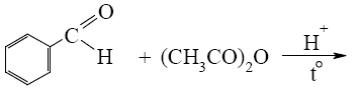
Which of the following pyrimindine derivative shall undergo the electrophilic substitution reactions?
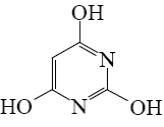
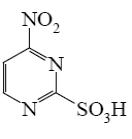
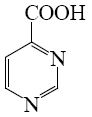
*
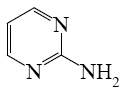
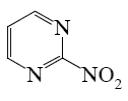
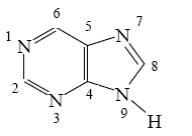
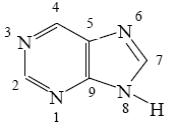
Choose the correct way for purine atoms numbering.
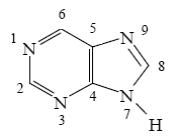
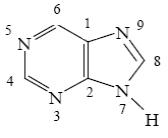
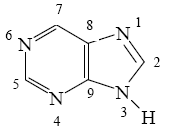
*
At what positions of pyridine N-oxide will electrophilic substitution reactions (SE) principally occur?
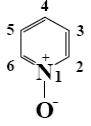
1, 4
3, 5
*2, 4, 6
1, 4, 6
1, 3, 5
At what position of pyridine shall electrophilic substitution reactions (SE) principally occur?
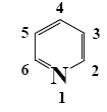
6
4
*3
2
1
At what positions of pyridine will nucleophilic substitution reactions (SN)
principally occur?
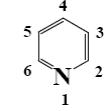
3, 5
2, 5
1, 3, 5
*2, 4, 6
2, 4, 5
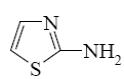
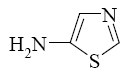
Choose the product of the following reaction.
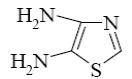
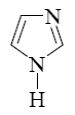
*
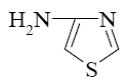
At what position of pyrazole will reaction with nitric acid (heat) principally
occur?
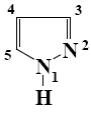
position 5
*position 4
position 3
position 2
position 1
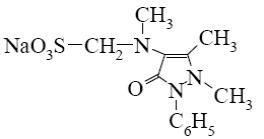
Choose the structure of analgin.
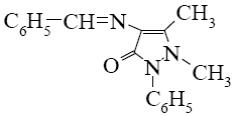
*
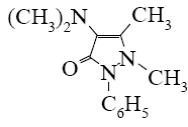
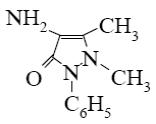

Which is the identity of the end-product (3) in the following scheme?
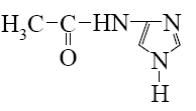
*
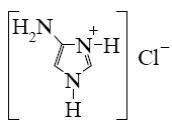
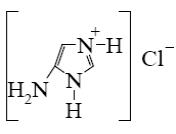
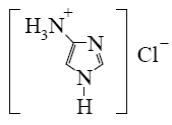
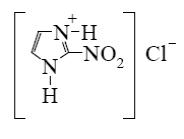
Which reagent shall react with cyclic nitrogen atom of 2-aminothiazole?
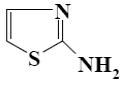
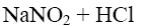

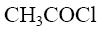
*
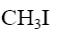
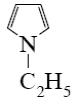
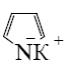
Which is the identity of the end-product (№3) in the following scheme?
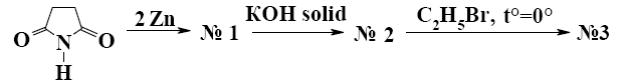
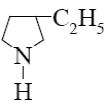
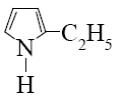
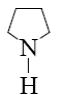
*
Which is the starting reagent in the synthesis of 5-methyl-1-phenylpyrazolone-5?
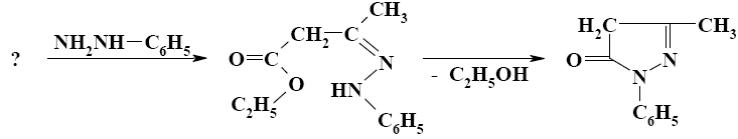
ethyl acetate
diethyl malonate
acetic acid
*acetoacetic ester
ethyl propionate
At what position of pyrazole will reaction with CH3I principally occur?
position 5
position 4
position 3
*position 2
position 1
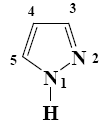
What is the product of imidazole sulfonation?
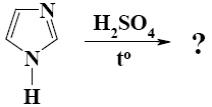
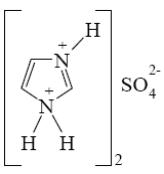
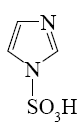
*
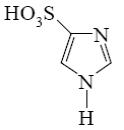

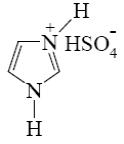
Which of the following compound can be used for furane chlorination?
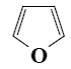
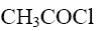
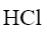
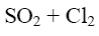
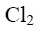
*
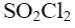
Which of the following heterocycle is acidophobic?
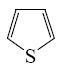
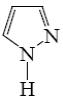
*
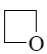
What is the end-product of reaction of potassium-pyrrolide with iodomethane?
α,α’-dimethylpyrrole
α,β-dimethylpyrrole
β- methylpyrrole
*α-methylpyrrole
N-methylpyrrole
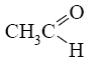
Which statement about furfural is not true?
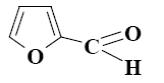
*it forms a-furamide with NH3
it forms hydrofuramide with NH3
it undergoes Cannizzaro reaction
can be obtained from aldopentose
it undergoes SE reactions at position 5
Which of the following heterocycle is acidophobic?
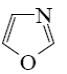
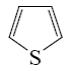
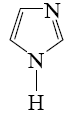
*
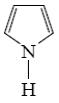
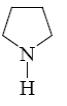
Which of the following reactions lead to formation of thiophene?
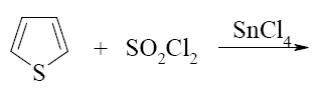
*
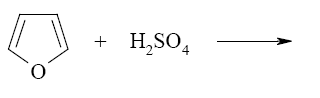
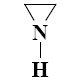
Three- and four-membered heterocycles, such as oxetane, aziridine, and azitidine are:
heterocycles with three heteroatoms
heterocycles with two heteroatoms
aromatic heterocycles
unsaturated heterocycles
*saturated heterocycles
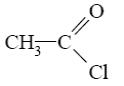
Which of the following compounds can be cyclized to aziridine?
*
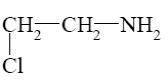
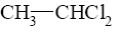
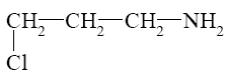
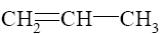
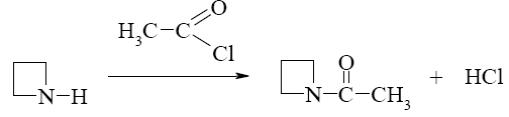
Which reaction characterize aziridine as secondary cyclic amine?

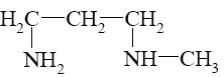
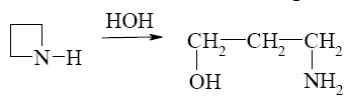
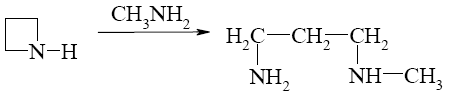
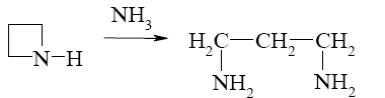
*
Which reaction does oxiran undergo?
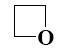
electrophilic addition
electrophilic substitution
nucleophilic substitution
free-radical substitution
*nucleophilic addition
Choose the products of the following reaction.
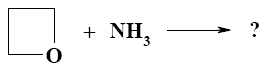
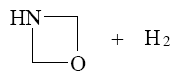
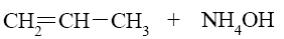
*
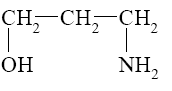
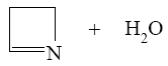
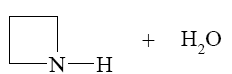
Which of the following reaction of oxiran are possible?
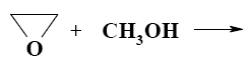
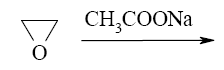
*
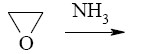
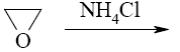
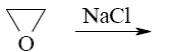
Choose the mechanism of the following reaction:
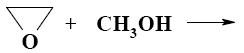
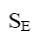
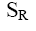
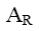
*
Heterocyclic compound pyrrole belongs to:
*fivemember heterocycles with one heteroatom
fivemember heterocycles with two heteroatoms
sixmember heterocycles with one heteroatom
fivemember heterocycles with two heteroatoms
condensed heterocycles
Heterocyclic compound pyrrole is a part of:
anesthetic means
nucleic acids
preparations for the tuberculosis treatment
bactericide means
*hem of hemoglobin
According to the level of saturation heterocyclic compounds are divided on:
condensed and non-condensed
*saturated, unsaturated, aromatic
azoth containing, oxygen containing, sulfur containing
fivemember, sixmember, sevenmember
cycles with one and two heteroatoms
According to the nature of heteroatom heterocyclic compounds are divided on:
saturated, unsaturated, aromatic
*nitrogen containing, oxygen containing, sulfur containing
fivemember, sixmember, sevenmember
cycles with one and two heteroatoms
condensed and non-condensed heterocycles
3- and 4-member heterocycles oxethane, azeridine, azetidine are:
*saturated heterocycles
unsaturated heterocycles
aromatic heterocycles
heterocycles with tree heteroatoms
heterocycles with trwo heteroatoms
How does pyrrole basic properties change in the comparison with the products of its partial and complete reduction?
does not change
*increases from pyrrole to pyrolidine
increases in the row of pyrolidine, pyroline, pyrrole
decreases in the row of pyroline, pyrolidine, pyrrole
increases in the row of pyrolidine, pyrrole, pyrroline
Nitrogen atom in the pyrrole molecule can react with:
*potassium amide
potassium chloride
potassium sulfate
sulfate acid
chloride acid
For three- and fourmember heterocycles the following types of reactions are characteristic:
radical substitution
electrophilic and nucleophilic substitution
*electrophilic and nucleophilic accession
radical accession
polymerization
According to the size of cycle (total number of atoms in the cycle) heterocyclic compounds can be classified on:
saturated, unsaturated, aromatic
azoth containing, oxygen containing, sulfur containing
*fivemember, sixmember, sevenmember
cycles with one or two heteroatoms
condensed and non-condensed heterocycles
To fourmember heterocyclic compounds with one atom of oxygen belongs the following one:
*oxethane
pyrazole
oxyrane
pyrimidine
pyridine
To threemember heterocyclic compounds with one atom of oxygen belongs the following one:
pyrimidine
oxethane
*oxyrane
pyrrole
pyridine
To fourmember heterocyclic compounds with one atom of sulfur belongs the following one:
thiophene
pyrazole
pyrrole
pyridine
*thiethane
To threemember heterocyclic compounds with one atom of sulfur belongs the following one:
thiophene
thiethane
pyrrole
*thiirane
pyridine
What compound with concentrated alkali solution will form oxyrane?
*HOCH2—CH2—Cl
HOCH2—CH2—CH2—Cl
H2C=CH2
HOCH2—CH2—OH
H3C—CH3
Among of the following compounds choose nitration reagent for the acidophobic compounds:
HNO3 conc
CH3COOH
H3BO3
NaNO2 + HCl
*(CH3CO)2O + HNO3
To fivemember heterocyclic compounds with one atom of sulfur belongs the following one:
pyrimidine
pyrazole
pyrrole
*thiophene
pyridine
To fivemember heterocyclic compounds with one atom of nitrogen belongs the following one:
pyridine
pyrazole
*indole
furane
pyrimidine
Furacilline – medical drug that is used for the treatment of pyoinflammatory processes cased by microorganisms. What heterocycle is a primer compound for furacilline synthesis?
pyrrole
*furan
thiophene
imidazole
pyridine
Furfural (2-furylcarbaldehyde) – primer compounf for the synthesis of furacilline, furazolidone and furadonine. Choose reagent that can be used to obtain semicarbazone.
H2N–C6H5
H2N–OH
*H2N–NH–C(O)–NH2
H2N–NH–C(S)–NH2
H2N–NH2
5 – nitrofurfural is a primer compound for the synthesis of furacilline, furazolidone and furadonine. Choose the type of reaction of furfural nitration by conc. nitrate acid in the medium of acetic anhydride?
AN
SR
E
SN
*SE
5 – nitrofurfural is a primer compound for the synthesis of furacilline, furazolidone and furadonine. Choose the mechanism of furfural nitration by conc. nitrate acid in the medium of acetic anhydride?
*radical
ionic
nucleophilic
substitutin by m-position
substitutin by o- and p-position
Choose compound, which with 5-nitrofurfural forms furacilline.
*semicarbazide
phenylhydrazide
hydrazine
hydraxylamine
sodium hydrosulfite
Nitrogen atom in the pyrrole molecule can react with:
*potassium amide
potassium chloride
potassium sulfate
sulfate acid
chloride acid
Choose the more correct name for complete thiophene hydration:
1,2,3,4,5-pentahydrothiophene
2,3-dihydrothiphene
1,2-dihydrothiophene
3,4-dihydrothiophene
*2,3,4,5-tetrahydrothiophene
Which of the following substances can not be sulfonated with concentrated sulfate acid?
thiophene
pyridine
toluene
*pyrrole
naphthalene
Which of the following substances has acidophobic properties?
pyridine
pyrazole
*pyrrole
pyrimidine
imidazole
Name product of the pyrrole sulfonation:
3-pyrrole sulfoacid
*2-pyrrole sulfoacid
4-pyrrole sulfoacid
5-pyrrole sulfoacid
1-pyrrole sulfoacid
Choose the reagent for furan nitration:
HNO3; H2SO4
HNO3 (dil.)
HNO3 (conc.)
*CH3COONO2
HNO2
Pyrrole and furan are sulfonated by:
concentrated sulfate acid
*pyridinesulfotrioxide
diluted sulfate acid
mixture of sulfate and nitrate acids
oleum
To fivemember heterocyclic compounds with one atom of nitrogen belongs the following one:
pyrimidine
pyrazole
*pyrrole
furan
pyridine
Which of the following reagents will react with pyrrole by heteroatom?
*NaNH2
СН3СОOH
(CH3CO)2O
SnCl4
SO2Cl2
Weak acidic properties the following heterocyclic compound has:
pyridine
thiophene
quinoline
furane
*pyrrole
To fivemember heterocyclic compounds with one atom of oxygen belongs the following one:
pyrimidine
pyrazole
pyrrole
*furane
pyridine
To fivemember heterocyclic compounds with one atom of sulfur belongs the following one:
pyrimidine
*thiphene
pyrrole
pyrazole
pyridine
Heterocyclic compound pyrrole belongs to:
*fivemember heterocycles with one heteroatom
fivemember heterocycles with two heteroatoms
sixmember heterocycles with one heteroatom
fivemember heterocycles with two heteroatoms
condensed heterocycles
Heterocyclic compound pyrrole is a part of:
anesthetic means
nucleic acids
preparations for the tuberculosis treatment
bactericide means
*hem of hemoglobin
What substance will form as a result of interaction of acetoacetic ester with phenylhydrazine?
Amidopyrine
Analgin
Antipyrine
*3-methyl-1-phenylpyrazolone-5
2,3-dimethyl-1-phenylpyrazolone-5
What substance will form as a result of interaction of 4-methylaminoantipyrine with formalin and sodium hydrosulfite?
Amizon
Antipyrine
Aspirin
*Analgin
Amidopyrine
1,3-diazol is isomer of:
Indole
Benzimidazole
*Pyrazole
Pyrole
Pyridine
1,2-diazole is isomer of:
Indole
Benzimidazole
*Imidazole
Pyrole
Pyridine
Oxazole is isomer of:
Azole
Thiazole
Furan
*Isooxazole
Pyrrole
Which of the following heterocycles does belong to azoles?
Indole
*Thiazole
Thiophene
Pyrrole
Furan
Which of the following heterocycles has basic properties?
*Pyrazole
tetrahydrofurane
Thiophene
Pyrolidine
Pyrroel
What heterocycle is in the content of vitamin В1 (thiamin)?
Thiophene
Pyridine
*Thiazole
Oxazole
Purine
Which of the following medical compounds does contain imidazole heterocycle?
analgin
*histidine
antipyrine
amidopyrine
furacilline
If oxazole cycle is activated by electronodonor subtitution the reactions of SE takes place. Specify the position, by which this reaction will go:
3 and 2
2 and 5
*4 and 5
3 and 4
2 and 1
What reaction does case pyrazole formation?
Intramolecular dehydration of ethanol
Melting with alkali solution of benzolsulfoacid
Cyclotrimerization of acetylene
Pentose dehydratation
*Accession of diazoalkanes to acetylenes
What reaction does case pyrazole formation?
Intramolecular dehydration of ethanol
Melting with alkali solution of benzolsulfoacid
Cyclotrimerization of acetylene
Pentose dehydratation
*Interaction of hydrazine with pentadione-2,4
Pyrazole according to its physical properties is:
Crystalline orange compound
Liquid, good soluble in water
Gaseous substance
*Colorless crystalline compound, good soluble in water
Liquid, insoluble in water
Alkylation and acylation of pyrazole conduct with formation of the following products:
*N–substitution
m–substitution
p–substitution
o- and p-substitution
Mixture of N- and m-substituution
Choose the product of pyrazole reduction:
Pyridine
Hydropyrazole
*Pyrazoline–2
Pyrazolidine
Pyrrole
Choose the product of pyrazole partial reduction:
Pyridine
*3,4-dihydropyrazole
Hydropyrazole
1-,2-dihydropyrazole
Trihydropyrazole
Choose the product of pyrazole complete reduction:
Pyridine
Dihydropyrrole
Trihydropyrazole
Pyrrole
*Pyrazolidine
Choose the product of pyrazole complete reduction:
Pyridine
*Tetrahydropyrazole
3,4-dihydropyrazole
Trihydropyrazole
Pyrrole
Choose reagent for pyrazole partial reduction:
CH3COOH
C2H5OH
2H2(Pt)
*2H(C2H5OH+Na)
KMnO4
Choose reagent for pyrazole complete reduction:
CH3COOH
2H(C2H5OH+N
*2H2(Pt)
C2H5OH
KMnO4
Choose chemical name for antipyrine:
4-nitrozoantipyrine
*2,3-dimethyl-1-phenylpyrazolone-5
3-methyl-1-phenylpyrazolone-5
2,3-dimethyl-4-dimethylamino-1-phenylpyrazolone-5
sodium 2,3-dimethyl-4-dimethylamino-1-phenylpyrazolone-5-N-methanesulfonate
Choose chemical name for amidopyrine:
4-nitrozoantipyrine
2,3-dimethyl-1-phenylpyrazolone-5
3-methyl-1-phenylpyrazolone-5
*2,3-dimethyl-4-dimethylamino-1-phenylpyrazolone-5
sodium 2,3-dimethyl-4-dimethylamino-1-phenylpyrazolone-5-N-methanesulfonate
Choose chemical name for analgin:
4-nitrozoantipyrine
2,3-dimethyl-1-phenylpyrazolone-5
3-methyl-1-phenylpyrazolone-5
2,3-dimethyl-4-dimethylamino-1-phenylpyrazolone-5
*sodium 2,3-dimethyl-4-dimethylamino-1-phenylpyrazolone-5-N-methanesulfonate
Choose chemical name for sodium methamizole:
4-nitrozoantipyrine
2,3-dimethyl-1-phenylpyrazolone-5
3-methyl-1-phenylpyrazolone-5
2,3-dimethyl-4-dimethylamino-1-phenylpyrazolone-5
*sodium 2,3-dimethyl-4-dimethylamino-1-phenylpyrazolone-5-N-methanesulfonate
Choose correct name of the preparation with the chemical name 2,3-dimethyl-1-phenylpyrazolone-5:
*Antipyrine
Aspartic acid
Aspirin
Amidopyrine
Analgin
Choose correct name of the preparation with the chemical name 2,3-dimethyl-4-dimethylamino-1-phenylpyrazolone-5:
Antipyrine
Aspartic acid
Aspirin
*Amidopyrine
Analgin
Choose correct name of the preparation with the chemical name sodium 2,3-dimethyl-4-dimethylamino-1-phenylpyrazolone-5-N-methanesulfonate:
Antipyrine
Aspartic acid
*Analgin
Amidopyrine
Aspirin
Choose correct name of the preparation with the chemical name sodium 2,3-dimethyl-4-dimethylamino-1-phenylpyrazolone-5-N-methanesulfonate:
*Sodium methamizole
Aspartic acid
Aspirin
Amidopyrine
Antipyrine
Analgin is used in the medical practice as:
Form of vitamin PP
Antibacterial mean
*Analgesic mean
Vasodilator
Drug against tuberculosis
For imidazole obtaining use interaction of the following compounds:
Acetoacetic ester and phenylhydrazine
*Glyoxal, ammonia, formaldehyde
Ethanol and alkali
Ethanoic acid and ethyl alcohol
Acetylene and ammonium
Imidazole is:
Crystalline yellow compound
Liquid, insoluble in water
*Colorless crystalline compound, good soluble in water
Gaseous compound
Liquid with sharp smell
To the imidazole derivatives the following compound belongs:
*Histidine
Vitamin PP
Furfural
Norsulfazole
Cordiamine
To the imidazole derivatives the following compound belongs:
Vitamine PP
Norsulfazole
Furfural
*Histamine
Cordiamine
To the imidazole derivatives the following compound belongs:
Vitamine PP
*Pilocarpine
Furfural
Norsulfazole
Cordiamine
Benzimidazole can be obtained by the interaction of:
*О-phenylenediamine with formic acid;
Acetylene with ammonia
Ethanoic acid and ethanol
Glyoxal, ammonia, formaldehyde
Acetoacetic ester and phenylhydrazine
Benzimidazole has:
Oxidative properties
Reductive properties
Acidic properties
*Amphoteric properties
Basic properties
Benzimidazole cycle is a part of vitamin:
*В12;
С;
А;
Н;
РР.
Benzimidazole cycle is a part of the following drug:
Analgin
*Dibazole
Norsulfazole
Phthalazol
Furacilline
Thiazole is a part of the following natural compound:
*Vitamin В1
Vitamin С
Vitamin А
Vitamin РР
Vitamin Н
Thiazole is a part of the following natural compound:
Vitamin РР
Vitamin Н
*Penicillin
D–carotene
itamin С
Thiazole is a part of the following medical drug:
Isoniazide
Phenobarbital
Cordiamine
*Norsulfazole
Furacilline
Thiazole is a part of the following medical drug:
Isoniazide
Phenobarbital
Cordiamine
*Phthalazol
Furacilline
A thizole nucleus is a part of natural penicillins. The drug has:
Analgesic properties
*Antimicrobial properties
Vasodilatation activity
Bronchodilatation activity
Antituberculosis properties
By the presence of free pare of electrons of pyridine type nitrogen atom oxazole has the following properties:
*Weak basic properties
Strong basic properties
Weak acidic properties
Strong acidic properties
Amphoteric properties
Isooxazole has the following properties:
Amphoteric
Strong acidic
Weak acidic
Strong basic
*Weak basic
Qualitative reaction on antipyrine is reaction with:
H2
HCl
NH3
CH3OH
*FeCl3
Qualitative reaction on antipyrine is intereaction with:
H2
*NaNO2(H+)
NH3
CH3OH
HCl
Qualitative reaction on antipyrine is reaction with FeCl3. As a result complex salt (ferropyrine) will form. What is the color of this complex?
Red
Yellow
Brown
*Orange
Blue
Qualitative reaction on antipyrine is reaction with FeCl3. As a result orange color complex salt will form. This is:
*Ferropyrine
Furazolidone
Furadonine
Furfural
Furacilline
Qualitative reaction on antipyrine is reaction with NaNO2(H+). As a result 4–nitrozoantipyrine will form. This compound has the following color:
Colorless
Orange
Blue
Yellow
*Emerald-green color
Qualitative reaction on antipyrine is reaction with NaNO2(H+). As a result emerald-green compound will form. This is:
3–aminoantipyrine
Amidoantipyrine
4–aminoantipyrine
2–nitrozoantipyrine
*4–nitrozoantipyrine
Qualitative reaction on amidopyrine is intereaction with:
H2
*FeCl3 (Н+)
CH3OH
H2SO4
HCl
Qualitative reaction on anmidopyrine is intereaction with:
H2
*К3[Fe(СN)6] and Fe3+
CH3OH
H2SO4
HCl
Choose the reaction that can be used to distinguish analgin from amidopyrine:
H2
H2SO4
NaNO2
*FeCl3 (Н+)
HCl,t
Choose the reaction that can be used to distinguish analgin from amidopyrine:
H2
H2SO4
NaNO2
*К3[Fe(СN)6] Fe3+
HCl,t
As a result of interaction of amidopyrine with К3[Fe(СN)6], in the presence of FeCl3 blue color complex will form with the following content:
Fe[Fe(СN)6]
*Fe4[Fe(СN)6]3
К4[Fe(СN)6]
КFe[Fe(СN)6]
К2Fe[Fe(СN)6]
To the preparation, which is a derivative of pyrazolone-5, solution of FeCl3 is added. Observe the appearance of the intense orange coloration. Choose this preparation:
Penicilline
Anesthesin
Amidopyrine
*Antipyrine
Analgine
As a result of antipyrine nitrozation with the following reduction the next compound will form:
*4-nitrozoantipyrine
2-aminoantipyrine
Amidopyrine
3-aminoantipyrine
4-aminoantipyrine
As a result of 4-aminoantupyrine methylation the following compound will form:
*Amidopyrine
3-methyl-1-phenylpyrazolone-5
2,3-dimethyl-1-phenylpyrazolone-5
4-nitrozoantipyrine
Analgin
Why quinoline and isoquinoline give reactions of eletrophilic substitution previously by the positions 5 and 8?
nitrogen atom has bigger electronegativity than carbon atom
*positions 5 and 8 have bigger electronic density
nitrogen atom has sp2 –hybridization of the electronic
benzene cycle has three double bounds
nucleophilic substitution reactions are not possible
For pyridine reactions of electrophilic (SE) nucleophilic (SN) substitution are characteristic. Lower reaction ability of pyridine in the reactions of SE is caused by:
size of the cycle
aromatic character of the pyridine cycle
basic properties
carbon atom hybridization атомів вуглецю
*electron acceptor properties of nitrogen atom
How many π-electrons do form aromatic system of pyridine?
14
10
*6
8
12
Choose the mechanism of pyridine hydroxylation in position 2:
*SN
SE
AE
SR
AN
Point the mechanism of the 2-aminopyridine formation by Chichibabin:
AR
SE
AE
SN
*SR
Choose the way of piperidine from pyridine obtaining in one stage:
pyridine amination
pyridine nitration
pyridine methylation
*pyridine hydration
pyridine interaction with hydrochloric acid
For pyridine the following reactions are characteristic:
electrophilic accession andта electrophilic substitution
*electrophilic and nucleophilic substitution
nucleophilic accession and nucleophilic substitution
nucleophilic substitution and elimination
radical substitution and electrophilic accession
Pyridine – aromatic heterocycle, which is a part of many medical drugs. Determine how many monomethyl substituted pyridines exist.
1
2
*3
4
5
According to the Hukel rule quantity of π-electrons in the aromatic system can be determined by the following formula 4n+2. What number of π-electrones does acridine molecule contain?
10
*14
8
6
12
Nitrogen atom in the pyridine molecule can react with:
*hydrochloric acid
potassium hydroxyde
calcium oxide
potassium carbonate
potassium amide
Nicotinic acid amide (vitamin РР) is the derivative of:
pyrazole
thiphene
pyrrole
furan
*pyridine
Acridine gives reactions of electrophilic substitution previously by the position:
2 and 3
*2
5
5 and 8
2 and 7
Reactions of electrophilic and nucleophilic substitution in the quinoline nuclei go in the following positions:
SE in position 5, SN – in position 4
SE in position 2, SN – in position 4
SE in position 3, SN – in positions 2 and 4
*SE in positions 5 and 8, SN – in position 2
SE in position 6, SN – in positions 3 and 4
After the nicotine oxidation in the hard conditions the following compound will form:
pyridine-3,4-dicarboxylic acid
pyridine-2-carboxylic acid
pyridine-4-carboxylic acid
pyridine-2,3-dicarboxylic acid
*pyridine-3-carboxylic acid
Derivatives of cyclic and heterocyclic compounds are the structural fragment of the many medical drugs. Which of the following compounds does not have carbon atom in sp2 – hybridized state?
*piperidine
pyridine
pyrrole
pyroline
pyridazine
Which of the following acids is pro-vitamin РР?
pycolinic
isonicotinic
*nicotinic
salicylic
anthranilic
Which of the following compounds after the oxidation will form nicotinic acid?
pyrazine
*β-pycoline
γ-pycoline
propylene glycol
α-pyrone
Which of the following cycles is a structural fragment of alkaloid lobeline, anabazine, is a part of analgesic mean promedol?
*piperidine
piperazine
pyrimidine
pyridazine
pyridine
Pyrimidine is an aromatic heterocyclic compound; its derivatives are in the content of nucleic acids, vitamins, antibiotics, medical drugs. Enter the number of electrons involved in the formation of the closed conjugated system and corresponded to the Huckel’s rule.
*6
14
10
26
18
Pyrimidine is an aromatic heterocyclic compound. Determine the number of electrons that take part in the formation of aromatic system of the pyrimidine molecule:
2
4
*6
8
10
Barbituric acid is one of the most important pyrimidine derivatives. What type of tautomery is characteristic for barbituric acid?
Azol and nitro-acy-nitro tautomery
Keto-enol and nitro-acy-nitro tautomery
Lactam-lactim and nitro-acy-nitro tautomery
*Keto-enol and lactam-lactim
Cyclic-chain and nitro-acy-nitro tautomery
Pyrazole – aromatic heterocycle. Determine the product of pyrazole interaction with conc. НNO3 at the heating:
3-Nitropyrazole
*4-Nitropyrazole
Pyrazolyl nitrate
5-Nitropyrazole
3,5-Dinitropyrazole
Barbituric acid is in the base of some medical preparations. What heterocycle is in the base of barbituric acid?
*Pyrimidine
Pyrazine
Pyridazine
Pyridine
Insole
Point the type of tautomery of pyramiding foundations – thymine, uracil, and cytosine:
azol
nitro-acy-nitro
keto-enol
thion-thiol
*Lactam-lactim
Derivatives of which heterocycle has azol tautomery?
pyridazine
pyrazine
*pyrazole
thiazole
oxazole
What reaction can be used to obtain pyridazine?
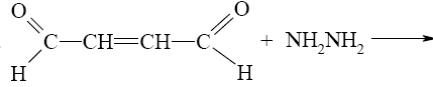
Condensation of malondialdehyde with hydrazine
*Condensation of maleinedialdehyde with hydrazine
Condensation of acetaldehyde with ammonia
Condensation of ethylenediamine with glyoxal
Diethylmalonate interaction with urea
Choose heterocycle that is in the base of barbituric acid, which derivatives are used in the medicine as medical drugs and have hypnotic and anticonvulsion action.
pyridine
pyridazine
pyrazine
piperidine
*pyrimidine
Sixmember azotcontaining heterocyclic compounds have basic properties. Specify the compound, which has the biggest basic properties.
Pyrazine
Pyridine
Pyrimidine
*Piperazine
Pyridazine
To the sixmember heterocycles with two nitrogen heteroatoms the following compound belongs:
Pyrrolidine
Purine
*Pyrimidine
Pyrrole
Pyridine
Choose the compound, which derivatives are used in the medicine as hypnotic means:
Pyridine
Nicotinic acid
Xanthine
Uric acid
*Barbituric acid
Derivatives of barbituric acid are used in the medical practice as:
Antipyretic means
Antiseptic means
Antibiotics
*Hypnotic means
Preparations with anti-mycosis action
For diazines is cheracteristic:
The high reactivity in the reactions of Е
Low reactivity in the reactions of SN
The high reactivity in the reactions of SR
The high reactivity in the reactions of SЕ and SN
*The high reactivity in the reactions of SN and low reactivity in the reactions of SЕ
What compound can be obtained by the interaction of maleinealdehyde with hydrazine?
Pyrrole
*Pyridazine
Pyrimidine
Pyrazine
Pyridine
Pyridazine is:
*A weak base
An inert compound
A strong base
A weak acid
a strong oxidant
What compound will form after the pyridazine interaction with HCl?
5-chloropyridazine
3-chloropyridazine
*pyridazinium chloride
pyrimidinium chloride
pyrazinium chloride
What compound will form after the pyridazine interaction with CH3I?
6-methylpyridazine iodide
*N-methylpyridazine iodide
3-methylpyridazine iodide
4-methylpyridazine iodide
5-methylpyridazine iodide
Under the action of peroxyacid (CH3COOOH) pyridazine oxidizes with formation of:
*pyridazine N-oxide
pyrimidine N-oxide
pyrazine N-oxide
pyridazinone-4
pyridazinone-5
At the pyridazine reduction by sodium in alcohol solution the following compound will form:
Butylamine
Diethylamine
Piperidine
*Tetramethylenediamine
Pyrimidine
Choose the chemical name of pyrimidine:
1,5-diazine
diazepine
1,4-diazine
1, 2-diazine
*1,3 -diazine
Choose the mechanism of the reaction of the pyrazine interaction with sodium amide:
SE
SR
*SN
E
AN
The reaction of the pyrazine interaction with sodium amide will go in the following position:
5
*2
1
3
4
Under the action of peroxyacids pyrazine oxidizes with formation of:
*Pyrazine mono-N-oxide
Pyrazone-2
Pyrazine di-N,N-oxide
Pyrazone-3
Pyrazone-5
Choose the product of pyrazine reduction by sodium in ethanol:
Pyrrole
*Piperazine
Pyrimidine
Pyridazine
Pyridine
Choose systematic name of phenothiazine:
Dibenzo-1,4-thiophene
Benzo-2-thiazole
Benzo-1-thiazole
*Dibenzo-1,4-thiazine
Dibenzo-1,5-thiazine
What products will form after the phenothiazine interaction with iodomethane?
7-methyl derivatives
*N-methyl derivatives
S-methyl derivatives
2-methyl derivatives
5-methyl derivatives
What products will form after the phenothiazine interaction with chloroanhydride of acetic acid?
S-acetyl derivatives
S-methyl derivatives
N-methyl derivatives
*N-acetyl derivatives
N-chloroderivatives
Oxidation of phenothiazine goes by:
*S atom
N atom
С2 atom
С4 atom
С6 atom
Which of the following preparations does include phenothiazine nuclei?
Phthivazide
Furacylline
Cordiamine
*Aminazine
Vitamin РР
What gas will evaporates after the melting of barbituric acids with NaOH:
SO3
CO
SO2
NO2
*NH3
After the barbiturates interaction with NaOH solution forms:
Black precipitate
White precipitate
*Mono- and disodium salts
NH3
Gas CO2
After the adding of an excess of AgNO3 to the barbital sodium salt will form:
Gas NH3
White precipitate of disilver salt
*Yellow precipitate of disilver salt
Gas СО
Black precipitate of Ag
Barbituric acid can exist in these two forms:
Acy- and nitro-
*Oxo- and hydroxy-
Lactim and lactam
Cyclo- and oxo-
Keto- and enol
For its physical properties pyrimidine is:
Gaseous substance
Liquid, insoluble in water
A black crystalline substance
Yellow liquid
*Colorless crystalline substance, easily soluble in water
Pyrimidine molecule in the reactions with mineral acids forming salts of:
Complex compounds
*With the participation of one nitrogen atom
Involving two nitrogen atoms
Acidic salts
Basic salts
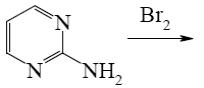
Electronodonor substituents in the pyrimidine nuclei:
Promote the passage of the АN reactions
Promote the passage of the АЕ reactions
*Promote the passage of the SЕ reactions
Promote the passage of the SN reactions
Promote the passage of the Е reactions
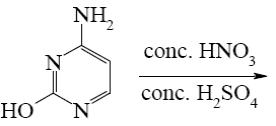
Nitration of the pyrimidine derivative (SЕ) is conducted with the following reagent:
*HNO3(conc.), H2SO4(conc.)
CH3COONO2
HNO3(dil.)
NO2, H2SO4(conc.)
N2, H2SO4(conc.)
Sulfonation of the pyrimidine derivative (SЕ) is conducted with the following reagent:
SO3
*H2SO4 (conc.)
SO2
C6H5SO3H
S
Halogenation of the pyrimidine derivative (SЕ) is conducted with the following reagent:
HClO3
HBrO
*Br2(AlCl3)
HBr
HCl
Choose the positions in the pyrimidine molecule for SN reactions:
2,5,6
1,4,6
*2,4,6
2,3,5
1,2,3
Choose the mechanism of the pyrimidine interaction with NaNH2:
АЕ
АN
Е
SE
*SN
Reaction of pyrimidine interaction with HNО3 (conc.) in the presence of H2SO4 (conc.) will go by the following mechanism:
АЕ
SR
SN
*SE
E
Interaction of pyrimidine derivative with Br2 in the presence of H2SO4 (conc.) will go by the following mechanism:
АЕ
SR
SN
*SE
E
Barbiturates - 5,5-disubstituted barbituric acid derivatives show:
*Hypnotic and antispasmodic action
Analgesic effect
Antituberculosis action
Expectorant action
Hemostatic effect
Barbital - 5,5-disubstituted barbituric acid derivative. R and R’ are:
*C2H5, C2H5
CH3, CH3
C2H5, iso-C5H11
CH3, C6H5
C6H5, C2H5
Phenobarbital - 5,5-disubstituted barbituric acid derivative. R and R’ are:
C2H5, C2H5
CH3, CH3
C2H5, iso-C5H11
CH3, C6H5
*C6H5, C2H5
Barbamil - 5,5-disubstituted barbituric acid derivative. R and R’ are:
C2H5, C2H5
CH3, CH3
*C2H5, iso-C5H11
CH3, C6H5
C6H5, C2H5
To the pyrimidine bases the following compound belongs:
Pteridine
Guanine
Purine
*Thymine
Adenine
The pyrimidine bases the following compound belongs:
Pteridine
Guanine
Purine
*Uracil
Adenine
To the pyrimidine bases the following compound belongs:
Pteridine
Guanine
Purine
*Cytosine
Adenine
Uracil is a part of:
Phthalazol
*Nucleic acid
Aminoacid
Barbiturates
Norsulfazolum
Thymine is a part of:
Phthalazol
*Nucleic acid
Aminoacid
Barbiturates
Norsulfazolum
Cytosine is a part of:
Phthalazol
*Nucleic acid
Aminoacid
Barbiturates
Norsulfazolum
For uracil is characteristic the following type of tautomery:
*Lactim-lactam tautomery
Acy-nitro tautomery
Cyclo-oxo tautomery
Keto-enol tautomery
Oxo-hydroxy tautomery
For cytosine is characteristic the following type of tautomery:
*Lactim-lactam tautomery
Acy-nitro tautomery
Cyclo-oxo tautomery
Keto-enol tautomery
Oxo-hydroxy tautomery
For thymine is characteristic the following type of tautomery:
*Lactim-lactam tautomery
Acy-nitro tautomery
Cyclo-oxo tautomery
Keto-enol tautomery
Oxo-hydroxy tautomery
What compound does include pyrimidine cycle?
Vitamin РР
Vitamin Н
Vitamin С
Vitamin А
*Vitamin В1
Which of the following alkaloids does not have optical activity?
Nicotine
*Caffeine
Anabasine
Lobeline
Quinine
Which of the following alkaloids does not have optical activity?
*Theophylline
Nicotine
Lobeline
Anabasine
Quinine
Which of the following alkaloids does not have optical activity?
Nicotine
Lobeline
Anabasine
Quinine
*Theobromine
Which of the following alkaloids does not have optical activity?
Anabasine
Nicotine
*Papaverine
Quinine
Lobeline
Which of the following alkaloids does not have optical activity?
Lobeline
Nicotine
Anabasine
*Codeine
Quinine
Which of the following alkaloids does not have optical activity?
Nicotine
*Scopolamine
Anabasine
Lobeline
Quinine
Which of the following alkaloids does not have optical activity?
*Cocaine
Anabasine
Nicotine
Quinine
Lobeline
Which of the following alkaloids does not have optical activity?
Quinine
Nicotine
Lobeline
Anabasine
*Reserpine
Which of the following alkaloids does not have optical activity?
Nicotine
Anabasine
Quinine
*Strychnine
Lobeline
Which of the following reagents can be used to show basic properties of alkaloids?
NH4OH
HNO2
*HCl
NaOH
NaCl
Uric acid belongs to:
*Dibasis, triatomic acids
Onebasic diatomic acids
Tribasic, oneatomic acids
Dibasic, diatomic acids
Tribasic, triatomic acids
Atropine - belladonna alkaloid. Determine reagent that can be used to identify primary alcoholic group in the atropine molecule:
*K2Cr2O7 (H+)
HNO3
H2SO4
FeCl3
Ag(NH3) 2OH
Which of the following heterocycles is the base of uric acid?
*Purine
Indole
Pyrimidine
Imidazole
Pyridine
Adenine, guanine, xanthine and hypoxantine are purine derivatives. How many and what heteroatoms are in the primer structure of these compounds?
*four nitrogen atoms
one nitrogen atom and three oxygen atoms
two nitrogen atoms and two oxygen atoms
three nitrogen atoms and one oxygen atom
nothing
Morphine – alkaloid of isoquinoline and phenanthrene isoquinoline group. At the interaction with FeCl3 solution gives blue color. This reaction is qualitative on:
Primary amino-group
*Phenol hydroxyl
Aldehyde group
Secondary nitrogroup
α-diol fragment
A purine nucleus is the main structural fragment of caffeine, theophylline, theobromine, adenine, guanine and uric acid, which have higher physiological activity. Purine is an aromatic heterocycle. Determine the number of ?-electrons that take part in the formation of aromatic system.
*10
6
14
18
26
The most used method for alkaloids extraction is the following one:
Filtration
*Extraction
Sublimation
Recrystallization
Distillation
Extraction in the form of salts is one of the methods of alkaloids elimination. In this case raw materials are processed by:
Hexane
Formalin
Carbon tetrachloride
Chloroform
*Water or ethyl alcohol acidified by tartaric acid
Extraction in the form of bases is one of the methods of alkaloids elimination. In this case raw materials are processed by:
Hexane
Formalin
Carbon tetrachloride
Chloroform
*Water or ethyl alcohol acidified by tartaric acid
From the following list choose general alkaloid reagent:
Frede
Lughole
Felling
*Mayer
Selivanov
From the following list choose general alkaloid reagent:
Frede
Lughole
*Zonnenstein
Felling
Selivanov
From the following list choose general alkaloid reagent:
Frede
*Berthran
Lughole
Felling
Selivanov
From the following list choose general alkaloid reagent:
*Sheibler
Lughole
Frede
Felling
Selivanov
From the following list choose general alkaloid reagent:
Frede
Lughole
*Dragendorff
Felling
Selivanov
From the following list choose general alkaloid reagent:
Frede
Lughole
Selivanov
Felling
*Wagner-Bushard
From the following list choose specific alkaloid reagent:
Felling
*Erdman
Lughole
Selivanov
Mayer
From the following list choose specific alkaloid reagent:
Felling
Selivanov
Lughole
*Frede
Mayer
From the following list choose specific alkaloid reagent:
*Marky
Felling
Lughole
Selivanov
Mayer
From the following list choose specific alkaloid reagent:
Felling
Mayer
Lughole
Selivanov
*Mandelin
From the following list choose specific alkaloid reagent:
Felling
Lughole
*Sodium nitroprusside
Selivanov
Mayer
Which of the following alkaloids does belong to pyridine and piperidine group?
Quinine
*Nicotine
Morphine
Codeine
Atropine
Which of the following alkaloids does belong to pyridine and piperidine group?
Isoquinoline
Scopolamine
Morphine
Codeine
*Anabasine
Which of the following alkaloids does belong to pyridine and piperidine group?
Quinoline
Codeine
Papaverine
*Lobeline
Atropine
Which of the following alkaloids does belong to quinoline group?
*Quinine
Nicotine
Morphine
Codeine
Atropine
Which of the following alkaloids does belong to isoquinoline and phenenthrene isoquinoline group?
Nicotine
Scopolamine
Quinine
*Papaverine
Anabasine
Which of the following alkaloids does belong to isoquinoline and phenenthrene isoquinoline group?
Nicotine
*Morphine
Quinine
Lobeline
Anabasine
Which of the following alkaloids does belong to isoquinoline and phenenthrene isoquinoline group?
Atropine
Papavarine
*Codeine
Quinine
Anabasine
Which of the following alkaloids does belong to tropane group?
*Atropine
Nicotine
Papaverine
Quinine
Morphine
Which of the following alkaloids does belong to tropane group?
Nicotine
*Scopolamine
Codeine
Quinine
Morphine
Which of the following alkaloids does belong to tropane group?
Papaverine
Lobeline
*Cocaine
Quinine
Morphine
Which of the following alkaloids does belong to indole group?
Quinine
*Reserpine
Nicotine
Morphine
Cocaine
Which of the following alkaloids does belong to indole group?
Codeine
Cocaine
Nicotine
Morphine
*Strychnine
To which group of alkaloids does theophylline belong?
Indole
Tropane
*Purine
Quinoline
Pyridine and piperidine
To which group of alkaloids does theobromine belong?
Indole
Phenanthrene isoquinoline
Quinoline
*Purine
Pyridine and piperidine
To which group of alkaloids does caffeine belong?
Pyridine and piperidine
Indole
Isoquinoline
Quinoline
*Purine
To which group of alkaloids does nicotine belong?
*Pyridine and piperidine
Tropane
Purine
Quinoline
Indole
To which group of alkaloids does anabasine belong?
Phenanthrene
Tropane
Purine
*Pyridine and piperidine
Quinoline
To which group of alkaloids does lobeline belong?
Indole
*Pyridine and piperidine
Piperidine
Isoquinoline
Pyridine
To which group of alkaloids does quinine belong?
Isoquinoline
Tropane
Purine
*Quinoline
Pyridine and piperidine
To which group of alkaloids does papaverine belong?
*Isoquinoline and phenanthrene isoquinoline
Quinoline
Tropane
Indole
Purine
To which group of alkaloids does morphine belong?
Isoquinoline
Quinoline
*Isoquinoline and phenanthrene isoquinoline
Indole
Phenanthrene
To which group of alkaloids does codeine belong?
Purine
Pyridine and piperidine
Indole
Tropane
*Isoquinoline and phenanthrene isoquinoline
To which group of alkaloids does atropine belong?
Isoquinoline and phenanthrene isoquinoline
Quinoline
*Tropane
Indole
Purine
To which group of alkaloids does scopolamine belong?
Phenanthrene isoquinoline
Quinoline
Isoquinoline
*Tropane
Indole
To which group of alkaloids does cocaine belong?
Purine
*Tropane
Isoquinoline
Indole
Quinoline
To which group of alkaloids does reserpine belong?
Isoquinoline and phenanthrene isoquinoline
Quinoline
Tropane
*Indole
Purine
To which group of alkaloids does strychnine belong?
Tropane
Quinoline
*Indole;
Isoquinoline
Putine
Nicotine – alkaloid of pyridine and piperidine group in the little amount nicotine has:
Spasmolytic action
*Arousing effect on the autonomic system
Antituberculosis action
Antipyretic action
Analgesic action
Nicotine, being a poisonous substance is used as:
Flavor
Stain
Bleach
Solvent
*Insecticide
Anabasine – alkaloid of pyridine and piperidine group. Anabasine is used in the medicine as:
*Mean against smoking
Antituberculosis mean
Expectorant mean
Spasmolytic mean
Sedative mean
Quinine – alkaloid of quinoline group. Quinine is used in the medicine as:
*Antimalarial remedy
Antituberculosis mean
Expectorant mean
Spasmolytic mean
Sedative mean
Papaverine – alkaloid of quinoline and phenanthrene isoquinoline group. Papaverine is used in the medicine:
Antimalarial remedy
Antituberculosis mean
Expectorant mean
*Spasmolytic mean
Sedative mean
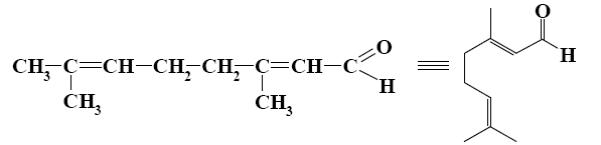
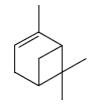
What is the name of the following terpene?
α-pinene
squalene
limonene
*ocimene
myrcene
What is the name of the following terpene compound?
camfora
squalene
*limonene
ocimene
myrcene
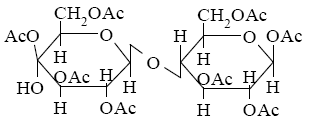
Choose the product of β-lactose interaction with excess of acetic anhydride

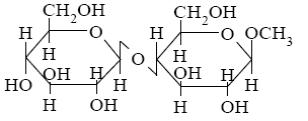
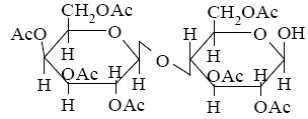
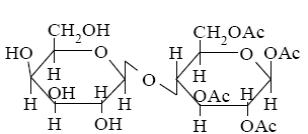
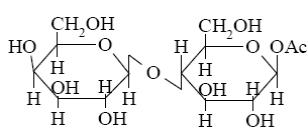
*
What is the name of the following terpenoid?
menthol
*α-terpineol
farnesol
nerol
geraniol
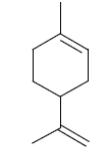
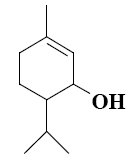
Which group of compounds does menthol belong?
*diene aldehyde
diene alcohol
alicyclic aldehyde
bicyclic alcohol
monocyclic aldehyde
Which group of compounds does menthol belong?
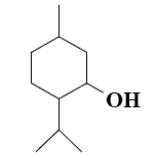
bicyclic ketone
aliphatic alcohol
cycloalkane
*monocyclic alcohol
bicyclic alcohol
Which group of compounds does squalene belong?
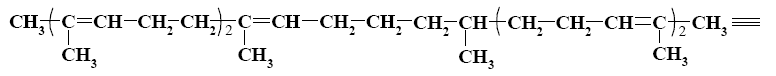
monocyclic alkane
monocyclic alcohol
bicyclic alkane
*polyene
bicylic aldehyde
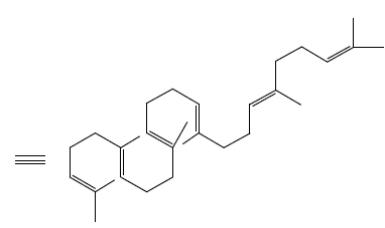
Which group of compounds does farnesol belong?
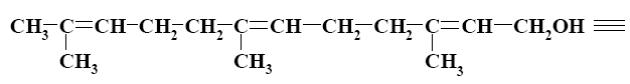

saturated alcohol
bicyclic ketone
*polyene alcohol
monocyclic alcohol
bicyclic alcohol
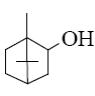
Choose the product of the following reaction?
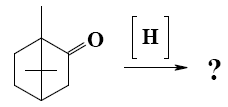
camphene
terpin hydrate
terpin
α-pinene
*borneol
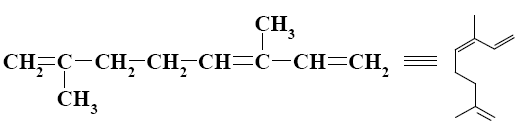
What is the name of the following terpene?
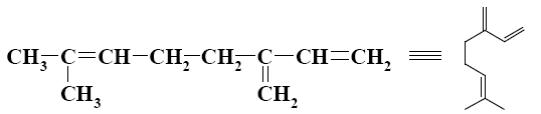
α-pinene
squalene
limonene
ocimene
*myrcene
What is the product of primary oxidation of camphor with nitric acid?
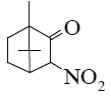
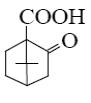
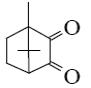
*
What is the product of nerol cyclization in acidic media?
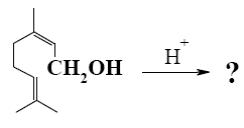
![]()
![]()
*
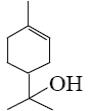
![]()
![]()
![]()
Choose the number of chiral atom in the molecule of ¥á-terpineol.
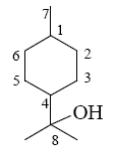
5
*4
3
2
1
Choose the number of chiral atom in the molecule of limonene.
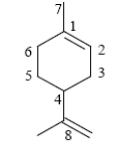
5
*4
3
2
1
Which group of compounds does geraniol belong?
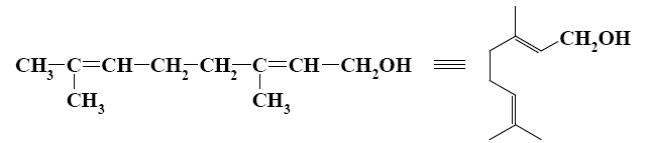
bicyclic diene
aliphatic alcohol
diene alcohol
*diene alcohol
diene aldehyde
Which group of compounds does myrcene belong?

cycloalkane
bicyclic aldehyde
monocyclic aldehyde
*aliphatic polyene
aliphatic alcohol
Which of the following reagents can be used to distinguish phenylalanine from tyrosine?
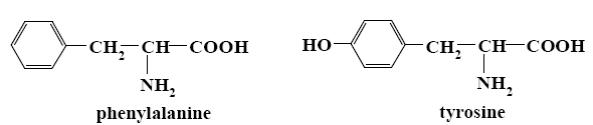
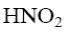

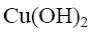
*
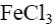
Choose the correct definition of nucleotide.
*nucleotide is the phosphoric acid ester of nucleoside
nucleotide is N-glycoside, which consist of nucleobase and D-ribose
nucleotide is the phosphoric acid ester of pyrimidine nucleobase
nucleotide is the phosphoric acid ester of purine nucleobase
nucleotide is the compound which consist of carbohydrate and heterocyclic nucleobase
What is the product of α-amino acids reaction with nitrous acid
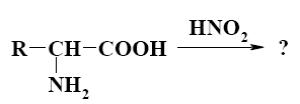 ?
?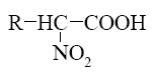
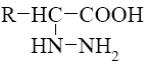
*
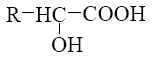
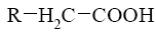
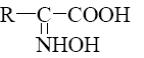
Choose the systematic name of α-cellobiose.
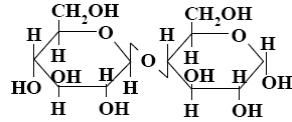
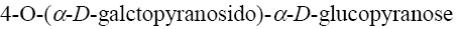
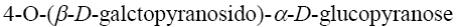
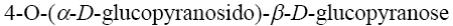
*
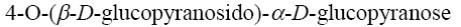
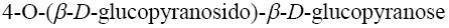
Choose the name of the following disaccharide.
*
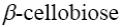
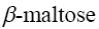

How many chiral carbon atomes does β-D-fructofuranose have?
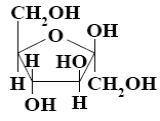
three
three
five
*four
one
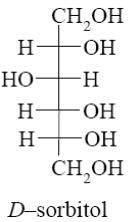
Choose the product of D-glucose reduction.
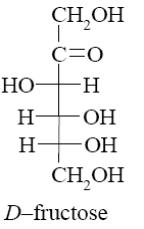
*
How many asymmetric carbon atoms does β-D-glucopyranose have?
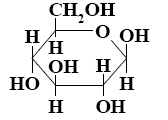
six
*four
five
one
three
Among the peptides listed below choose the one with peptide sequence: alanine, glutamine and glycine (Ala-Glu-Gly).
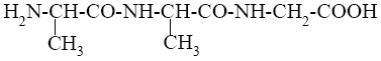
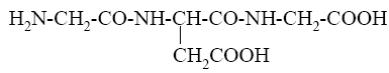
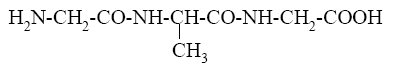
*
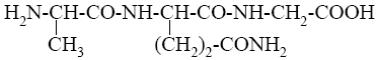
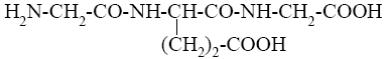
Among the peptides listed below choose the one with peptide sequence: glutamic acid, glycine and alanine (Glu-Gly-Ala).
*

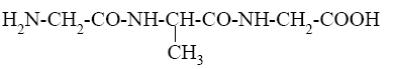
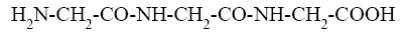
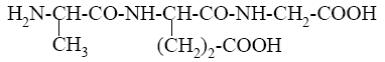
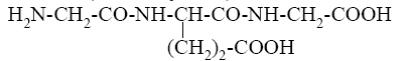
What is the name of the following terpenoid?
*α-pinene
squalene
limonene
ocimene
myrcene
What is the name of the following terpenoid?
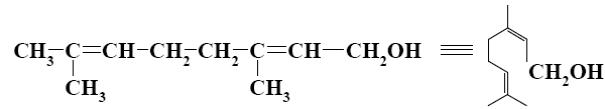
menthol
α-terpineol
farnesol
*nerol
geraniol
What is the name of the following terpenoid?
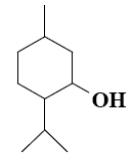
*menthol
α-terpineol
farnesol
nerol
Geraniol
What is the name of the following terpenoid?
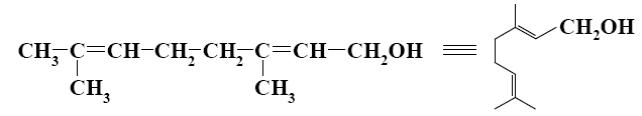
menthol
α-terpineol
farnesol
nerol
*geraniol
What is the name of the following terpenoid?
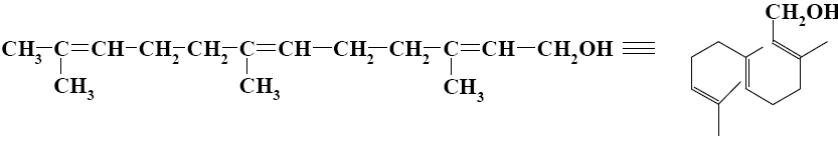
menthol
α-terpineol
*farnesol
nerol
geraniol
Which of the following reagents can be applied to obtain acyl halide from alanine?
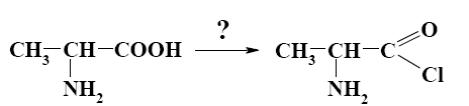
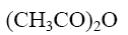
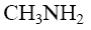
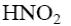
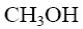
*
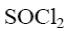
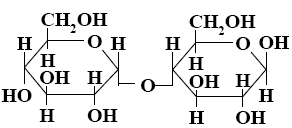
Choose the name of the following disaccharide.
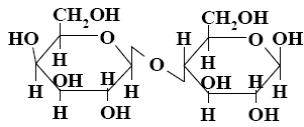
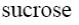
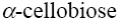
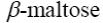
*
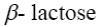
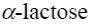
Choose the systematic name of β-maltose.
*
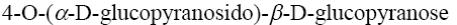
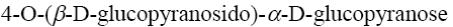
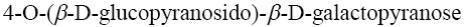
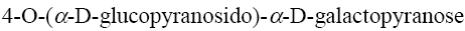
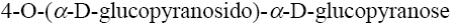
Choose the name of the following disaccharide.
β- maltose
*β-cellobiose
β- lactose
sucrose
α- maltose
Which of the following disaccharides gives galactose and glucose after hydrolysis?
mannose
cellobiose
*lactose
maltose
sucrose
Choose the systematic name of beta-cellobiose.
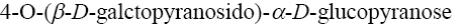
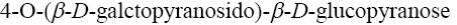
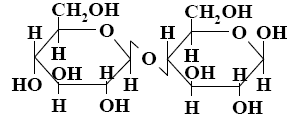
*
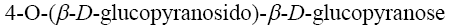
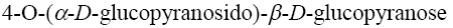
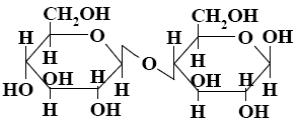
Choose the systematic name of α-maltose.
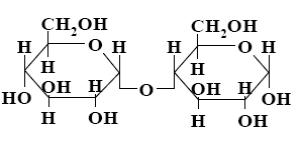
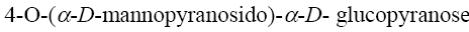
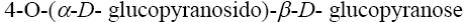
*
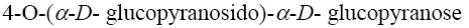

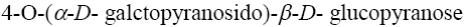
The change of the specific rotation of sucrose solution caused by its hydrolysis is called:
in all possible tautomeric forms
*inversion
mutorotation
isomerization
epimerization
The following monosaccharide belongs to:
deoxymonosaccharide
aldohexose
ketohexose
*ketopentose
aldopentose
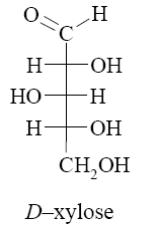
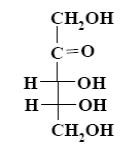
What is the name of the following monosaccharide?
D–xylose
D–galactose
*D–glucose
D–mannose
D–fructose
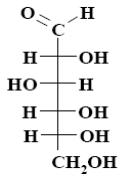
What is the name of the following monosaccharide?
*L– mannose
L– galactose
D–galactose
L– glucose
D–glucose
Choose the correct definition for protein denaturation.
*destruction of the protein form, with retention of primary structure of protein
destruction of quaternary structure, with retention of primary secondary and tertiary structures of protein
destruction of tertiary structure, with retention of primary and secondary structures of protein
destruction of secondary structure, with retention of primary structure of protein
destruction of primary structure of protein
What are the products of nucleic acids complete hydrolysis?
*nucleobases, monosaccharides and phosphoric acid
nucleobases, monosaccharides and water
glycosides and phosphoric acid
nucleosides and phosphoric acid
nucleotides
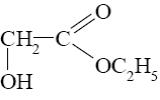
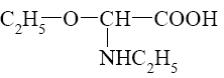
What is the product of glycine reaction with ethanol?
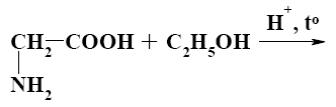
*

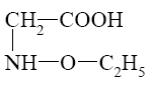
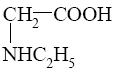
Choose the cationic form of amino acids.

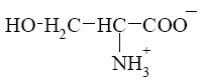
*
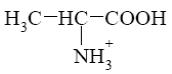
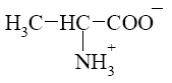

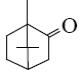
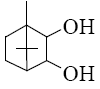
Choose the product of borneol oxidation.
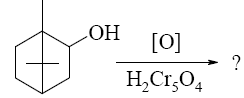
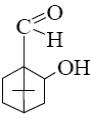
*

Choose the systematic name of β-lactose.
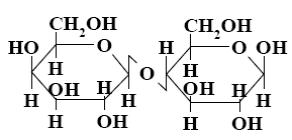
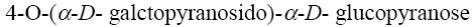
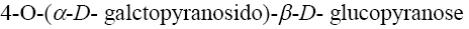
*
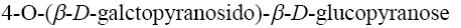
What are the products of glucose oxidation with Fehling’s reagent?
*mixture of oxidation products + Cu2O
glucaric acid + CuO
gluconic acid + Cu
glucuronic acid + Cu2O
sorbitol + CO2
Which is the correct definition of epimeric monosaccharides?
monoses, which have the different configuration of all chiral carbon atoms
monoses, which have the different configuration of four chiral carbon atoms
monoses, which have the different configuration of three chiral carbon atoms
*monoses, which have the different configuration of one chiral carbon atom
monoses, which have the different configuration of two chiral carbon atoms
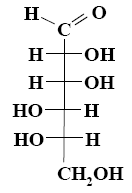
What is the name of the following monosaccharide?
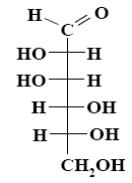
*D–mannose
L– galactose
D–galactose
L– glucose
D–glucose
What is the name of the following monosaccharide?
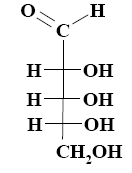
L–galactose
D–xylose
*D–ribose
L–arabinose
D–arabinose
Choose the correct systematic name of α -lactose.
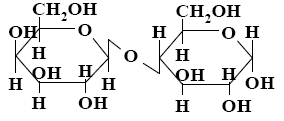

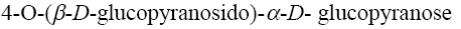
*
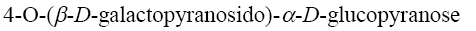
Amylose (water-soluble fraction of starch) is planar polymer which consists of:
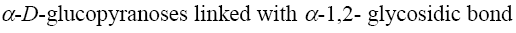
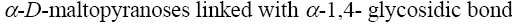
*
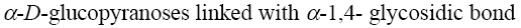
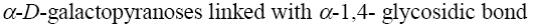
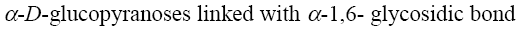
Choose the correct complementary pair of nucleobases among the listed below.
hypoxanthine - cytosine
thymine - uracil
uracil - hypoxanthine
*adenine - thymine
guanine - uracil
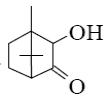
Which group of compounds does camphor belong?
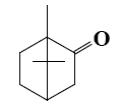
cycloalkanol
aliphatic alcohol
bicyclic alkene
*bicyclic ketone
aliphatic ketone
Which group of compounds does limonene belong?