*Acids and Bases*
Bronsted-Lowry acid: a hydrogen ion (proton) donor
Bronsted-Lowry base: a hydrogen ion (proton) acceptor
Lewis acid: an electron pair accepter
Lewis base: an electron pair donor
|
Properties |
Example |
Strong Acid |
Completely dissociates in water to donate protons. pH (1 – 3) Good conductor of electricity as has many free moving ions. |
Hydrochloric acid, HCl
HCl(aq) + H2O(l) H3O+(aq) + Cl-(aq) |
Weak Acid |
Partially dissociates in water. pH (4 – 6) Poor conductor of electricity |
Ethanoic acid, CH3COOH
CH3COOH(aq) + H2O(l) ⇄ CH3COO-(aq) + H3O+(aq) |
Strong Base |
Readily accepts protons. pH (11 – 14) Good conductor of electricity due to many free moving ions. |
Sodium hydroxide, NaOH
NaOH(aq) Na+(aq) + OH-(aq) |
Weak Base |
Partially accepts protons. pH (8 – 10) Poor conductor of electricity |
Ammonia, NH3
NH3(aq) + H2O(l) ⇄NH4+(aq) + OH-(aq) |
*Energetics*
The energy change for a reaction is given the symbol ΔH (units: kJ mol-1)
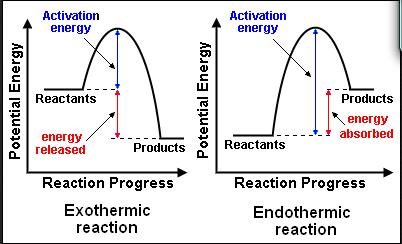
Exothermic reactions: energy is released to the surroundings, negative ΔH.
Endothermic reactions: energy is absorbed from the surroundings, positive ΔH.
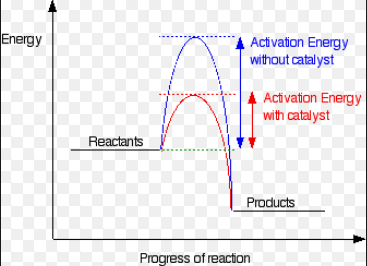
Activation energy, Ea = the minimum energy a particle must have to react
Using average bond energies to calculate ΔH:
ΔH = [total bonds broken in reactants] – [total bonds made in products]
*Kinetics*
The rate of a reaction is a measure of how fast or slow a reaction occurs.
Collision Theory: for a successful reaction to occur, particles must:
collide
with energy equal to or greater than the activation energy, Ea
in the correct orientation
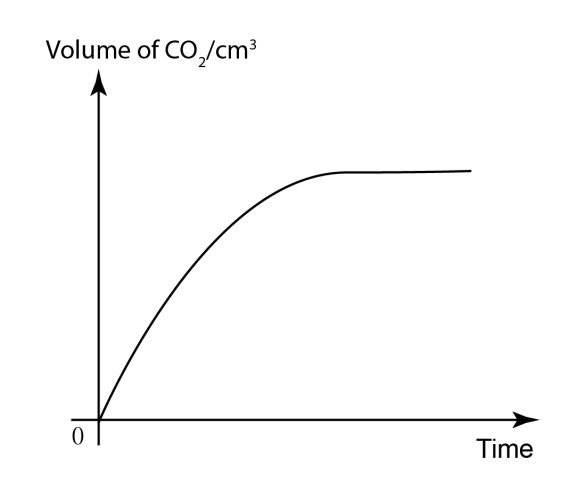
Rate of Reaction Graph
At
first the gradient is steepest, the reaction is quickest, there are
most reacting particles. The
gradient becomes less steep, the reaction slows, there are less
reacting particles. The
gradient is horizontal, the reaction is complete, there are no
reacting particles remaining.
Factors that increase the rate of reaction
Increase in Temperature: particles gain heat energy, move more quickly, collide more often, so there is increased chance of a successful collision. Also, more particles will have energy greater than the activation energy.
Increase in Concentration/Pressure: particles are closer together, therefore collide more often, so there is increased chance of a successful collision.
Increase in Surface Area: more particles are available to collide, therefore there are more collisions and an increased chance of a successful collision.
Addition of a Catalyst: provides an alternative route of lower activation energy, so more particles have energy equal to or greater than the activation energy, so there is an increased chance of a successful collision.