
Use the following to answer questions 71-75:
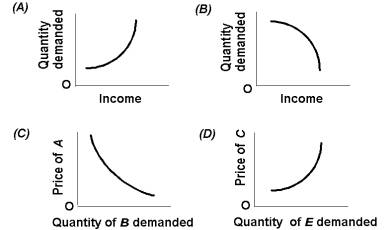
71. In which case would the coefficient of income elasticity be positive?
A) A.
B) B.
C) C.
D) D.
72. The case of an inferior good is represented by figure(s):
A) A only.
B) B only.
C) C.
D) D.
73. In which case would the coefficient of cross elasticity of demand be negative?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
74. The case of complementary goods is represented by figure:
A) A.
B) B.
C) C.
D) D.
75. In which case would the coefficient of cross elasticity of demand be positive?
A) A.
B) B.
C) C.
D) D.
76. The demand for a luxury good whose purchase would exhaust a significant portion of one's income is:
A) perfectly inelastic
B) perfectly elastic
C) relatively inelastic
D) relatively elastic
77. Which of the following will not cause the demand for product K to change?
A) a change in the price of close-substitute product J
B) an increase in consumer incomes
C) a change in the price of K
D) a change in consumer tastes
78. Suppose that a 20% increase in the price of normal good Y causes a 10% decline in the quantity demanded of normal good X. The coefficient of cross elasticity of demand is:
A) negative and therefore these goods are substitutes.
B) negative and therefore these goods are complements.
C) positive and therefore these goods are substitutes.
D) positive and therefore these goods are complements.
79. Assume you are spending your full budget and purchasing such amounts of X and Y that the marginal utility from the last units consumed is 40 and 20 utils respectively. Assume (a) the prices of X and Y are $8 and $4 respectively; (b) it takes 3 hours to consume a unit of X and 1 hour to consume a unit of Y; and (c) your time is worth $2 per hour. You
A) should substitute X for Y until the marginal utility per hour is the same for both products.
B) are consuming X and Y in the optimal amounts.
C) should consume less of Y and more of X.
D) should consume less of X and more of Y.
80. In which of the following instances is the effect on equilibrium price indeterminate, that is, dependent on the magnitude of the shifts in supply and demand?
A) demand rises and supply rises
B) supply falls and demand remains constant
C) demand rises and supply falls
D) supply rises and demand falls
81. If the demand for product X is inelastic, a 4% increase in the price of X will:
A) decrease the quantity of X demanded by more than 4%.
B) decrease the quantity of X demanded by less than 4%.
C) increase the quantity of X demanded by more than 4%.
D) increase the quantity of X demanded by less than 4%.
82. Other things equal, the shortage associated with a price ceiling will be greater the:
A) smaller the elasticity of both demand and supply.
B) greater the elasticity of both demand and supply.
C) greater the elasticity of supply and the smaller the elasticity of demand.
D) greater the elasticity of demand and the smaller the elasticity of supply.
83. The rate at which marginal utility for a product diminishes tells us something about:
A) its cross elasticity of demand.
B) its income elasticity of demand.
C) its price elasticity of demand.
D) whether it is a normal or an inferior good.
84. A leftward shift in the supply curve of product X will increase equilibrium price to a greater extent the:
A) more elastic the supply curve.
B) larger the elasticity of demand coefficient.
C) more elastic the demand for the product.
D) more inelastic the demand for the product.
85. The price elasticity of supply measures how:
A) easily labor and capital can be substituted for one another in the production process.
B) responsive the quantity supplied of X is to changes in the price of X.
C) responsive the quantity supplied of Y is to changes in the price of X.
D) responsive quantity supplied is to a change in incomes.
86. The theory of consumer behavior assumes that :
A) consumers behave rationally, maximizing their satisfactions.
B) consumers have unlimited money incomes.
C) consumers do not know how much marginal utility they obtain from succesive units of various products.
D) marginal utility is constant.
87. An effective price floor will:
A) force some firms in this industry to go out of business.
B) result in a product surplus.
C) result in a product shortage.
D) clear the market.
88. Which of the following generalizations is not correct?
A) The larger an item is in one's budget, the greater the price elasticity of demand.
B) The price elasticity of demand is greater for necessities than it is for luxuries.
C) The larger the number of close substitutes available, the greater will be the price elasticity of demand for a particular product.
D) The price elasticity of demand is greater the longer the time period under consideration.
89. Suppose that MUx/Px exceeds MUy/Py. To maximize utility the consumer who is spending all her money income should buy:
A) less of X only if its price rises.
B) more of Y only if its price rises.
C) more of Y and less of X.
D) more of X and less of Y.
90. In constructing a stable demand curve for product X:
A) consumer preferences are allowed to vary.
B) the prices of other goods are assumed constant.
C) money incomes are allowed to vary.
D) the supply curve of product X is assumed to be fixed.
