
- •Water Treatment Basics
- •1. Memorise the following technical words:
- •Waste water treatment
- •1.Memorise the following technical words:
- •Drainage
- •1.Memorise the following technical words:
- •2.Read and translate:
- •Principles of soil drainage
- •1.Memorise the following technical words:
- •2.Study the meanings of the following misleading words:
- •Types of drainpipe
- •1.Memorise the following technical words:
- •2.Study the meanings of the following misleading words:
- •Excavating the drain layout
- •1.Memorise the following technical words:
- •2.Study the meanings of the following misleading words:
- •Testing drains
- •1.Memorise the following technical words:
- •2. Study the meanings of the following misleading words:
- •Building a manhole
- •1.Memorise the following technical words:
- •Septic tanks
- •1.Memorise the following technical words:
- •Discharging the effluent
- •1 . Memorise the following technical words:
- •Above-ground drainage
- •1 . Memorise the following technical words:
- •The sanitary fittings
- •1 . Memorise the following technical words:
- •3. Read and translate: 1
- •1. Memorise the following technical words: 2
- •1. Memorise the following technical words: 35
- •Rainwater disposal
- •1 . Memorise the following technical words:
- •The cold water supply
- •1 . Memorise the following technical words:
- •Hot water installations
- •Memorise the following technical words:
1. Memorise the following technical words: 35
2.Read and translate the text 35
The pipework for hot water systems Cold water enters the hot water cylinder at the bottom of the tank (Figure 7). The source may be: 36
basin; shower.
They should be made of materials that are durable, waterproof and easy to clean,
A WC is usually in two parts:
1. the pan and seat. The pan is made of vitreous china and includes a 50 mm trap. The outlet, which is either a ‘P’ or ‘S’ shape, is 100 mm in diameter. The seat, which can be china, plastic or wood, is hinged and bolts to holes in the top of the pan.
2. the cistern, which is made from plastic or china. It consists of the body, the lid and the internal mechanisms. The body has connections for the water supply and overflow pipe. The internal mechanism consists of a ball valve, float and a flushing siphon with an operating handle.
A bath can be made of cast iron, pressed steel or plastic. The standard size is 1700 x 700 mm. The bath has holes for fixing the taps, overflow and waste outlet.
A basin is made of vitreous china and has an overflow built in.
A sink in a kitchen is usually stainless steel so that it will be lightweight and durable. It may come with a draining board, which stands on a timber cupboard to conceal the waste and supply pipes.
A shower may have an independent plastic, concrete or glazed fireclay base. It can be attached to mixer taps on a bath or it can flow directly from pipes attached to the wall onto the floor. Access to the trap can be a problem if the tray is shallow. In suspended timber floors the trap can be housed between the joists. In concrete floors, the trap may need to be below the ceiling.
3. Check your understanding
- Above-ground drainage consists of the soil and waste pipes from the sanitary fittings.
- Above-ground drainage is connected to the underground drainage at floor or ground level.
- Above-ground drainage should be connected to a trapped gully.
All fittings discharge water through a trap which prevents smells and gases from the drains entering the building.
- The soil vent pipe allows any pressures from gases in the system to be released above roof level.
- Sanitary fittings are made of materials that are waterproof, durable and easy to clean.
- Waste and soil pipes above ground are usually made of uPVC.
Text 14(4000)
Rainwater disposal
1 . Memorise the following technical words:
bracket fixing – крепление скобами
roof overhang – выступ крыши
fascia– доска, закрывающая концы стропильных ног
rainwater pipe – водосточная труба
valley gutter – разжелобок, ендова, желоб на стыке двух скатов кровли
shoe pipe – отвод водосточной трубы, башмак
parapet – парапетное ограждение
gutter – водосточный желоб
grating – решетка
flood – паводок, наводнение; затоплять, заливать
rubble fill – каменная засыпка, засыпка щебнем
swan neck – S-образное колено (трубопровода)
fiber cement – волокнистый цемент
spout – водосточная труба, желоб
2.Read and translate the text:
If rainwater flowed off the roof of a building in an uncontrolled way, then it could flood the areas around the building and inconvenience the occupants. Water can also flow off shallow eaves and find its way into a building through the walls and windows. For these reasons, it is better to collect water at the eaves in a gutter and direct it down to the ground in a rainwater pipe. The rainwater can then drain away underground and discharge into soakaways.
A soakaway is a rubble-filled pit in the ground which absorbs water quickly. The soakaway should be at least 3 metres from the building.
Gutters. A gutter is a channel fixed to the long edge of a roof. The bracket fixings on the fascia should be at 900 mm intervals. A gutter will have an outlet which is a spout that points down to connect with a rainwater pipe.
In most domestic buildings, one outlet is usually enough to take the rainwater during normal wet weather. The distribution of water along the length of the gutter pushes it naturally towards the outlet. Any residue of water soon evaporates.
Some gutters are not attached to the edge of roofs such as:
- gutters formed in the surface of flat roofs beside parapets;
- valley gutters, which are formed at the junction of two roof slopes.
The most common gutter shapes are the half- round and the box (Figure 6).
(a)
(b)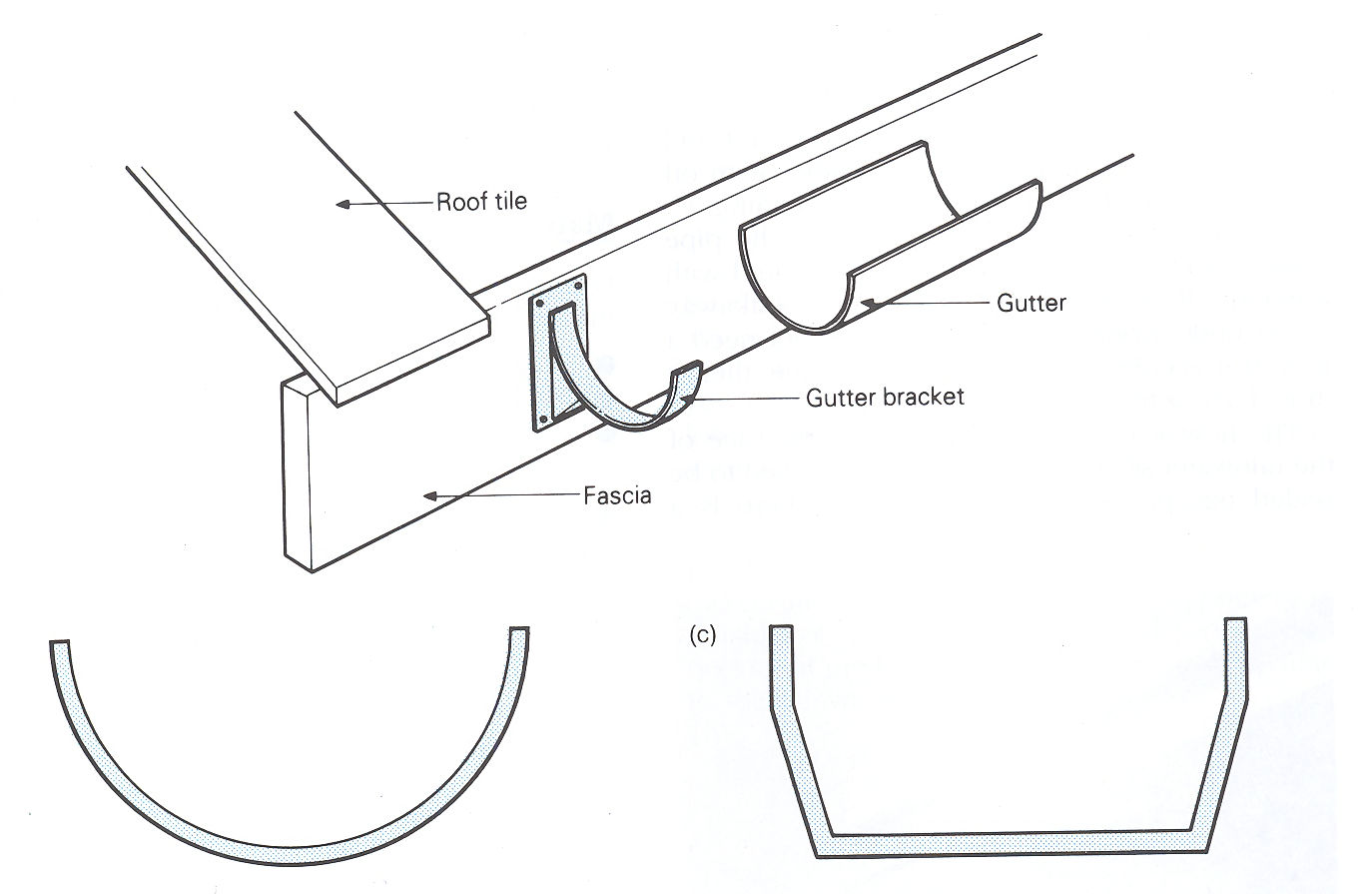
Figure 6. Details of bracket gutters and a connection: (a) a gutter bracket connection; b) a half-round gutter; (c) a box gutter.
Rainwater pipes. The rainwater pipes are attached to the gutter outlets and fixed vertically on the building. The roof overhang requires a rainwater pipe to bend in more than one direction to reach past the gutter to the surface of the building. This bend is called a swan neck junction .
The pipes are fixed with brackets, plugged and screwed to the wall surface, which hold them off the surface to allow for painting and cleaning.
The water runs out of the bottom of the pipe from a shoe or angled pipe into a gully fitted with a grating. If this gully is connected to a soakaway by an underground pipe, then it does not need a trap. If it is connected to the soil drainage, then it must have a trap.
The flow should run down against the face of the rainwater sockets. The joints do not need to be sealed except to stiffen the pipes. If there is a blockage in a pipe, then the water can leak out through the joints and alert you to the problem. If the pipes are inside a building, then the joints must be watertight.
Materials. Gutters and rainwater pipes are most commonly made from:
uPVC; fibre cement; zinc.
UPVC is the most popular material because it does not need decoration, it is lightweight and easy to fix. UPVC does not rot or corrode. However, this material is more easily damaged and is unsuitable for areas where it could be hit by moving vehicles. UPVC also expands and contracts more than the other materials as a result of temperature changes.
Fibre cement is a durable and heavier material than plastic that requires more joints and supports. It is often used for larger roofs that take big gutters, like those on industrial buildings. Fibre cement is not affected by temperature changes and it can be painted or left in its natural grey colour. You need to be very careful if you cut it that you do not inhale toxic dust.
Zinc is not a strong material because it dents easily and corrodes in some climates. It is popular since it can be made almost anywhere by folding and soldering zinc sheets into the desired shapes.
Valley gutters. When pitched roofs meet at right angles, then the junction is called the valley. You make a gutter in the valley that runs from top to bottom. Since
this is almost an internal gutter, water could enter the building if it overflowed. These gutters must be a minimum 300 mm across to avoid blockages and overflows.
Surface water.Water that falls on the hard surfaces surrounding a building such as paths, terraces and driveways can be collected by open channels or gullies. Hard surfaces should slope away from the walls towards these collecting points. If the drains running from the gullies go to a soakaway, then they do not have traps, but they should be fitted with removable silt buckets to make them easier to clean.
3.Check your understanding:
Pitched roofs should have gutters and downpipes.
Rainwater that falls on and around a building should be collected and piped away.
Water on flat roofs without parapets should fall to eaves’ gutters.
Flat roofs with parapets should have a built-in gutter with a cesspool if the rainwater pipe is external.
Rainwater pipes should not be connected to the soil drainage system.
Rainwater pipes should take the water to soakaways at least 6 metres from the house.
Gutters and rainwater pipes are usually made out of uPVC, zinc or fibre cement.
If pitched roofs form an internal angle, then a valley gutter is formed.
The size of gutters and downpipes should .match the roof area to be drained.
Hard surfaces should slope to drain off water into gullies and channels.
Text 15 (3000)
