
- •Content
- •Literature
- •Home work
- •Subject 3 the role of perception in human safety, physiological factors of its protection.
- •Introduction.
- •1. Classification of harmful and dangerous factors that can affect people in the environment.
- •2. Harmful and dangerous factors of active group and how to protect from them.
- •Increase of man immunity to infection.
- •3. Perception of hdf by a person. Person analyzers.
- •Physiological man’s analyzer Receptor-Main nerves-Cerebral centre
- •Image.3.1. Analyzer adaptation (changed Sl).
Subject 3. The role of perception in human safety, physiological factors of its protection.
Session 1. The role of perception in human safety, physiological factors of its protection.
Content
Name of issue |
Time |
Introduction. |
5' |
|
15' |
|
30' |
|
35' |
The final part. |
5' |
Literature
1. Заплатинський В.М. Безпека життєдіяльності. Опорний конспект лекцій для всіх спеціальностей. – К.: КДТЕУ, 1999. – 208 с.
2. Бедрій Я.І., Нечай В.Я. Безпека життєдіяльності. Навчальний посібник. – Л.: Магнолія-2006, 2007. – 499 с.
3. Желібо Є.П., Заверуха Н.М., Зацарний В.В. Безпека життєдіяльності. Навчальний посібник / За ред. Є.П. Желібо. 6-е вид. – К.: Каравела, 2008. –344 с.
4. Лапін В.М. Безпека життєдіяльності людини. Навчальний посібник. – К.: Знання, 2007. – 332 с.
5. Закон України “Про захист населення і території від НС техногенного та природного характеру”, 2000 р.
Home work
Study lecture material.
Familiarize yourself with the features of the human-operator, the parameters of working capacity and reliability of human-operator [2], p. 30-44.
Subject 3 the role of perception in human safety, physiological factors of its protection.
Classification of harmful and dangerous factors that can affect people in the environment.
Harmful and dangerous factors of active group and how to protect from them.
Perception HDF of man. Analyzers of man.
Introduction.
At the previous lecture we learned the model of the source of danger in a dangerous situation and harmful factors. Noticed, that the person also protects from HF using collective and individual protectors and moving beyond the zone of danger. Today we will get acquainted with the mechanism of sensation of man in dangerous situation. To do this, you must study the classification of HDF based on human effect.
1. Classification of harmful and dangerous factors that can affect people in the environment.
Safety Of Living study man and his environment in a system 'Man - Living space ".
Living space - is part of the Universe, where a person may live and where systems of its livelihood operate. (second definition - a combination of natural and anthropogenic factors with which a person interacts directly or indirectly during his life).
In the theory of SofL the concept "Environment" is also examined. It is all the totality of natural and anthropogenic factors, among which person lives. It consists of the atmosphere, lithosphere, hydrosphere, biosphere, infosphere, the noosphere.
Atmosphere — |
outer gas shell of the Earth with thickness about 3000 km, its composition: nitrogen - 78% oxygen - 21% carbon dioxide, ozone, water vapor, inert gases and other gases and impurities - 1%. |
Lithosphere — |
outer hard shell of the Earth, including the earth's crust with part of the upper mantle. The the earth's crust has a thickness of 80 km, consisting of 99.5% of oxygen, silicon, hydrogen, aluminum, iron, magnesium, sodium and calcium, and other elements - 0.5%. |
Hydrosphere — |
set of oceans, seas, glaciers, water of continents and islands, which is 16 billion m3 of water, or 0.25% of the mass of the planet. |
Biosphere — |
domain of existence of living organisms on the Earth, including the part of the atmosphere, the lithosphere and the hydrosphere. The upper line of the biosphere is 85 km, the lower - 2 km in the lithosphere and up to 11 km in the hydrosphere. |
Infosphere — |
information space in which the man exists. |
Noosphere (the sphere of mind, brain) — |
phase of development of the biosphere, during which intelligent human activity is a major determinant of its functioning. |
Living
environment is a part of the environment and is determined separately
for each individual.
determined separately
for each individual.
Living environment of mankind is practically the environment.
Human environment can be classified as follows:
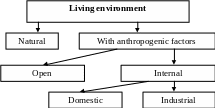
Natural environment - an environment in which there are no anthropogenic factors.(in it such natural factors influence a man: atmosphere pressure, variation of t ° C, humidity, the level of solar radiation, cloudiness, precipitation wind, etc.).
Open environment - an environment in which natural factors are predominate over anthropogenic factors (streets of towns, villages, territory of stadiums, parks, etc.).
Internal environment - an environment in which the specific gravity of anthropogenic factors exceeds the specific gravity of natural factors (closed space, open areas of warehouses, workshops, etc.).
Industrial environment - the most dangerous for humans, at works elevated levels of noise, vibration act on a man; acutely psychophysiological factors become apparent (stress, fatigue); in air of working zone often toxic substances are present; person works with machines and mechanisms on works, which is potentially dangerous. Spending a third of his life, or almost a half of time at work, you must take care of ensuring safe and acceptable working conditions.
Domestic environment - a human habitation, a set of residential buildings and edifices, and also communal-general organizations and institutions. With the increasing of anthropogenic effect on the nature, there appeared the necessity to control the domestic environment conditions of which until recently were determined independently by each family. State of water and air pollution, level of humidity, noise, radiation in home areas were not considered a problem, but studies suggest about dangerous excess of these parameters in dwellings.
To such conditions lead a number of factors:
- Close proximity to business that do not have the buffer zone;
- Emissions of businesses, located near, exceed standards;
- Specific climatic and microclimatic conditions;
- Close proximity to roads with heavy traffic;
- Usage of a variety of means;
- The usage of chemicals (detergents, paints, plastics, etc.)
EXAMPLE. Every 3 minutes in the world as a result of industrial accidents and occupational diseases a man dies. Every year in Ukraine in manufacturing injures ~ 60 thousand persons> 2 thousand dies. In the domestic environment in Ukraine injures 12 - 14 million, ~ 70 thousand fatalities. 10 thousand people acquire occupational diseases, 6 thousand each year become disabled. Annually as a result of accidents on manufacture, Ukraine suffers a loss of about 4 billion.
According to the system of safety standards (SSBP) there are harmful and dangerous factors. These factors were identified in the previous lecture.
Harmful factors - such factors, action of which under certain conditions lead to disease and decrease working capacity.
Dangerous factors – factors, action of which under certain circumstances lead to injury, a sharp health deterioration, death.
Between dangerous and harmful factors, there is no fundamental difference. The same factor depending on the magnitude and time of action may be dangerous or harmful. Dangerous and harmful factors can be objects, tools, products, labor, technology, actions and climatic environment (storms, floods, flora, fauna), people.
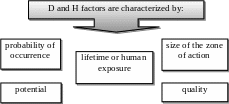
Potential - quantitative measure of the factor, such as noisiness, voltage of electrical current, levels of air pollution.
The quality of the factor reflects its specific characteristics that affect human body, such as the dispersion of dust, frequency content of the noise, a kind of electric current.
Danger Zone (action) - a space in which continuously or periodically appear dangerous and harmful factors.
The maximum permissible level of negative factor (GDR) – level of factor, which during the daily (except weekends) work during 8 hours or another time, but not more than 41 hours a week, throughout the working life can not cause disease or variations in health, which are found that the modern methods of research in the process or in the long term or life of future generations.


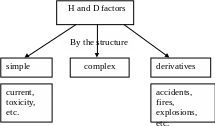
By the structure all the factors are divided into simple (current, toxicity), complex and derivative (accidents, fires, explosions).
Active factors are those that can act upon people through different types of energy.
Factors of active group are divided into subgroups:
- Mechanical;
- Thermal;
- Electrical;
- Electromagnetic;
- Chemical;
- Biological;
- Psychophysiological.
Passive-active group includes factors that occur as a result of the action of man .
Passive-active group includes: acute immovable objects, small friction factor and roughness of surfaces, and also bows and downs.
The group of passive factors includes those factors that occur indirectly.
Passive factors include: corrosion of materials, scale, lack of strength of structures, increased load on the mechanisms and machines and so on. Form of appearance of these factors is destruction, explosions, accidents.
