
- •History of electricity
- •I. Listening and reading
- •II. Vocabulary
- •III. Reading comprehension
- •1. Answer the Questions
- •4. Complete the sentences
- •IV. Analyze
- •V. Translate
- •VI. Speak
- •I. Listening and reading
- •What is energy?
- •II. Vocabulary
- •III. Reading comprehension
- •1 . Answer the Questions
- •4. Complete the sentences
- •IV. Analyze
- •V. Translate
- •VI. Speak
- •Nuclear energy
- •I. Listening and reading
- •N uclear problems
- •II. Vocabulary
- •III. Reading comprehension
- •1 . Answer the Questions
- •4. Complete the sentences
- •IV. Analyze
- •V. Translate
- •VI. Speak
- •Energy sources
- •I. Listening and reading
- •II. Vocabulary
- •III. Reading comprehension
- •1. Answer the Questions
- •4. Complete the sentences
- •IV. Analyze
- •V. Translate
- •V I. Speak
- •Solar energy
- •I. Listening and reading
- •The energy of the sun
- •II. Vocabulary
- •III. Reading comprehension
- •1 . Answer the Questions
- •4. Complete the sentences
- •IV. Analyze
- •V. Translate
- •VI. Speak
- •I. Listening and reading
- •Types of mechanical energy
- •II. Vocabulary
- •III. Reading comprehension
- •IV. Analyze
- •V. Translate
- •VI. Speak
- •Tidal energy
- •I. Listening and reading
- •Tidal energy
- •II. Vocabulary
- •III. Reading comprehension
- •1. Answer the Questions
- •4. Complete the sentences
- •IV. Analyze
- •V. Translate
- •VI. Speak
- •Energy conservation
- •I. Listening and reading
- •Energy conservation
- •II. Vocabulary
- •III. Reading comprehension
- •1 . Answer the Questions
- •4. Complete the sentences
- •IV. Analyze
- •V. Translate
- •VI. Speak
V. Translate
С
 траны,
использующие атомные электростанции
могут также научиться делать ядерное
оружие
самостоятельно……………………………………...……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
траны,
использующие атомные электростанции
могут также научиться делать ядерное
оружие
самостоятельно……………………………………...……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………Cверхдержавы уже имеют более чем достаточно ядерного оружия, чтобы уничтожить планету пятьдесят раз……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………...………………………………………………………………………………….
Ядерные реакторы производят мощное излучение, которое в больших дозах может убивать…………………………………………………...………
……………………………………………………………….…………………..
Радиация может послужить причиной рака………………..………………..
Они предприняли меры предосторожности против утечки радиации…...…
…………………………………………………………………………………...
Вода была радиоактивна……………………………………………………….
1000 единиц ядерного оружия находится в руках других государств…...
………………………………………………………………………………….
Больше не существует двух сверхдержав……………………………………
VI. Speak
1 .
Interview
.
Interview
Work in pairs and prepare an interview
Student A is an environmental activist who wants to know more about nuclear problems.
Student B is an expert in nuclear energy.
2. Prepare a report on the dangers of nuclear energy
U NIT
4
NIT
4
Energy sources
Preview
Answer the questions. Then talk about your answers.
|
I. Listening and reading
Listen to the text
![]()
Read and translate the text
ENERGY SOURCES
M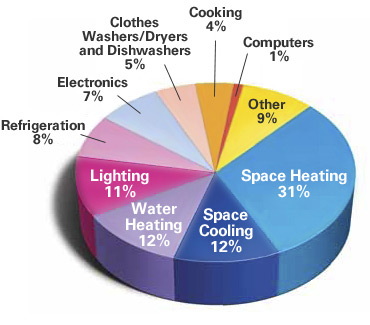
 ost
of our energy comes from fossil fuels. Coal,
oil
and natural gas supply about
85 percent
of US primary
energy
consumption.
Although
the supplies
of
these fossil fuels are vast,
they
are not unlimited. And more important, the earth's atmosphere and
biosphere may not survive
the
environmental
impact of
burning such enormous
amounts of
these fuels. Carbon stored over millions of years is being released
in
a matter of decades, disrupting
the
earth's carbon cycle
in
unpredictable
ways.
ost
of our energy comes from fossil fuels. Coal,
oil
and natural gas supply about
85 percent
of US primary
energy
consumption.
Although
the supplies
of
these fossil fuels are vast,
they
are not unlimited. And more important, the earth's atmosphere and
biosphere may not survive
the
environmental
impact of
burning such enormous
amounts of
these fuels. Carbon stored over millions of years is being released
in
a matter of decades, disrupting
the
earth's carbon cycle
in
unpredictable
ways.
But fossil fuels are not the only source of energy, and burning fuel is not the only way to produce heat and motion. Renewable energy offers us a better way. Some energy sources are "renewable" because they are naturally replenished, because they can be managed so that they last forever, or because their supply is so enormous that they can never be meaningfully depleted by humans. Moreover, renewable energy sources have much smaller environmental impacts than fossil and nuclear fuels.
O ur
fossil fuels - coal, gas, oil - are quickly disappearing. This energy
capital takes millions of years to replace. We must use less energy
and find other energy sources.
ur
fossil fuels - coal, gas, oil - are quickly disappearing. This energy
capital takes millions of years to replace. We must use less energy
and find other energy sources.
'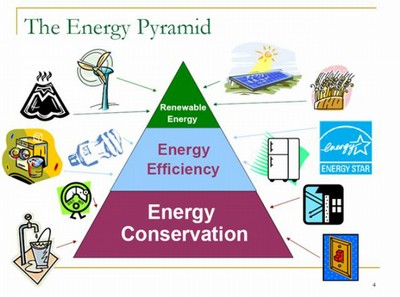 Conservation
of
energy' can have two different meanings. One meaning is the saving of
energy.
We should not waste
it.
If we use our fuel sources carefully, they will last longer. Another
meaning is that energy is neither created nor destroyed. This is the
scientific meaning of conservation. It is the
First Law of Thermodynamics.
Conservation
of
energy' can have two different meanings. One meaning is the saving of
energy.
We should not waste
it.
If we use our fuel sources carefully, they will last longer. Another
meaning is that energy is neither created nor destroyed. This is the
scientific meaning of conservation. It is the
First Law of Thermodynamics.
As fossils disappear, we must find other sources of energy. Nuclear energy brings many dangers. We need to find other - and safer - sources of energy, e.g. the sun, the wind and the sea. These are called alternative energy sources.
