
- •Give the definition of the stream line, write its differential equation.
- •Give the definition of the stream surface, infinitesimal stream tube.
- •Essence of Eulers method for investigation of fluid motion .
- •Essence of Lagrange method for investigation of fluid motion .
- •Accordance between path line, streamline, Eulers and Lagrange methods for investigation of fluid motion
- •What is the base for obtaining continuity equation?
- •Write integral form of continuity equation and call its members.
- •Write differential form of continuity equation and call its members.
- •Write differential form of continuity equation for steady flow and call its members.
- •Write differential form of continuity equation for incompressible flow and call its members.
- •W rite continuity equation for infinitesimal stream tube, one dimensional flow with finite cross section area and call its members.
- •Which physical values are considered as gas state parameters?
- •Write the gas state equation and call its members.
- •Give the definition of the gas compressibility; which index is used in order to characterize compressibility.
- •Give the definition of the gas viscosity; which index is used in order to characterize viscosity.
- •Write the Newton’s formula for internal friction and call its members.
- •Write formula for calculation Reynolds number (Re). Call its members.
- •Write the formula for calculation the speed of sound using gas temperature; and call its members.
- •How (quality) does change dynamic coefficient of viscosity when temperature of gas changes? The same for liquid.
- •Call physical values whose fields completely describe the phenomenon of flow around the solid body.
- •Which type of thermodynamic process in aerodynamics usually is used ? Call this thermodynamic process, write its formula, call members of this formula.
- •Write formulas for calculation gas parameter relation in flow stagnation point and free stream condition. Call members of these formulas.
- •Give the definition the critical or sonic flow regime.
- •What is critical speed of sound?
- •Write formula for calculation theoretical maximum speed of flow and call its members.
- •What is the velocity factor? What is difference between the velocity factor and Mach number?
- •Write formula for calculation flight Mach number using instrumental measured pressure values.
- •Call the conformity between flight regimes and Mach number values. Subsonic and Supersonic speed
- •Write Gugonio equation, call its members.
- •Name and give definitions of two viscosity flow regimes.
- •Give the definition of the boundary layer.
- •Draw schemes of viscose air flow about solid body surface. Mark main elements of this flow.
- •Relation between which forces does Reynolds number (Re) characterize? Write the formula for Reynolds number calculation, call physical values used in this formula.
- •Relation between which forces does Fruds number (Fr) characterize? Write the formula for Fruds number calculation, call physical values used in this formula.
- •Relation between which forces does Eulers (Eu) number characterize? Write the formula for Eulers number calculation, call physical values used in this formula.
- •Relation between which forces does Mach number (m) characterize? Write the formula for Mach number calculation, call physical values used in this formula.
- •Relation between which forces does Struhal number (St) characterize? Write the formula for Struhal number calculation, call physical values used in this formula.
- •Relation between which forces does turbulance degree (ε) characterize?
Call physical values whose fields completely describe the phenomenon of flow around the solid body.
Which type of thermodynamic process in aerodynamics usually is used ? Call this thermodynamic process, write its formula, call members of this formula.
An adiabatic process is any process occurring without gain or loss of heat within a system (i.e. during the process the system is thermodynamically isolated- there is no heat transfer with the surroundings). This is the opposite of a diabatic process, where there is heat transfer. A key concept in thermodynamics, many rapid chemical and physical processes are described or approximated in this way.

Where P-pressure
density
 is
specific heat ration
is
specific heat ration
Write formulas for calculation gas parameter relation in flow stagnation point and free stream condition. Call members of these formulas.
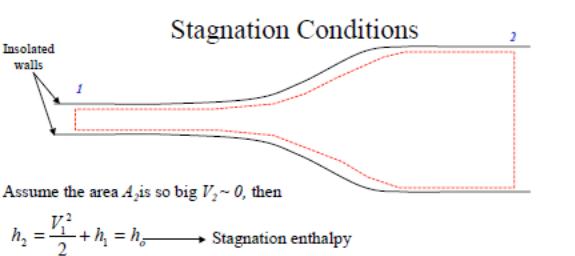

Stagnation condition – maximum velocity
If the temperature, T is taken down to absolute zero, then that formula can be solved for the maximum velocity:

No higher velocity is possible unless energy is added to the flow though heat transfer or shaft work
Stagnation condition – Mach number relations
Recall,
that the Mach number is defined as:



For
ideal gases



Stagnation condition – Isentropic pressure and density relationships



Give the definition the critical or sonic flow regime.
Regime where in some point local speed of sound is equal to the speed of flow is called critical flow regime.















P0 is stagnation pressure
For each point acr is the same
acr - critical speed of sound
Write formula for calculation critical speed of sound and call its members.
Condition when M=1


c* - is the critical speed of sound
What is critical speed of sound?
Critical speed of sound is the speed of flow equal to the local speed of sound
Write formula for calculation theoretical maximum speed of flow and call its members.
If the temperature, T is taken down to absolute zero, then that formula can be solved for the maximum velocity:
What is the velocity factor? What is difference between the velocity factor and Mach number?
The velocity
factor (VF),[1] also
called wave
propagation speed or velocity
of propagation (VoP or ![]() ),[2] of
a transmission
medium is
the speed at which a wavefront (of an acoustic signal, for example,
or an electromagnetic signal, a radio signal,
a light pulse in a fibre
channel or
a change of the electrical voltage on a copper
wire)
passes through the medium, relative to the speed of light. For
optical signals, the velocity factor is the reciprocal of
the refractive
index.
),[2] of
a transmission
medium is
the speed at which a wavefront (of an acoustic signal, for example,
or an electromagnetic signal, a radio signal,
a light pulse in a fibre
channel or
a change of the electrical voltage on a copper
wire)
passes through the medium, relative to the speed of light. For
optical signals, the velocity factor is the reciprocal of
the refractive
index.
The speed of radio signals in a vacuum, for example, is the speed of light, and so the velocity factor of a radio wave in a vacuum is unity, or 100%. In electrical cables, the velocity factor mainly depends on the insulating material (see table below).
The use of the terms velocity of propagation and wave propagation speed to mean a ratio of speeds is confined to the computer networking and cable industries. In a general science and engineering context, these terms would be understood to mean a true speed or velocity in units of distance per time,[3] while velocity factor is used for the ratio.
In fluid
mechanics, Mach
number (![]() or
or ![]() )
(/ˈmɑːx/)
is a dimensionless
quantity representing
the ratio of speed of an object moving through a fluid and
the local speed
of sound.[1][2]
)
(/ˈmɑːx/)
is a dimensionless
quantity representing
the ratio of speed of an object moving through a fluid and
the local speed
of sound.[1][2]
![]()
where
![]() is
the Mach number,
is
the Mach number,
![]() is
the velocity of the source relative to the medium, and
is
the velocity of the source relative to the medium, and
![]() is
the speed of sound in the medium.
is
the speed of sound in the medium.
Mach number varies by the composition of the surrounding medium and also by local conditions, especially temperature and pressure. The Mach number can be used to determine if a flow can be treated as an incompressible flow. If M < 0.2–0.3 and the flow is (quasi) steady and isothermal, compressibility effects will be small and a simplified incompressible flow model can be used.[1][2]
