
- •Тема I. Вводно-коррективный курс
- •Vocabulary exercises
- •Unit 2. My Biography Моя биография topical vocabulary
- •Introductory text My Biography
- •Compare
- •Remember!
- •Unit 3. Kazan State Medical University Казанский государственный медицинский университет
- •Topical vocabulary
- •Introductory text Kazan State Medical University
- •Vocabulary exercises
- •Unit 4. Working Day of a pharmaceutical Student Рабочий день студента фармацевтического факультета
- •Topical vocabulary
- •Introductory text Working Day of a pharmaceutical Student
- •Vocabulary exercises
- •Unit 5. Our English Lesson. Урок английского языка
- •Topical vocabulary
- •Introductory text Our English Lesson
- •Vocabulary exercises
- •Questionnaire
- •Vocabulary exercises
- •Are you a good student?
- •Theme II. What pharmacy is
- •Topical vocabulary Definition of the pharmacy
- •Vocabulary exercises
- •Community Pharmacy
- •Plural of nouns
- •Possessive’s
- •Опущение некоторых слов после существительных в притяжательном падеже
- •TexTs for written translation Clinical pharmacy
- •International Pharmaceutical Federation
- •Theme III. Pharmaceutical training in the united kingdom
- •Topical vocabulary
- •Introductory text The School of Pharmacy University of London
- •Vocabulary exercises
- •TexTs for reading Pharmaceutical Training in English-speaking countries
- •The Strategic Plan of the American College of Clinical Pharmacy
- •Grammar comparatives and superlatives
- •Irregular comparison
- •Neither….Nor
- •Theme IV. Development of pharmacy in the world
- •Topical vocabulary
- •Internet Pharmacy
- •The future of pharmacy
- •Pharmacy Practice in 2015
- •Introductory text The development of Pharmacy in the world
- •Vocabulary exercises
- •TexTs for written translation
- •Hospital pharmacy
- •Consultant pharmacy
- •Compounding pharmacy
- •Вопросительная форма
- •Написание некоторых глаголов с окончанием –s
- •Past simple
- •V erbs
- •Past Simple используется:
- •Наречия времени, с которым используется Past Simple
- •Написание глаголов с окончанием –ed:
- •Future simple Future Simple используется:
- •Наречия времени, с которыми используется Future Simple:
- •Спряжение глаголов в Future Simple
- •Shall используется:
- •Theme V. Parts of the body and organ systems
- •Topical vocabulary
- •Introductory text Parts of the Body
- •Vocabulary exercises
- •TexTs for written translation
- •Human musculoskeletal system
- •Human cardiovascular system
- •Funny reading
- •Infinitive without to (Examples: go, speak)
- •Infinitive with to (Examples: to go, to speak)
- •Modal verbs
- •Passive structure
- •Theme VI. In the chemical laboratory
- •Topical vocabulary
- •Introductory text
- •In the chemical Laboratory
- •Vocabulary exercises
- •Measurements
- •Text for written translation o utstanding Russian Chemist d.I. Mendeleev
- •Grammar present progressive Present Progressive используется:
- •Наречия времени, с которыми используется Present Progressive:
- •Спряжение глаголов в Present Progressive
- •Past progressive
- •Theme VII. Pharmaceutical chemistry
- •Topical vocabulary
- •Introductory text Pharmaceutical Chemistry
- •Vocabulary exercises
- •Texts for written translation Drug Discovery
- •Lead Optimization
- •Process chemistry and Development
- •Funny and useful reading
- •Grammar present perfect Present Perfect используется:
- •Наречия времени, с которыми используется Present Perfect:
- •Спряжение глаголов в Present Perfect:
- •Написание глаголов с окончанием -ed
- •Theme VIII. Medicinal plants
- •Topical vocabulary
- •Introductory text Medicinal Plants
- •Vocabulary exercises
- •TexTs for written translation Herbal Medicine
- •Preservation of Arnica Montana l.
- •Theme IX. Pharmacognosy
- •Topical vocabulary
- •Introductory text Pharmacognosy
- •Vocabulary exercises
- •TexTs for written translation Natural products chemistry
- •Loss of biodiversity
- •Theme X. At the chemist’s
- •Topical vocabulary
- •Introductory text At the Chemist’s
- •Vocabulary exercises
- •The Pharmacist
- •Chloraseptic
- •TexTs for written translation
- •At the Chemist’s
- •Tetracycline
- •Funny and useful reading
- •Women and Men
- •It’s a man’s world…
- •Theme XI. Technology of drugs
- •Topical vocabulary
- •Introductory text Technology Trends of Drug Delivery and Development
- •Stages in drug discovery and development
- •Vocabulary exercises
- •An overview of drug delivery technologies
- •TexTs for written translation Structure-Based Enhancement Techniques
- •Theme XII. Pharmacology
- •Topical vocabulary
- •Introductory text Pharmacology
- •Vocabulary exercises
- •Clinical pharmacology
- •TexTs for written translation Neuropharmacology
- •Psychopharmacology
- •Contents
Наречия времени, с которыми используется Future Simple:
Tomorrow tonight next week /month in two /three days the day after tomorrow soon in a week / month in 2067
Спряжение глаголов в Future Simple
Утвердительная форма S + will +V
I will play He will play We will play
Отрицательная форма S + will not + V
I will not play He will not play We will not play
Вопросительная форма Will + S + V
Will I play? Will he play? Will we play?
Shall используется:
Только с местоимениями I / we в утвердительных и вопросительных предложениях или, когда мы просим совет:
Shall we go to the cinema tonight?
Exercise 29. Match the sentences on the left with the tenses on the right.
1. There’ll be ‘Moon cities’ in the year 3000. 2. I have practical classes every day. 3. They will have two hours of Chemistry tomorrow. 4. They have examinations in summer. 5. I saw her yesterday. 6. His house is far from the university. 7. She lives in New York. 8. I was present at the meeting of our group. |
a) Present Simple b) Past Simple c) Future Simple
|
Theme V. Parts of the body and organ systems

Topical vocabulary
appendage - придаток
adulthood – зрелый возраст
average – средний
average height – средний рост
bumps – шишка, опухоль, выпуклость
cells - клетки
circulate - циркулировать
circulatory - циркулирующий
entire – полный, совершенный
eventually – в конечном счете, в конце концов
influence – оказывать влияние, влиять
integumentary - покровный
layer – слой, пласт, наслоение
pump – качать, пульсировать
sebaceous – сальный
sebaceous glands – сальные железы
size – размер, величина, объем
sternum - грудина
tendon - сухожилие
tissue - ткань
torso – туловище, торс
vary – меняться, изменять, разнообразить
ventricle – желудочек (сердца, мозга)
vertebral – позвоночный
vertebral column – позвоночный столб, спинной хребет
Introductory text Parts of the Body
The human body is the entire structure of a human organism, and consists of a head, neck, torso, two arms and two legs. By the time the human reaches adulthood, the body consists of close to 100 trillion cells, the basic unit of life. These cells are organised biologically to eventually form the whole body.

Size. The average height of an adult male human (in developed countries) is about 1.7–1.8 m tall and the adult female about 1.6–1.7 m tall. This size is firstly determined by genes and secondly by diet. Body type and body composition are influenced by postnatal factors such as diet and exercises.
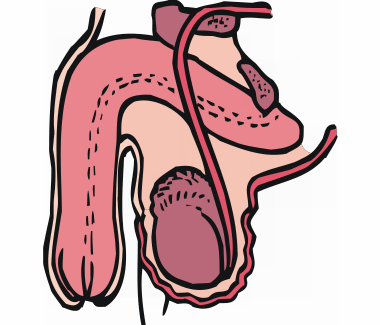
Systems. The organ systems of the body include the musculoskeletal system, cardiovascular system, digestive system, endocrine system, integumentary system, urinary system, lymphatic system, immune system, respiratory system, nervous system and reproductive system.
The cardiovascular system. It comprises the heart, veins, arteries and capillaries. The primary function of the heart is to circulate the blood, and through the blood, oxygen and vital minerals are transferred to the tissues and organs that comprise the body. The left side of the main organ (left ventricle and left atrium) is responsible for pumping blood to all parts of the body, while the right side (right ventricle and right atrium) pumps only to the lungs for re-oxygenation of the blood. The heart itself is divided into three layers called the endocardium, myocardium and epicardium, which vary in thickness and function.
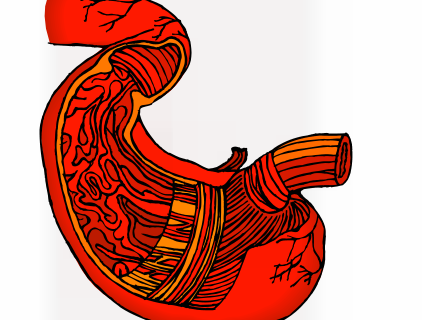
The digestive system. It provides the body's means of processing food and transforming nutrients into energy. The digestive system consists of the buccal cavity, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine ending in the rectum and anus. These parts together are called the alimentary canal (digestive tract).
The integumentary system. It is the largest organ system in the human body, and is responsible for protecting the body from most physical and environmental factors. The largest organ in the body is the skin. The integument also includes appendages, primarily the sweat and sebaceous glands, hair, nails and arrectores pili (tiny muscles at the root of each hair that cause goose bumps).
The lymphatic system. The main function of it is to extract, transport and metabolise lymph, the fluid found in between cells. The lymphatic system is very similar to the circulatory system in terms of both its structure and its most basic function (to carry a body fluid).
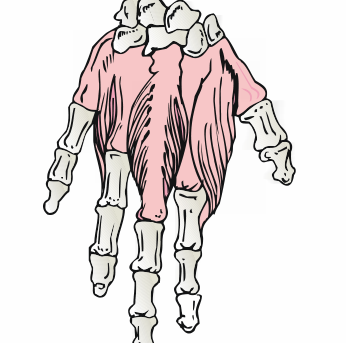
The human musculoskeletal system. It consists of the human skeleton, made by bones attached to other bones with joints, and skeletal muscle attached to the skeleton by tendons.
Bones. An adult human has approximately 206 distinct bones: Spine and vertebral column (26), Cranium (8), Face (14), Hyoid bone, sternum and ribs (26), Upper extremities (70), Lower extremities (62).
Exercise 1. Name the parts of the human body.
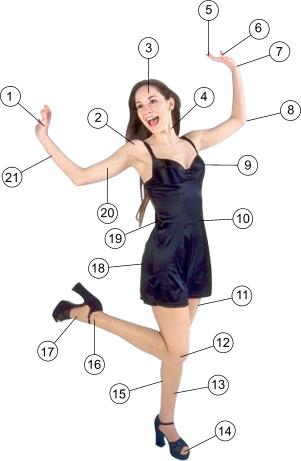
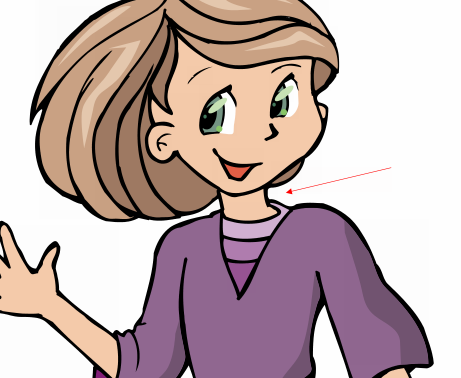
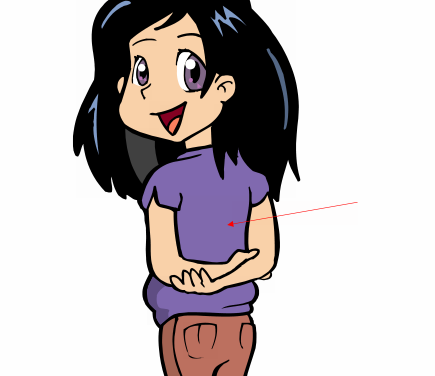
Exercise 2. Name the pictures about “Parts of the body”.
1. 2.
2. 3.
3.
4. 5.
5. 6.
6.
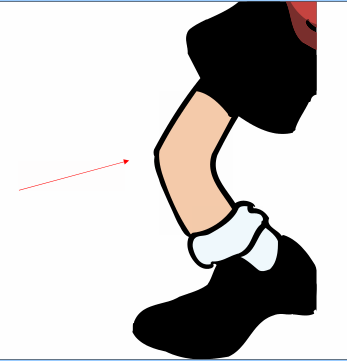
7. 8.
8.
 9.
9.
10. 11.
11. 12.
12.
13.
 14.
14.
Exercise 3. Name the pictures about “Organ Systems”.
1. 2.
2. 3.
3.

4. 5.
5.
 6.
6.

7.
 8.
8.
 9.
9.

10.
 11.
11.
 12.
12.
13. 14.
14.
 15.
15.

16.
