
- •Institute of ecological safety
- •Methods of cytogenetics
- •1.Introduction
- •2. History
- •3. Caryotyping by differential staining
- •4. Standard cytogenetic studies (scs)
- •5. Fish метод (Fluorescence in situ Hybridization)
- •5.1 Principle of the method of fluorescence in situ hybridization is the following:
- •5.2 Key benefits of fish-analysis:
- •6.Other methods of cytogenetics researchers:
4. Standard cytogenetic studies (scs)
Using SDH analyze chromosome metaphase plates treated in this way, so that you can get the characteristic striations of chromosomes, which allows to identify them (Fig. 1), and to identify the individual adjustment of chromosomal segments, called loci.
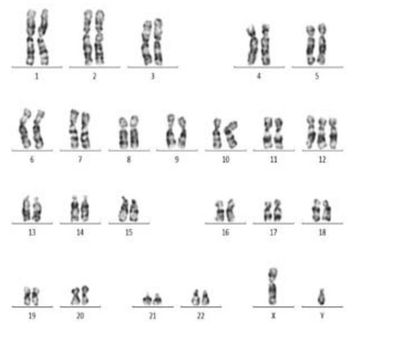
Fig. 1. Standard cytogenetic studies (47, XY, +12).
For many types of Leukemia known recurrent marker chromosome abnormalities: translocations, deletions, inversions, as well as numerical abnormalities (monosomes, trisomes). Detection of such marker chromosomes allows the unambiguous diagnosis and control the dynamics of the growth of the tumor mass. In addition, the tumor cells in patients with hematological malignancies often have additional chromosomal breakage, this phenomenon is called clonal evolution of the tumor. Clonal evolution of the tumor, which is found by SCI is an important prognostic factor. The ability to identify multiple chromosome defects with SCI is an important advantage of this method. However, the sensitivity cms less than 5%, so with a significant reduction in tumor mass on a background therapy further monitoring should be implemented with the help of molecular techniques, as well as by FISH.
5. Fish метод (Fluorescence in situ Hybridization)
FISH is based on the use of long DNA probes complementary to the same chromosomal locus, which occur in hematologic diseases adjustment. Modern FISH probes are in a group consisting of fluorescent, allowing the probes to visualize the attachment point with the corresponding loci, not only in the chromosomes of the metaphase plate, but also when they are in interphase nuclei (Fig. 2).

Fig. 2. FISH LSI C-MYC.
Therefore, the sensitivity of FISH is an order of magnitude higher than that of SCI, but still inferior to 1-2 times the sensitivity of molecular techniques.
FISH-analysis method to objectively identify individual chromosomes and their individual sites on metaphase plates (chromosomes in a state of maximum condensation and visualization) or interphase nuclei (decondensation chromosome, with no clear morphological structure) based on the characteristics of their molecular and genetic structure. The object of investigation in this case are the specific features of the nucleotide composition of the chromosome or a single site.
FISH-classical method of analysis is based on the hybridization of a known Nucleotide composition of DNA probe with a section of the chromosome test and subsequent detection by hybridization on the label - the fluorescent signals in the expected location. FISH-analysis method has become a necessary analytical procedure in cytogenetics and has become popular today in pre-and postnatal diagnosis, monitoring zygotes after in vitro fertilization, the procedure for pre-implantation genetic diagnosis (PGD) in the selection of embryos with normal karyotype, etc. .
5.1 Principle of the method of fluorescence in situ hybridization is the following:
1. Prepare a single-stranded DNA region of chromosome or part thereof, which is to be investigated. This site has added labels - biotin and dioksigenin (labeled DNA fragment is called DNA-probe)
2. On the drug used for microscopic examination in situ, conducted alkaline treatment of DNA, under the influence of alkali DNA "unwinds" in two threads.
3. Added to the threads of DNA probe. Because DNA strands complementary (one nucleotide pair joined another couple well-defined), the probe connected to the corresponding part of the chromosome. This restores the double helix (renaturation of DNA).
4. The resulting product is treated with chemical compounds that have a chemical affinity to biotin (this is a matter for biotin streptovidin) or digoxigenin (antidioksigenic antibody).
5. The resulting complex is attached to more fluorescent dyes (red - or rhodamine green - isothiocyanate).
6. Color paint allows the analysis of chromosomes with fluorescent microscope quite clearly against the unpainted chromosomes. Number of colors can be increased by other colors, if there is such a need (three color fluorescent hybridization, etc.).
