

Governments should make reductions of public debt and fiscal deficits their immediate priority.
Report on Debate
Debate
2 – Group B Araik
Badalyan Ablay
Dosmaganbetov Anna
Hobisch Elena
Krugliakova
March,
6th 2013
1. Introduction
Fiscal austerity is a hotly debated topic in many countries. While some economists believe that cutting governmental expenditure is the only way out of the crisis, others think that decreasing spending while the economy is weak will just worsen the crisis. In this report, the effects of fiscal consolidation will be analysed with the help of the IS-LM-FX model, in order to highlight what outcomes governments can expect following a cut in fiscal spending.
2. Methods of fiscal consolidation
If we are speaking about the debt, we should mention that there are two generally used ways/practices to decrease the debt: either to decrease governmental expenditures, or to increase the taxes. Both methods can be very effective, but there are obvious differences. Increase in taxes can be implemented to some certain extent and it can't be done «each time». Anyway, the influence of both measures on the macroeconomic data is practically the same, so we have discovered all possible negative effect on the economy, which derive when the fiscal austerity policy is implemented.
3. Effects of fiscal consolidation
Our analysis of fiscal austerity is based on IS-LM model implemented for two cases separately: for economies with Flexible and Fixed Exchange rates. We highlighted the consequences only of decrease in governmental expenditures, skipping the effect of changes in tax regime. It is a deliberate decision in order to provide a clear logic of the model not overloaded with complexity. Also we concentrated only on the short-term as the fiscal austerity in the long term could be reasonable and beneficial under certain conditions.
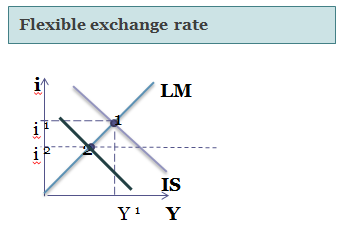
Assuming that governmental expenditures decreases in order to decrease fiscal deficit, an aggregated demand in the country would also fall (Keynesian cross model could be implied). Consequently, these changes cause the fall of the goods market and shit of market equilibrium state, because of excessive supply.
3.1 Interest Rate
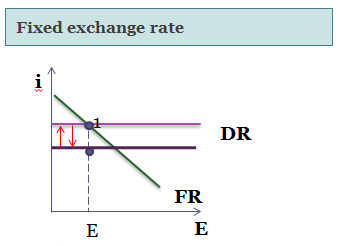
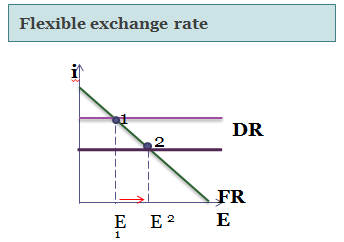
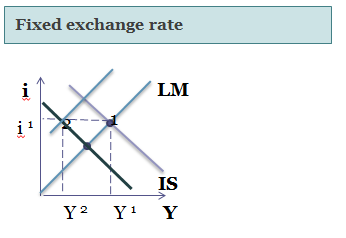
Decrease in governmental expenditures has, off course, generally negative effect on economy. But we can’t skip the benefits of the decrease in debt. And in this sense the most important merit of debt reduction is decrease in interest rate. (Shift of the IS curve in the IS-LM model leads not only to decrease in GDP, but also to the lower interest rate). Then there is change in the interest rates in the flexible exchange rate models, as IS curve shifts to the left the interest rates goes down. The result in model with fixed exchange rate is different. Because currency is pegged to foreign one, there shouldn’t be any change in domestic return, interest rate remain the same. Monetary policy of the Central Bank (decrease in money supply) leads in this case to the shift of LM curve to the left, thus keeping the equilibrium of Domestic return with Foreign. Because flexible exchange rate is more common for economics, we will speak about them.
Low interest rate has significant impact on the investments in the country. Governmental investments are cut, but private investors and investors from non-governmental sector have intense to invest under the low interest rate.
Reductions in interest rates usually support output during episodes of fiscal consolidation. Central banks offset some of the contractionary pressures by cutting policy interest rates and longer-term rates also typically decline, cushioning the impact on consumption and investment. For each 1 percent of GDP of fiscal consolidation, interest rates usually fall by about 20 basis points after two years. The model simulations also imply that, if interest rates are near zero, the effects of fiscal consolidation are more costly in terms of lost output.
And also we should remember the simple equation: more investment now – less savings now – less investment in the future (there won’t be possibility to invest if all available funds are already used, so, if huge investments are done now, it will exhaust overall financial resources).
