
- •Institute of higher education
- •Abstract
- •Contents
- •List of the conditional indication and reduction
- •Introduction
- •1 The calculation of baSic electrical quantities
- •2 The calculation of base scales of transformer
- •3 Choice of the designing and calculation of windings
- •4 Definitions of the characteristics of short circuit
- •Figure 4.2 – Distribution of compressing forces for our case
- •5 Calculation of transformer magnetis system
- •6 Thermal computatuion of the transformer
- •Figure 6.2 – Pipes radiator with direct pipes
- •7 Definition of weight of constructional materials and oil of the transformer
- •8 The summary data of account of the transformer
- •Conclusion
- •Tpansformer
- •The list of the literature
- •Appendix а The list of the remarks to course work
6 Thermal computatuion of the transformer
6.1 Thermal computation of the windings
6.1.1 Internal difference of temperature in LV winding for rectangular winding from aluminum wire:
λiz = 0.17 Wt/(m·оС) – thermal conductivity of insulation (by tabl. 9.1, р. 424 [1]);
δ = δiz/2 = 0.0005/2 = 0.00025 – thickness of insulation on one side, m.
Θ01=q1 . δ/ λiz
Θ01 = 972.314. 0.00025/0.17 = 1.43 оС
6.1.2 Difference of temperature on surface of LV winding:
ΘО.М1
= 0.285·![]() = 0.285·972.3140.6
= 17.682 оС.
= 0.285·972.3140.6
= 17.682 оС.
6.1.3 Average excess of temperature of LV winding under temperature of oil:
ΘМ.СР1 = ΘO1 + ΘО.М1 = 1.43 + 17.682 = 19.112 оС.
6.1.4 Internal difference of temperature in HV winding (for rectangular winding from aluminum lead):
ΘО2
=
![]() ,
,
Where р
=
 ,
,
К´Р = 2.71 – for aluminum lead;
λСР
=
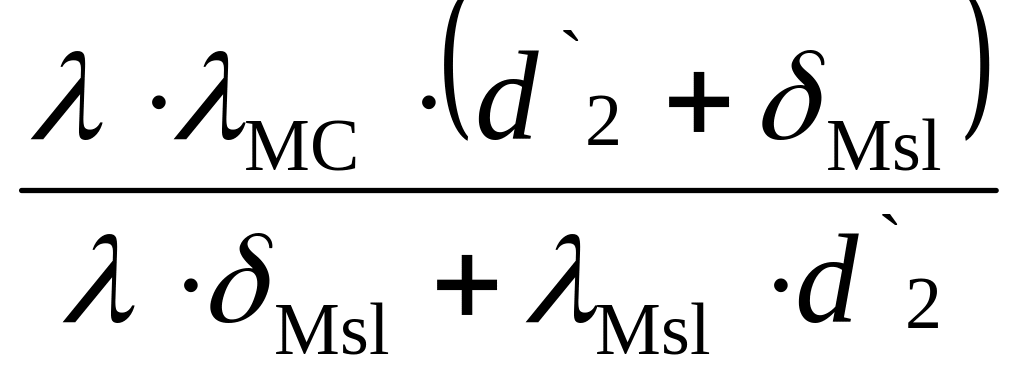 ,
,
Where λ
=
 =
=
 = 0.629
= 0.629
δМsl = 0.48 mm – thickness of interlayer isolation.
λСР
=
![]() = 0.484
= 0.484
р =
![]() =70890.704 Wt/m3.
=70890.704 Wt/m3.
ΘО2
=
![]() = 8.207 оС.
= 8.207 оС.
6.1.5 Average difference of temperature of HV winding under temperature of oil:
ΘОМ2
= 0.285·![]() = 0.285·589.8490.6
= 13.101 оС.
= 0.285·589.8490.6
= 13.101 оС.
6.1.6 Difference of temperature under surface of HV winding:
ΘОМСР2 = ΘО2 + ΘОМ2 = 8.207 + 13.101 = 21.308 оС.
6.1.7 Allowable excess of temperature of oil above air:
ΘМv = 65 - ΘОМСР1 = 65 –19.186 = 45.814 оС.
6.1.8 Allowable excess of temperature tank’s wall above air:
Θbv = ΘМv – ΘМδ = 45.814 – 5 = 40.814 оС,
Where ΘМδ = 5 оС.
6.1.9 Temperature of oil upper layers:
ΘМbv = 1.2· Θbv = 1.2·40.814 = 48.977 оС < 55 оС.
Figure 6.1 – Basic sizes of tank
6 .2
Thermal calculation of tank design of
the transformer is chosen by taking into account power of the
transformer (table. 9.4, р. 429 [1], I choose a tank with hanging
radiators with oil cooling of windings. Definition of insulation
intervals from lead-ins of HV and LV windings and wall of the tank is
made on figure 6.1.
.2
Thermal calculation of tank design of
the transformer is chosen by taking into account power of the
transformer (table. 9.4, р. 429 [1], I choose a tank with hanging
radiators with oil cooling of windings. Definition of insulation
intervals from lead-ins of HV and LV windings and wall of the tank is
made on figure 6.1.
S1 = 22 mm – insulation interval from lead-in of HV winding to HV winding (table. 4.11, р. 199 [1]).
S2 = S1 =22 mm– insulation interval from lead-in of HV winding to wall of the tank (tabl. 4.11, р. 199 [1]).
d1 = 20 mm – diameter of insulation S = 250 kVA < 10000 kVA.
S3 = 25 mm – insulation interval from lead-in of LV winding to LV winding (tabl. 4.12, р. 201 [1]). D´´2=323
S4 = 22 mm – insulation interval from lead-in of LV winding to wall of the tank (tabl. 4.11, р. 199 [1]).
d2 = 20 mm – diameter of isolation lead-in of HV winding is equal d1.
6.2.1 Minimal width of tank:
B = D´´2 + (S1 + S2 + d1 + S3 + S4 + d2)·10-3
B = 0.283 + (22 + 22 + 20 + 25 + 24 + 20)·10-3 = 0.414 m.
6.2.2 Minimal length of a tank:
А = 2·С + D´´2 + 2·S5·10-3 = 2·0.293 + 0.283 + 2·67·10-3 = 1.174m,
where S5 = S3 + S4 + d2 = 67 mm – interval from external surface of winding to wall of the tank ( fig. 6.1).
6.2.3 Height of an active part of the transformer:
H`а,p = Lleg + 2·hyoke + n·10-3 = 0.545 + 2·0.155 + 40·10-3 = 0.975 m,
where n = 40 mm – thickness of a lining under bottom yoke.
6.2.4 Total depth of a tank:
Нyokee = 300·10-3 m (tabl.9.5, p.431[1] )
Нb = Нa,p. + Нyokee. = 0.895 + 300·10-3 = 0.895 m.
The tank with hanging radiators.
6.2.5 At the tabl. 9.9, р. 442 [1] is chosen tube radiator with two lines of direct pipes with interval between axes of flanges AP = 900 mm, with pipe’s surface ПТР = 2.135 m2 and surface of collectors ПКК = 0.34м2. This radiator is shown on fig. 6.2.
Hanging radiators with direct pipes by natural movement of cooling air use in large diapason of transformer power – from 100 to 6300 kVA Direct pipes are welded by the ends in lower and upper collectors of radiator (fig. 6.2). Sizes В and С of radiator with two lines of pipes is equal 505 and 253 mm.
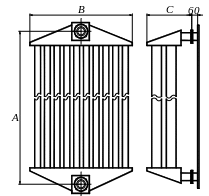 The
depth of a tank for installation of these radiators should be:
The
depth of a tank for installation of these radiators should be:
