
- •Exercises
- •1. Learn the following active words and use them in the sentences of your own
- •3. Look through the text and write out the English equivalents of the following words and word combinations. Use them in the sentences of your own.
- •7. Give short answers to the following questions:
- •9. Translate the following sentences:
- •Exercises
- •1. Learn the following active words and use them in the sentences of your own.
- •2. Translate the following chains of words. Define what parts of speech they are
- •3. Look through the text and find the English equivalents to the following words and word combinations; use tem in the sentences of your own.
- •5. Translate the following sentences paying attention to the participle:
- •10. Translate the following sentences:
- •11. State the power change that takes place in each of the following devices.
- •12. Retell the text.
- •Exercises
- •1. Learn the following active words and expressions. Use them in the sentences of your own.
- •4. Answer the following questions:
- •5. Work in pairs. Put questions to your partner and he (she) will answer them.
- •8. Translate the following sentences paying attention to the words need and turn:
- •9. Put all possible questions to the following sentences:
- •10. Define the following words according to the model given below.
- •Exercises
- •Learn the following active words and use them in the sentences of your own:
- •2. Translate the following sentences, paying attention to the gerund:
- •7. Translate the following sentences paying attention to the words in bold type:
- •8. Put 5 questions to the text beginning with what.
- •9. Speak on the story told by the early Scandinavians.
- •Exercises
- •1. Learn the following active words and use them in the sentences of your own.
- •2. Look through the text and find the English equivalents of the following words and word combinations, use them in the sentences of your own:
- •5. Find the gerund in the text, define its function.
- •7. Put questions to the words in bold type.
- •8. Translate the following sentences paying attention to both, both...And:
- •9. Fill in the blanks with prepositions:
- •10. Translate into Russian:
- •11. Form five sentences combining suitable parts of the sentence given in Columns I and II:
- •12. Describe Franklin's kite experiment.
- •13. Give a short summary of the text.
- •Exercises
- •1. Learn the following active words and Expressions
- •3. Look through the text and find the English equivalents of the following words and word combinations, use them in the sentences of your own:
- •7. Make up a story of Franklin's kite experiment using the following sentences and sentences of your own (our sentences are given in a disorderly way):
- •10. Use the following expressions in sentences of your own:
- •11. Speak on magnetism.
- •Exercises
- •8. For the names of the countries given in Column I find the names of the nations given in Column II:
- •10. Speak on:
- •11. Make an outline of the text.
- •12. Retell the text.
- •Exercises
- •1. Learn the following active words and use them in the sentences of your own:
- •2. Define the functions of the participle and the gerund in the text.
- •4. Answer the following questions:
- •5. Fill in the blanks with suitable words and word combinations given below:
- •6. For the verbs in (a) find suitable nouns in (b).
- •7. For the nouns in (a) find suitable attributes in (b):
- •8. (A) Translate the following word combinations:
- •11. The following statements are not true to the fact. Correct them:
- •12. Retell the text.
- •Exercises
- •1. Learn the following active words and use them in the sentences of your own:
- •2. Translate the following word chains into Russian, define what part of speech the words are.
- •4 Translate into Russian:
- •8. Form 10 sentences using the following words:
- •10. Translate the following sentences paying special attention to the words in bold type:
- •11. Retell the text.
- •12. (A) Fill in the blanks with prepositions, if necessary; (b) retell the text:
- •Exercises
- •1. Learn the following active words and use them in the sentences of your own:
- •2. Look through the text and find the English equivalents to the following words and word combinations. Use them in your own situations.
- •3. Write out antonyms to the following words:
- •4. Translate the following sentences paying attention to the infinitive
- •5. Translate the following sentences paying special attention to the words in bold type:
- •6. Translate the following sentences paying special attention to the infinitive:
- •7. Fill in the blanks with the words one or for:
- •8. Write out from the text all the sentences where the infinitive is used, and define its function.
- •Exercises
- •1. Learn the following active words and use them in the sentences of your own:
- •3. According to the models given below form sentences combining suitable parts of the sentence given in Columns I, II, III, IV,
- •5. Work in pairs, ask your fellow-students the following questions:
- •6. Form six sentences combining suitable parts of the sentence given in Columns I and II:
- •7. Explain why:
- •8. Define the meaning of the following words:
- •Exercises
- •1. Learn the following active words and use them in the sentences of your own:
- •2. Translate the following sentences using the infinitive constructions:
- •Find in (b) synonyms to the words in (a):
- •5. Translate the following questions into English and answer them:
- •7. Translate the following sentences paying special attention to the words in bold type:
- •8. What are the different meanings of the following words?
- •10. Speak on the work of the following scientists using the words given below:
- •Exercises
- •2. Answer the following questions:
- •4. Compare:
- •6. Translate the following sentences paying special attention to the words in bold type:
- •8. Fill in the blanks with suitable prepositions if necessary and make up sentences with the following infinitives:
- •9. Translate the following sentences:
- •10. Speak on:
- •Exercises
- •1.Learn the following active words:
- •Conditional Sentences
- •2. Translate the following sentences:
- •3. Translate the following sentences paying special attention to the word provided:
- •5. Complete the following sentences:
- •6. Fill in the blanks with among or between:
- •8. Put all possible questions to the following sentences:
- •10. Form new words of the same root, define what parts of speech they are:
- •11. Speak on:
- •Exercises
- •1.Learn the following active words:
- •2. Look through the text and find the examples illustrating modality.
- •3. Answer the following questions:
- •4. Translate the following phrases into English using the word combinations given below:
- •5. Define the meaning of the prefixes in the following words and translate them into Russian:
- •6. Translate the following sentences:
- •7. Work in pairs. Put questions to your fellow-student and let him answer them:
- •8. Translate the following sentences paying special attention to the words in bold type:
- •10. Complete the following sentences:
- •11. Speak on the heating effect of an electric current.
- •12. Translate the following text.
- •Exercises
- •1. Learn the following active words:
- •2. Translate the following sentences into Russian:
- •4. Fill in the blanks with where, which, when, who, that:
- •5. Translate the following sentences paying special attention to the words in bold type:
- •6. Fill in the blanks with either should or would:
- •Exercises
- •12. Look at Fig. 11, name a, b, c, d, e and describe the figure.
- •Exercises
- •1. Learn the following active words:
- •2. Translate the following sentences paying special attention to the impersonal construction:
- •3. Answer the following questions:
- •4. Complete the following sentences:
- •5. Define the meaning of the following words:
- •6. Choose the right term and explain the statement:
- •7. Translate the following text:
- •8. Look at Fig. 12 and speak on power generation in Russia.
- •9. Retell the text.
- •Exercises
- •1. Learn the following active words:
- •Exercises
- •1. Learn the following active words:
- •2. Translate the following sentences:
- •3. Define the function of the words in bold type:
- •4. Translate the following sentences:
- •6. Define the function of the words one and bat:
- •7. Form sentences using the following word combinations.
- •8. Fill in the blanks with the following expressions:
- •9. Complete the following sentences:
- •11. Speak on:
- •12. Translate the following text:
- •Exercises
- •1.Learn the following active words:
- •2. Translate the following sentences paying attention to the participle:
- •3. Answer the following questions:
- •5. Make up six sentences using the following nouns qualified by adjectives.
- •6. Translate the following text without consulting a dictionary and retell the text.
- •If There Were No Electricity
- •7. Describe the following:
- •9. Form statements which are not true to the fact. Ask your fellow-students to correct them.
- •Exercises
- •1. Learn the following active words:
- •3. Define the function of the word do in the following sentences:
- •4. Translate the following questions and answer them:
- •Exercises
- •1 Learn the following active words and expressions and use them in the sentences of your own.
- •8. Answer the following questions:
- •10. Translate the following word combinations and use them in the sentences of your own:
- •Exercises
- •1. Learn the following active words:
- •2. (A) Give headings to each paragraph of the text.
- •3. Translate the following sentences:
- •4. Define the non-finite forms of the verb met in the text.
- •5. Put 10 questions to the text.
- •6. Translate the following sentences:
- •7. Speak on:
- •Exercises
7. Translate the following text:
Storage Batteries
Storage batteries are made up of a number of rechargeable cells, often called secondary cells to distinguish them from primary cells. Secondary cells are made of several different materials, but all work on the principle of reversible chemical action between two dissimilar electrodes (plates) impressed in an active solution (electrolyte). Particular battery designs are, of course, much more complicated and have several plates in parallel, closely packed with insulating separators.
8. Look at Fig. 12 and speak on power generation in Russia.
9. Retell the text.
LESSON NINETEEN
THE STRUCTURE OF TRANSFORMERS
The transformer is a device for changing the electric current from one voltage to another. As a matter of fact, it is used for increasing or decreasing voltage. A simple transformer is a kind of induction coil. It is well known that in its usual form it has no moving parts. On the whole, it requires very little maintenance, provided it is not misused and is not damaged by lightning.
We may say that the principal parts of a transformer are two windings, that is coils, and an iron core. They call the coil which is supplied with current "the primary winding," or just "primary" for short. The winding from which they take the current is spoken about as the "secondary winding" or "secondary", for short. It is not new to you that the former is connected to the source of supply, the latter being connected to the load.
The primary alternating current produces an alternating magnetic flux in the iron core, and this alternating magnetic flux passes through the turns of the secondary winding. According to well-known electro-magnetic laws, this flux produces an alternating e. m. f., or voltage, in the secondary winding. In spite of the fact that there is no electrical connection between the two circuits - the primary and the secondary - the application of a voltage to one is known to produce a voltage at the terminal of the other.
When the number of turns of wire on the secondary is the same as the number on the primary, the secondary voltage is the same as the primary, and we get what is called a "one-to-one" transformer. In case, however, the number of turns on the secondary winding is greater than those on the primary,
the output voltage is larger than the input voltage and the transformer is called a step-up transformer. On the other hand, the secondary turns being fewer in number than the primary, the transformer is known as a step-down transformer. One should add in this connection that to "step up" means to increase the voltage. On the contrary, to "step down" means "to reduce".
A transformer operates equally well to increase the voltage and to reduce it. By the way, the above process needs a negligible quantity of power. It is important to point out that the device-under consideration will not work on d. c, but it is rather often employed in direct-current circuits.
Inefficiency in a transformer is caused mainly by heat losses due not only to current flowing in the coils, but also to unwanted current induced in the core of the transformer.
Currents induced in the core are generally called "eddy currents." The flow of eddy currents is stopped in its progress and the efficiency of the transformer is increased by constructing the transformer core of flat sheets of soft iron,
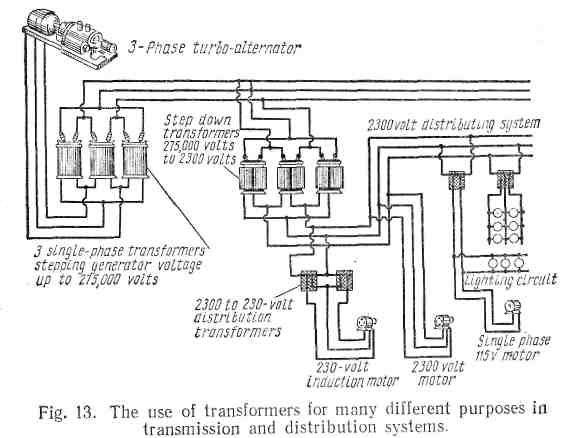
In Fig. 13 it is seen how transformers are used in stepping up the voltages for distribution or transmission over long distances and then in stepping these voltages down, where «4hey are to be used. In this figure, one may see three large step-up transformers which are used to increase the potential to 275,000 volts for transmission over long-distance transmission lines. At the consumer's end of the line, in some distant locality, three step-down transformers are made use of to reduce that value (i. е., 275,000 volts) to 2,300 volts. Local transformers, in their turn, are expected to decrease the 2,300 volts to lower voltages,
suitable for use with small motors arid lamps. One could have some other transformers in the system, such as those to be employed for operating door bells or powering radio sets and television sets, for example. They lower the voltage even further. On the whole all radio sets and all television sets are known to use two or more kinds of transformers. These familiar examples of electronic equipment could not work without transformers. The facts you have been given above illustrate the wide use of transformers and their great importance.
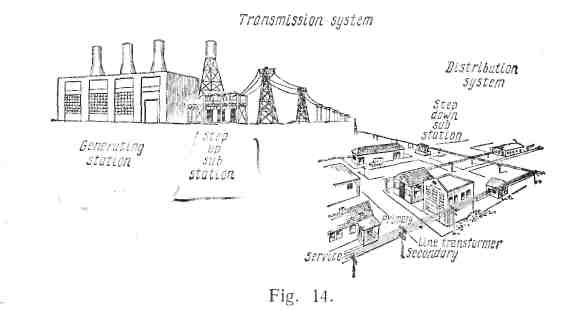
Another alternating-current system of transmission and distribution is shown in Fig. 14. You are asked to follow the whole process,, that is, to describe it from beginning to end.
