
- •Exercises
- •1. Learn the following active words and use them in the sentences of your own
- •3. Look through the text and write out the English equivalents of the following words and word combinations. Use them in the sentences of your own.
- •7. Give short answers to the following questions:
- •9. Translate the following sentences:
- •Exercises
- •1. Learn the following active words and use them in the sentences of your own.
- •2. Translate the following chains of words. Define what parts of speech they are
- •3. Look through the text and find the English equivalents to the following words and word combinations; use tem in the sentences of your own.
- •5. Translate the following sentences paying attention to the participle:
- •10. Translate the following sentences:
- •11. State the power change that takes place in each of the following devices.
- •12. Retell the text.
- •Exercises
- •1. Learn the following active words and expressions. Use them in the sentences of your own.
- •4. Answer the following questions:
- •5. Work in pairs. Put questions to your partner and he (she) will answer them.
- •8. Translate the following sentences paying attention to the words need and turn:
- •9. Put all possible questions to the following sentences:
- •10. Define the following words according to the model given below.
- •Exercises
- •Learn the following active words and use them in the sentences of your own:
- •2. Translate the following sentences, paying attention to the gerund:
- •7. Translate the following sentences paying attention to the words in bold type:
- •8. Put 5 questions to the text beginning with what.
- •9. Speak on the story told by the early Scandinavians.
- •Exercises
- •1. Learn the following active words and use them in the sentences of your own.
- •2. Look through the text and find the English equivalents of the following words and word combinations, use them in the sentences of your own:
- •5. Find the gerund in the text, define its function.
- •7. Put questions to the words in bold type.
- •8. Translate the following sentences paying attention to both, both...And:
- •9. Fill in the blanks with prepositions:
- •10. Translate into Russian:
- •11. Form five sentences combining suitable parts of the sentence given in Columns I and II:
- •12. Describe Franklin's kite experiment.
- •13. Give a short summary of the text.
- •Exercises
- •1. Learn the following active words and Expressions
- •3. Look through the text and find the English equivalents of the following words and word combinations, use them in the sentences of your own:
- •7. Make up a story of Franklin's kite experiment using the following sentences and sentences of your own (our sentences are given in a disorderly way):
- •10. Use the following expressions in sentences of your own:
- •11. Speak on magnetism.
- •Exercises
- •8. For the names of the countries given in Column I find the names of the nations given in Column II:
- •10. Speak on:
- •11. Make an outline of the text.
- •12. Retell the text.
- •Exercises
- •1. Learn the following active words and use them in the sentences of your own:
- •2. Define the functions of the participle and the gerund in the text.
- •4. Answer the following questions:
- •5. Fill in the blanks with suitable words and word combinations given below:
- •6. For the verbs in (a) find suitable nouns in (b).
- •7. For the nouns in (a) find suitable attributes in (b):
- •8. (A) Translate the following word combinations:
- •11. The following statements are not true to the fact. Correct them:
- •12. Retell the text.
- •Exercises
- •1. Learn the following active words and use them in the sentences of your own:
- •2. Translate the following word chains into Russian, define what part of speech the words are.
- •4 Translate into Russian:
- •8. Form 10 sentences using the following words:
- •10. Translate the following sentences paying special attention to the words in bold type:
- •11. Retell the text.
- •12. (A) Fill in the blanks with prepositions, if necessary; (b) retell the text:
- •Exercises
- •1. Learn the following active words and use them in the sentences of your own:
- •2. Look through the text and find the English equivalents to the following words and word combinations. Use them in your own situations.
- •3. Write out antonyms to the following words:
- •4. Translate the following sentences paying attention to the infinitive
- •5. Translate the following sentences paying special attention to the words in bold type:
- •6. Translate the following sentences paying special attention to the infinitive:
- •7. Fill in the blanks with the words one or for:
- •8. Write out from the text all the sentences where the infinitive is used, and define its function.
- •Exercises
- •1. Learn the following active words and use them in the sentences of your own:
- •3. According to the models given below form sentences combining suitable parts of the sentence given in Columns I, II, III, IV,
- •5. Work in pairs, ask your fellow-students the following questions:
- •6. Form six sentences combining suitable parts of the sentence given in Columns I and II:
- •7. Explain why:
- •8. Define the meaning of the following words:
- •Exercises
- •1. Learn the following active words and use them in the sentences of your own:
- •2. Translate the following sentences using the infinitive constructions:
- •Find in (b) synonyms to the words in (a):
- •5. Translate the following questions into English and answer them:
- •7. Translate the following sentences paying special attention to the words in bold type:
- •8. What are the different meanings of the following words?
- •10. Speak on the work of the following scientists using the words given below:
- •Exercises
- •2. Answer the following questions:
- •4. Compare:
- •6. Translate the following sentences paying special attention to the words in bold type:
- •8. Fill in the blanks with suitable prepositions if necessary and make up sentences with the following infinitives:
- •9. Translate the following sentences:
- •10. Speak on:
- •Exercises
- •1.Learn the following active words:
- •Conditional Sentences
- •2. Translate the following sentences:
- •3. Translate the following sentences paying special attention to the word provided:
- •5. Complete the following sentences:
- •6. Fill in the blanks with among or between:
- •8. Put all possible questions to the following sentences:
- •10. Form new words of the same root, define what parts of speech they are:
- •11. Speak on:
- •Exercises
- •1.Learn the following active words:
- •2. Look through the text and find the examples illustrating modality.
- •3. Answer the following questions:
- •4. Translate the following phrases into English using the word combinations given below:
- •5. Define the meaning of the prefixes in the following words and translate them into Russian:
- •6. Translate the following sentences:
- •7. Work in pairs. Put questions to your fellow-student and let him answer them:
- •8. Translate the following sentences paying special attention to the words in bold type:
- •10. Complete the following sentences:
- •11. Speak on the heating effect of an electric current.
- •12. Translate the following text.
- •Exercises
- •1. Learn the following active words:
- •2. Translate the following sentences into Russian:
- •4. Fill in the blanks with where, which, when, who, that:
- •5. Translate the following sentences paying special attention to the words in bold type:
- •6. Fill in the blanks with either should or would:
- •Exercises
- •12. Look at Fig. 11, name a, b, c, d, e and describe the figure.
- •Exercises
- •1. Learn the following active words:
- •2. Translate the following sentences paying special attention to the impersonal construction:
- •3. Answer the following questions:
- •4. Complete the following sentences:
- •5. Define the meaning of the following words:
- •6. Choose the right term and explain the statement:
- •7. Translate the following text:
- •8. Look at Fig. 12 and speak on power generation in Russia.
- •9. Retell the text.
- •Exercises
- •1. Learn the following active words:
- •Exercises
- •1. Learn the following active words:
- •2. Translate the following sentences:
- •3. Define the function of the words in bold type:
- •4. Translate the following sentences:
- •6. Define the function of the words one and bat:
- •7. Form sentences using the following word combinations.
- •8. Fill in the blanks with the following expressions:
- •9. Complete the following sentences:
- •11. Speak on:
- •12. Translate the following text:
- •Exercises
- •1.Learn the following active words:
- •2. Translate the following sentences paying attention to the participle:
- •3. Answer the following questions:
- •5. Make up six sentences using the following nouns qualified by adjectives.
- •6. Translate the following text without consulting a dictionary and retell the text.
- •If There Were No Electricity
- •7. Describe the following:
- •9. Form statements which are not true to the fact. Ask your fellow-students to correct them.
- •Exercises
- •1. Learn the following active words:
- •3. Define the function of the word do in the following sentences:
- •4. Translate the following questions and answer them:
- •Exercises
- •1 Learn the following active words and expressions and use them in the sentences of your own.
- •8. Answer the following questions:
- •10. Translate the following word combinations and use them in the sentences of your own:
- •Exercises
- •1. Learn the following active words:
- •2. (A) Give headings to each paragraph of the text.
- •3. Translate the following sentences:
- •4. Define the non-finite forms of the verb met in the text.
- •5. Put 10 questions to the text.
- •6. Translate the following sentences:
- •7. Speak on:
- •Exercises
7. Fill in the blanks with the words one or for:
1. Moscow is ... of the largest cities in the world. 2. ... must remember that it is necessary to study English at least an hour a day. 3. As ... rubber it was brought to Europe as early as the 15th century. 4. ... understands the importance of electricity when ... sees trams, trolley-buses and trains driven by it. 5. The power of the atom is used ... peaceful purposes in our country. 6. ... must know the chemical properties of the atom. 7. We produce rubber ... it is quite necessary ... the development of our industry. 8. In 1819 Volta returned to Como ... he wanted to spend the rest of his life there. 9. This is a more important problem than that ... .10. I haven't got a dictionary, I must have ... .
8. Write out from the text all the sentences where the infinitive is used, and define its function.
9. Make up sentences according to the model using the verbs given below.
Model: We could not help speaking about the achievements of Russian physicists.
to answer, to repeat, to mention, to observe, to change, to think, to remember
10. Give antonyms for the following words:
north pole, dark, on the one hand, small, arrangement, larger, magnetized, unfamiliar, like, positive, similar, to rest, in motion
11. Answer the following questions:
1. What types of electricity do you know? 2. What is the difference between electricity at rest and electricity in motion? 3. What kind of experiments did Galvani carry on? 4. What did Franklin prove? 5. What are the two kinds of electrical charges? 6. Who was the first to produce a steady continuous current? 7. What was Volta? 8. What can you: say about the behavior of static charges? 9. What did Volta take interest in? 10. What did Volta's discovery result in? 11. What did the Volta device consist of? 12. Where did he spend the rest of his life?
12. Explain the meaning of the following compound words:
newspaper, schoolboy, thunderstorm, icebreaker, waterfall, fisherman
13. Retell Volta's biography.
LESSON ELEVEN
THE PROPERTIES OF THE ELECTRIC CURRENT
Ever since Volta first produced a source of steady continuous current, men of science have been forming theories on this subject. For some time they could see no real difference between the newly-discovered phenomenon and the former understanding of static charge. Then the famous French scientist, Ampere (after whom the unit of current was named) determined the difference between the current and the static charges. In addition to it, Ampere gave the current direction: he supposed it to flow from the positive pole of the source round the circuit and back again to the negative pole. We know him to be right in his first statement but he was certainly wrong in the second, as to the direction of current. The flow of current is now known to be in a direction opposite to what he thought.
Now let us turn our attention to the electric current itself. The current which flows along wires consists of moving electrons. In other words, the flow of moving electrons is one form of the electric current. What can we say about the electron? We consider the electron to be a minute particle having an electric charge. We also know that charge to be negative. As these minute charges travel along a wire, that wire is said to carry an electric current.
In addition to travelling through solids, however, the electric current can flow through liquids, as well and even through gases. In both cases it produces some most important effects to meet industrial requirements. Some liquids, such as melted metals for example, conduct current without any change to themselves. Others, called electrolytes, are found to change greatly when the current passes through them.
The reader is certain to remember that a negatively charged electron moves to the positive end of the wire. It had been supposed to move in the wrong way,from the positive end of the circuit to the negative, long before the electrons were discovered. In fact, when a wire is said to be carrying a current from left to right, the electrons in it are really flowing from right to left.
When the electrons flow in one direction only, the current is said to be d. c, that is, direct current. The simplest source of power for direct currents is a battery, for a battery pushes the electrons in the same direction all the time (i. е., from the negatively charged terminal to the positively charged terminal).
The letters a. c. stand for alternating current. The current under consideration is known to flow first in one direction and then in the opposite one. The a. c. used for power and lighting purposes is assumed to go through 50 cycles in one second (Fig. 6).
One of the great advantages of a. c. is the ease with which power at low voltage can be changed into an almost similar
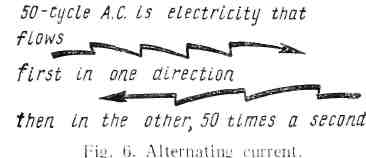
decrease it to meet industrial requirements as well as to operate various devices at home. In fact, at least 90 per cent of electric power to be generated at present is a. c. We know it to find a wide application for lighting, heating, industrial and other purposes.
The student may be probably asking himself: "Why is d. с ever used?" In spite of the fact that almost all electrical power is usually generated and transmitted in the form of a. c, there are numerous cases when d. с is required. For this reason, it is quite possible to generate a. c. then transform it into d. с
We cannot help mentioning here that Yablochkov, our Russian scientist and inventor, was the first to apply a. c. in practice.
