
- •2. Perpendicularity
- •I. The point is on the line.
- •I I. The point is not on the line.
- •5. State the followings as true or false
- •1. Distance Between a Point and a Plane
- •2. Distance Between a Plane and a Line Parallel to the Plane
- •3. Distance Between Two Parallel Planes
- •4. Distance Between Skew Lines
2. Perpendicularity
In this section we will learn the perpendicular lines, conditions of being perpendicular, the lines which are perpendicular to a plane and perpendicular planes. After that we will learn finding and using the distances in space.
A. PERPENDICULAR LINES
Definition: (perpendicular lines)
Two lines a and b are perpendicular to each other if the angle between them is 90°.
For intersecting lines we can easily define the perpendicularity. But, if the lines are skew lines then we will take any point on one of the lines and draw a parallel line to the other line. If the angle between these two intersecting lines is 90° then the given skew lines are said to be perpendicular.
Theorem: If one of two parallel lines is perpendicular to a third line, the other is perpendicular too.
Proof:
L et
m
and
b
be
two parallel lines and m
be
perpendicular to c
(Figure
1.36).
et
m
and
b
be
two parallel lines and m
be
perpendicular to c
(Figure
1.36).
Through any point A, let us draw lines m1 and c1 so that m1 // m and c1 // c.
Since m ⊥ c, the angle between m1 and c1 is 90°.
On the other hand, since m1 // m and m // b, we get m1 // b.
So the angle between b and c is also 90°.
That means b and c are perpendicular lines
Example 26: By using perpendicularity, prove that if two lines are parallel to the same line they are parallel.
S olution:
Let
m,
n
and
d
be
three lines. Let
olution:
Let
m,
n
and
d
be
three lines. Let
m // n and d // n. We need to prove that m // d.
Let A be a point on n. We can draw a plane α perpendicular to n at A. So n ⊥ α.
Since m // n and n ⊥ α, m ⊥ α because of the previous theorem.
Since d // n and n ⊥ α then d ⊥ α .
Since m and d are perpendicular to α by using the previous theorem they are parallel.
Check Yourself 8
1. State the followings as true or false.
a. Two lines d and k are parallel to the same plane. If a line l is perpendicular to line d it must be always perpendicular to line k.
b. Two perpendicular lines are given in space. If a line is perpendicular to these lines at their intersection point then this line is perpendicular to the plane, which includes the perpendicular lines.
c. Given that d, k and l are three lines in space. If d and k are perpendicular to line l they must be parallel to each other.
d. Two lines d and k in a plane are perpendicular to the same line l. Another line m is parallel to line l then m is perpendicular to d and k, also.
Answers
1. a) False b) True c) False d) True
B. LINE PERPENDICULAR TO A PLANE
Definition: (line perpendicular to a plane)
A line is said to be perpendicular to a plane if it is perpendicular to every line in this plane.
Let us say that m is a line and α is a plane. If it is given that m α then m is perpendicular to any line in α.
If m α then m intersects α. To prove this statement let us assume that m does not intersect α.
In this case there are two possibilities for m and α :
1. m is in α. Then since it is not perpendicular to a line in α, that is itself, m is not perpendicular to α.
2. m is parallel to α. In this case in α there can be found a line parallel to m. So m can not be perpendicular to α.
In both conditions m is not perpendicular to α.
Therefore, m intersects α.
Definition: (inclined line)
If a line intersects a plane but not perpendicular to the plane it is called an inclined line.
Theorems:
1. If a line is perpendicular to two intersecting lines lying in a plane then it is perpendicular to the plane.
2. Through any given point in space, there can be drawn one and only one plane perpendicular to a given line.
3. If one of two parallel lines is perpendicular to a plane then the other line is also perpendicular to the same plane.
4. Two lines perpendicular to the same plane are parallel.
5. Through a point in space, there can be drawn only one line perpendicular to a given plane.
6. If a line is perpendicular to one of two parallel planes, it is perpendicular to the other.
Proofs:
1. We need to prove that if a line is perpendicular to two intersecting lines in a plane it is perpendicular to any line in this plane.
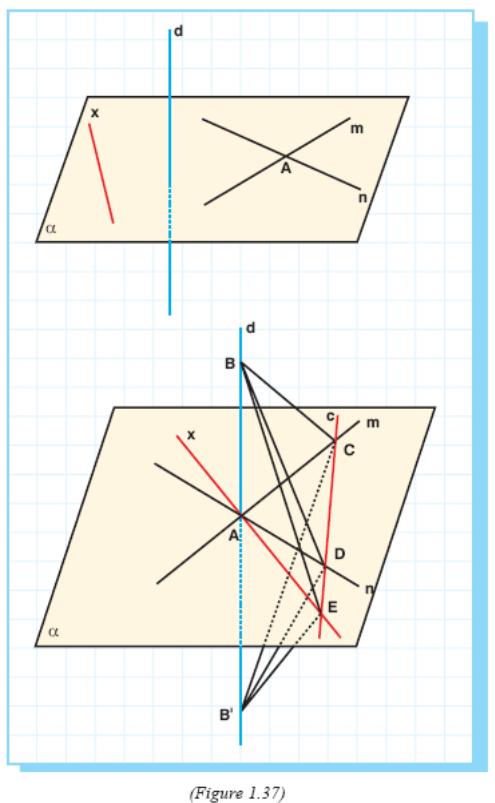
Let d be a line perpendicular to two lines m and n lying in α. Let A be the intersection point of m and n.
It is obvious that d is perpendicular to every line in α which is parallel to either one of m or n (Figure 1.37).
So we should check for the lines which are not parallel to neither m nor n.
Let x be any line intersecting both m and n.
We have to prove that d is perpendicular to x too.
Let us shift lines d and x so that A is on d and x.
Let c be any line in α intersecting m, n, x at
points C, D, E respectively.
On line d let us take two points B and B' so that BA = B'A.
Then BAC and B'AC are congruent, similarly BAD and B'AD are congruent (by S.A.S.).
So BD = B'D and BC = B'C.
Then BDC and B'DC are congruent (by S.S.S.). That means ∠BDC = ∠B'DC.
Then BDE and B'DE are congruent triangles (by S.A.S.).
So BE = B'E and BAE and B'AE are congruent (by S.S.S.).
Hence ∠BAE = ∠B'AE = 90°.
So d is perpendicular to x.
Therefore d is perpendicular to any line in α. So d ⊥ α.
2 .
We
have two cases:
.
We
have two cases:
