
- •Glycolysis and Fermentation
- •Diy Glycolysis Home Page
- •Introduction
- •The Task Ahead
- •Keeping Track
- •Summary of Reaction Types
- •Aldol Cleavage
- •Aldose-Ketose Isomerisation
- •Ketose-Aldose Isomerisation
- •Dehydration
- •Phosphorylation
- •Phosphoryl Shift
- •Dephosphorylation
- •Coupled Oxidation & Phosphorylation
- •Oxidation
- •Reduction
Aldose-Ketose Isomerisation
An aldose is a monosaccharide with an aldehyde group. Common ketoses have a ketone group at carbon 2. It is possible for a hydrogen atom to be moved from one carbon atom to another and so convert an aldose into a ketose. The Delta-G for the reaction will be near zero but there is a significant activation energy at physiological conditions which means the reaction requires an enzyme catalyst.
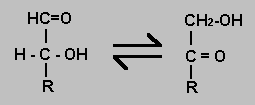
Ketose-Aldose Isomerisation
Just the reverse of an aldose-ketose isomerisation. See above.
This page can be annotated here. Select annotations above for info.
Dehydration
Dehydration of an organic molecule is often in the form shown in the equation. An OH group is removed as a hydroxyl ion and a hydrogen attached to an adjacent atom is removed as a hydrogen ion. A double bond is formed as a result. It is not itself a reduction despite the removal of an oxygen atom but could be a prelude to reduction which would be implemented as a hydrogenation of the double bond.
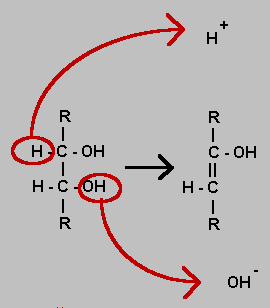
This page can be annotated here. Select annotations above for info.
Phosphorylation
In the simplest form a phosphate group replaces the hydrogen of a hydroxyl group. The Delta-G for phosphorylation of an alcohol with inorganic phosphate is usually very positive and needs to be coupled with another process such as dephosphorylation of ATP.
The usual biochemical shorthand for the phosphate group is a P with a circle around it.
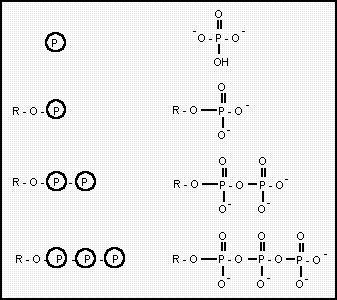
This page can be annotated here. Select annotations above for info.
Phosphoryl Shift
It is possible to remove a phosphate group from one hydroxyl group and put it on another using a single step. In fact it is easier for the enzyme to phosphorylate to a bisphosphate and then dephosphorylate. The net result is a phosphoryl shift. Phosphoryl shift is included here as a seperate reaction type because it can be acheived with a single enzyme.
This page can be annotated here. Select annotations above for info.
Dephosphorylation
In the simplest form a phosphate group is replaced with a hydrogen atom to give a hydroxyl group. The Delta-G for dephosphorylation of an alcohol is usually very negative and can be coupled with another energy requiring process such as phosphorylation of ADP.
This page can be annotated here. Select annotations above for info.
Coupled Oxidation & Phosphorylation
Oxidation of an aldehyde to a carboxylic acid has a highly negetive Delta-G even if the oxidising agent is weak. It is possible therefore to couple the process with the addition of inorganic phosphate. The product is a type of acid anhydride.
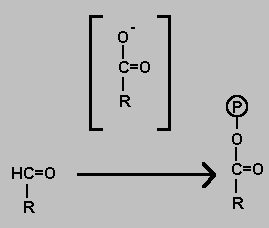
This page can be annotated here. Select annotations above for info.
Oxidation
Oxidation of organic molecules is often in the form of dehydrogenation. Two atoms of hydrogen are removed and a double bond forms. Hydration may preceed or follow dehydrogenation. An oxidising agent is required that can be recycled. In most organisms oxygen is the ultimate oxidiser used to recycle oxidising agents. In the absense of oxygen all oxidations must be balanced with reductions.
Some substrates can be oxidised to alcohols. Alcohols can be oxidised to aldehydes or ketones. Aldehydes can be oxidised to carboxylic acids.
This page can be annotated here. Select annotations above for info.
