
- •Contents
- •Introduction
- •§ 2. Two Approaches to Language
- •§ 3. Lexicology and Sociolinguistics
- •§ 4. Lexical Units
- •§ 5. Varieties of Words
- •§ 6. Course of Modern English Lexicology
- •Lecture 1. Methods and procedures of lexicological analysis
- •§ 1. Contrastive Analysis
- •§ 2. Statistical Analysis
- •§ 3. Immediate Constituents Analysis
- •§ 4. Distributional analysis and Co-occurence
- •§ 5. Transformational Analysis
- •§ 6. Componental Analysis
- •§ 7. Method of Semantic Differential
- •Practical tasks and exercises
- •1. Read and analyze the following extract on the basis of the above mentioned methods of linguistic analysis:
- •Lecture 2. Semasiology
- •§ 1. Referential Approach
- •§ 2. Meaning in the Referential Approach
- •§ 3. Functional Approach to Meaning
- •§ 4. Relation Between the Two Approaches
- •§ 5. Grammatical Meaning
- •§ 6. Lexical Meaning
- •§ 7. Part-of-Speech Meaning
- •§ 8. Denotational and Connotational
- •§ 9. Emotive Charge
- •§ 10. Stylistic Reference
- •§ 11. Emotive Charge and Stylistic Reference
- •§ 12. Lexical Meaning
- •§ 13. Functional (Parf-of-Speech) Meaning
- •§ 14. Differential Meaning
- •§ 15. Distributional Meaning
- •§ 16. Morphological Motivation
- •§ 17. Phonetical Motivation
- •§ 18. Semantic Motivation
- •Practical tasks and exercises
- •1. Translate the following words into Ukrainian paying attention to the difference in their meaning.
- •2. A) Comment on the lexical meaning of the words in bold type. B) Comment on their lexical and grammatical contexts. C) Translate the sentences into Ukrainian.
- •3. Classify the following words according to the type of motivation.
- •4. A) Translate the following sentences into Ukrainian. B) Classify the words in bold type into affixal and root antonyms.
- •5. A) Pick out synonyms from the sentences below. Comment on their shades of meaning and stylistic reference. B) Translate the sentences into Ukrainian.
- •Lecture 3. Word-groups and phraseological units
- •§ 1. Lexical Valency (Collocability)
- •§ 2. Grammatical Valency
- •§ 3. Distribution as the Criterion of Classification
- •§ 4. Lexical Meaning
- •§ 5. Structural Meaning
- •§ 6. Interrelation of Lexical and Structural Meaning in Word-Groups
- •Interdependence of structure and meaning in word-groups
- •§ 7. Syntactic Structure (Formula) and Pattern of Word-Groups
- •§ 8. Motivation in Word-Groups
- •§ 9. Free Word-groups Versus Set-phrases. Phraseological Units, Idioms, Word-equivalents
- •§ 10. Criteria of Stability and Lack of Motivation (Idiomaticity)
- •§ 11. Classification
- •§ 12. Phraseological Units and Idioms Proper
- •§ 13. Phraseology as a Subsystem of Language
- •Practical tasks and exercises
- •1. Comment on the structural types and patterns of the following words. Translate the words into Ukrainian.
- •2. Group the phraseological units in bold type according to their classification mentioned in the lecture. Translate the sentences into Ukrainian.
- •3. Group the following phraseological units according to the classification based on the structural principle. Give their Ukrainian equivalents.
- •4. Define the meanings of the following polysemantic units in bold type. Comment on the ways of developing their polysemy. Translate the sentence into Ukrainian.
- •5. Group the following phraseological units into synonymous pairs. Give their Ukrainian equivalents.
- •6. Choose antonyms to the following phraseological units (use the list in brackets below). Translate these antonymous pairs into Ukrainian.
- •Lecture 4. Word-structure
- •§ 1. Segmentation of Words into Morphemes
- •§ 2. Principles of Morphemic Analysis. Types of Word Segmentability
- •§ 3. Classification of Morphemes
- •§ 4. Procedure of Morphemic Analysis
- •§ 5. Morphemic Types of Words
- •§ 6. Derivative Relations
- •§ 7. Derivational Bases
- •§ 8. Derivational Affixes
- •§ 9. Semi-Affixes
- •§10. Derivational Patterns
- •§ 11. Derivational Types of Words
- •Practical tasks and exercises
- •1. Make the morphemic analysis of the following words. Translate the words into Ukrainian.
- •2. Classify the stems of the words given below into simple, derived, compound; free, bound, semi-bound.
- •3. Analyze the structure of the following words on the derivational and morphemic levels, use the method of ic and uc analysis:
- •4. Name the nouns formed with the following suffixes. State which of the suffixes are productive: -tion, -dom, -ness, -ism, -ship, -er, -ist, -th, -ige. Lecture 5. Word-formation
- •Various ways of forming words
- •§ 1. Various Types and Ways of Forming Words
- •§ 2. Word-formation. Definition.
- •§ 3. Word-formation as the Subject of Study
- •§ 4. Productivity of Word-formation
- •§ 5. Definition. Degree of Derivation. Prefixal and Suffixal Derivative
- •§ 6. Prefixation. Some Debatable Problems
- •§ 7. Classification of Prefixes
- •§ 8. Suffixation. Peculiarities of Some Suffixes
- •§ 9. Main Principles of Classification
- •§ 10. Polysemy and Homonymy
- •§ 11. Synonymy
- •§ 12. Productivity
- •§ 13. Origin of Derivational Affixes
- •§ 14. Definition
- •§ 15. Typical Semantic Relations
- •I. Verbs converted from nouns (denominal verbs).
- •II. Nouns converted from verbs (deverbal substantives).
- •§ 16. Diachronic Approach of Conversion. Origin
- •§ 17. Productivity. Traditional and Occasional Conversion
- •Practical tasks and exercises
- •5. Comment on the examples of converted words in the sentences below. State to what part of speech they belong and the derivational pattern оf conversion.
- •Lecture 6. Word-formation. Compounding
- •§ 2. Structure
- •§ 3. Meaning
- •§ 4. Structural Meaning of the Pattern
- •§ 5. The Meaning of Compounds. Motivation
- •§ 6. Relations between the iCs of Compounds
- •§ 7. Different Parts of Speech
- •§ 8. Means of Composition
- •§ 9. Correlation between Compounds and Free Phrases
- •§ 10. Sources of Compounds
- •Practical tasks and exercises
- •1. Analyse the structure of the iCs of the following compound words. Translate the compounds into Ukrainian.
- •2. Find compounds in the following sentences, define their structural type and state to what part of speech they belong. Translate the sentences into Ukrainian.
- •3. Discriminate between compounds proper and derivational compounds given in bold type. Translate the sentences into Ukrainian.
- •4. Translate the following words and phrases into English using the stems in brackets.
- •Lecture 7. Etymological survey of the english word-stock
- •§1 . Some Basic Assumptions
- •§ 2. Semantic Characteristics and Collocability
- •§ 3. Derivational Potential
- •§ 4. Causes and Ways of Borrowing
- •§ 5. Criteria of Borrowings
- •§ 6. Assimilation of Borrowings
- •§ 7. Phonetic, Grammatical and Lexical Assimilation of Borrowings
- •Interrelation between native and borrowed elements
- •§ 8. The Role of Native and Borrowed Elements
- •§ 9. Influence of Borrowings
- •Practical tasks and exercises
- •1. A) Using an etymological dictionary, classify the following words of native origin into: 1) Indo-European, 2) Germanic, 3) English proper.
- •3. Comment on the origin of the following geographical names.
- •4. A) Pick out the French borrowings from the sentences given below. Identify the period of borrowings. B) Translate the sentences into Ukrainian.
- •5. State from what languages the following words are borrowed. Comment on their meaning.
- •6. A) Classify the borrowings given in bold type according to the degree of their assimilation. State from what languages they are borrowed. B) Translate the sentences into Ukrainian.
- •Lecture 8. Various aspects of vocabulary units and replenishment of modern english word-stock
- •Interdependence of various aspects of the word
- •§ 1. Notional and Form-Words
- •§ 2. Development of Vocabulary
- •§ 3. Structural and Semantic Peculiarities of New Vocabulary Units
- •§ 4. Productive Word-Formation
- •§ 5. Various Ways of Word-Creation
- •§ 6. Borrowing
- •§ 7. Number of Vocabulary Items in Actual Use and Number of Vocabulary Units in Modern English
- •Variants and dialects of the english language
- •§ 8. General Characteristics of the English Language in Different Parts of the English-Speaking World
- •§ 9. Lexical Differences of Territorial Variants
- •§ 10. Some Points of History of the Territorial Variants and Lexical Interchange Between Them
- •Practical tasks and exercises
- •2. Pick out all the substantivized adjectives from the following sentences. Comment on their structural-semantic features and the degree of substantivation. B) Translate the sentences into Ukrainian.
- •3. Compare the following pairs of nouns and adjectives. Comment on their meanings. Use the adjectives in sentences of your own.
- •4. A) Comment on the formation of the clipped words given in bold type. B) Translate the sentences into Ukrainian.
- •5. A) Pick out all the abbreviations from the sentences given below. Comment on their formation. B) Translate the sentences into Ukrainian.
- •6. A) Comment on the formation of the following blends, b) Translate the blends into Ukrainian.
- •Lecture 9. Fundamentals of english lexicography
- •§ 1. Encyclopaedic and Linguistic Dictionaries
- •§ 2. Classification of Linguistic Dictionaries
- •§ 3. Explanatory Dictionaries
- •§ 4. Translation Dictionaries
- •§ 5. Specialised Dictionaries
- •§ 6. The Selection of Lexical Units for Inclusion
- •§ 7. Selection and Arrangement of Meanings
- •§ 8. Definition of Meanings
- •§ 9. Illustrative Examples
- •§ 10. Choice of Adequate Equivalents
- •§ 11. Setting of the Entry
- •§ 12. Structure of the Dictionary
- •Practical tasks and exercises
- •1. A) Consulting an etymological dictionary, analyse the structure and origin of the following words. Comment on the phenomenon of folk (false) etymology. B) Translate the words into Ukrainian.
- •2. A) Using an etymological dictionary, define the type of meaning of the words in bold type. B) Translate the sentences into Ukrainian.
- •Перелік рекомендованих джерел lecture 1 methods and procedures of lexicological analysis.
- •Lecture 2 semasiology
- •Lecture 3 word-groups and phraseological units
- •Lecture 4 word-structure
- •Lecture 5 word-formation. Various ways of forming words.
- •Lecture 6 word-formation. Compounding
- •Lecture 7 etymological survey of the english word-stock
- •Lecture 8
- •Various aspects of vocabulary units and replenishment of modern english word-stock. Variants and dialects of the english language
- •Lecture 9 fundamentals of english lexicography
§ 7. Method of Semantic Differential
All the methods of semantic analysis discussed above are aimed mainly or exclusively at the investigation of the denotational component of the lexical meaning.
The analysis of the differences of the connotational meaning is very hard since the nuances are often slight, difficult to grasp and do not yield themselves to objective investigation and verification.
An attempt to establish and display these differences was developed by a group of American psycholinguists. They set up a technique known as the semantic differential by means of which, as they claim, meaning can be measured. It is perfectly clear, however, that what semantic differential measures is not word-meaning in any of accepted senses of the term but the connotational component of meaning or to be more exact the emotive charge.
Their technique requires the subjects to judge a series of concepts with respect to a set of bipolar (antonymic) adjective scales. For example, a concept like horse is to be rated as to the degree to which it is good or bad, fast or slow, strong or weak, etc.
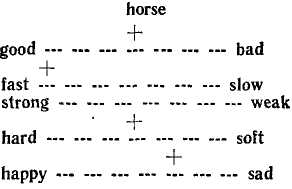
The meaning of the seven divisions is, taking as an example the first of the scales represented above, from left to right: extremely good, quite good, slightly good, neither good nor bad (or equally good and bad) slightly bad, quite bad, extremely bad.
In the diagram above horse is described as neither good nor bad, extremely fast, quite strong, slightly hard, equally happy and sad.
The responses of the subjects produce a semantic profile representing the emotive charge of the word.
The degree of agreement between the answers is treated as a significant and reliable factor.
It may be argued that the data with which they deal in these investigations are essentially subjective. Objectivity, however, concerns the role of the observer. In other words, each person records his own, entirely subjective reactions, but by the time the analysis has been completed the result will represent a kind of semantic average reached by purely objective statistical methods.
Practical tasks and exercises
1. Read and analyze the following extract on the basis of the above mentioned methods of linguistic analysis:
A barge is a flat-decked and usually flat-bottomed vessel. An empty barge rides high in the water, showing its draft marks, or waterline marks, on its side. As it is filled, the barge rides deeper and deeper in the water, and tonnage is estimated by reading the marks on the hull. Barges have no power to move on their own. They depend on tugboats, towboats, and water currents to move.
2. Take the English text of oil and gas field and analyze it according to the main principles of linguistic analysis.
Lecture 2. Semasiology
By definition Lexicology deals with words, word-forming morphemes (derivational affixes) and word-groups or phrases. All these linguistic units may be said to have meaning of some kind: they are all significant and therefore must be investigated both as to form and meaning. The branch of lexicology that is devoted to the study of meaning is known as Semasiology.
Semasiology is coming to the fore as the central problem of linguistic investigation of all levels of language structure.
Words, however, play such a crucial part in the structure of language that when we speak of semasiology without any qualification, we usually refer to the study of word-meaning proper, although it is in fact very common to explore the semantics of other elements, such as suffixes, prefixes, etc.
Meaning is one of the most controversial terms in the theory of language. The scientific definition of meaning however just as the definition of some other basic linguistic terms, such as word, sentence, etc., has been the issue of interminable discussions. Since there is no universally accepted definition of meaning we shall confine ourselves to a brief survey of the problem as it is viewed in modern linguistics both in our country and elsewhere.
WORD-MEANING
