
- •Передмова
- •Contents
- •Unit 1. Materials handling
- •Material Holding, Feeding and Metering
- •Hand chain hoists are portable lifting devices suspended from a hook and operated by _______ on a hand chain.
- •Unit 2. Gear and gearing (Part 1)
- •Gear and Gearing (part 1)
- •Unit 3. Geared systems and mechanisms (Part 2)
- •Gears and Gearing
- •Important, stock, reduced, figures, to be left,
- •Getting into shape: some basics
- •Unit 4. Metal-removal processes and machine tools
- •Material Removal Processes
- •Manufacturing techniques evaluation: cutting operations
- •Unit 5. Motion control systems overview
- •Motion Control System
- •Installation, shaft, servomotor, smooth, force, unit accumulate
- •Unit 6. Tool wear and sharpening
- •Tool wear
- •Unit 7. Bearings
- •Bearings. Components and specifications
- •Fig.1 Radial contact bearing terminology.
- •Principal standard bearing types
- •Unit 8. Mechanical elements (Part 1)
- •Machine Elements: Keys and Pins
- •Unit 9. Mechanical elements (Part 2)
- •Mechanical Elements: Rivets, Belts and Pulleys.
- •Write a list of all fasteners that you know. Compare it with the one of your groupmate.
- •Give the definition to the following terms and make sentences of your own with each of them:
- •Imagine that you are a young crazy inventor and someone presented you a large sum of money. In what field of science would you invest them or what would you do?
- •Unit 10. Mechanical failure modes
- •Mechanical Failure Modes
- •References:
- •How to make a presentation
- •Key phrases for preparing presentation
- •Why is writing an essay
- •Technical translation
- •Methods and Practices
- •Reading techniques
- •Skimming
- •Scanning
- •Using Context
- •Writing techniques
- •The Introduction
- •The body Paragraphs
- •The Conclusion
- •Irregular verbs
Unit 7. Bearings
Task 1. Discuss the following questions:
a ) How much do you know about bearings?
b) Where is bearing used today? Make a list of possible applications of bearing. Compare it with those of your groupmates.
Do you know any complex machines? What are their constituents?
T ask 2. A) The students are at the workshop on mechanical parts production. Listen to their discussion and learn what properties bearing has and where it can be used.
B) Decide whether the following statements are true or false:
The balls in ball bearings are made from another type of steal than races.
A gage check each ring with an acid.
Grinding machine check the inner diameter of each ring.
Water-based liquid keeps rings from overheating.
Abrasive stone lubricated with oil polishes the outer ring until you can see a reflection.
Raceways are cleaned with oil.
Steel balls are classified according to their shapes.
Steel balls are made of steel wires.
Just few hours are needed to grind rough balls.
Hopper sends necessary quantities of balls through several tubes to the raceways of the bearing.
After hardening balls should be washed with cleaning solvent.
12. Ball cage retain the balls in position around the raceways.
Task 3. Read and translate the following text.
Bearings. Components and specifications
Rolling-contact bearings are designed to support and locate rotating shafts or parts in machines. They transfer loads between rotating and stationary members and permit relatively free rotation with a minimum of friction. They consist of rolling elements (balls or rollers) between an outer and inner ring. Cages are used to space the rolling elements from each other. Figure 1 illustrates the common terminology used in describing rolling-contact bearings.
The inner and outer rings of a rolling-contact bearing are normally made of SAE 52100 steel, hardened to Rockwell C 60 to 67. The rolling-element raceways are accurately ground in the rings to a very fine finish (16 min or less). Rings are available for special purposes in such materials as stainless steel, ceramics, and plastic. These materials are used in applications where corrosion is a problem.
N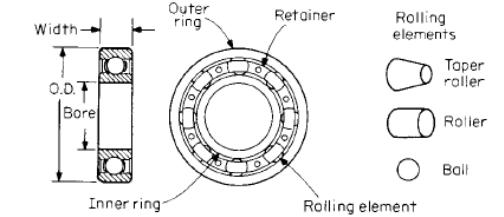 ormally
the rolling
elements,
balls or rollers, are made of the same material and finished like the
rings. Other rolling-element materials, such as stainless steel,
ceramics and plastics, are used in conjunction with various ring
materials where corrosion is a factor.
ormally
the rolling
elements,
balls or rollers, are made of the same material and finished like the
rings. Other rolling-element materials, such as stainless steel,
ceramics and plastics, are used in conjunction with various ring
materials where corrosion is a factor.
Fig.1 Radial contact bearing terminology.
Cages, sometimes called separators or retainers, are used to space the rolling elements from each other. Cages are furnished in a wide variety of materials and construction. Pressed-steel cages, riveted or clinched and filled nylon, are most common. Solid machined cages are used where greater strength or higher speeds are required. They are fabricated from bronze or phenolic-type materials. At high speeds, the phenolic type operates more quietly with a minimum amount of friction. Bearings without cages are referred to as full-complement.
A wide variety of rolling-contact bearings are normally manufactured to standard boundary dimensions (bore, outside diameter, width) and tolerances which have been standardized by the AFBMA. All bearing manufacturers conform to these standards, thereby permitting interchangeability.
