
- •Содержание
- •Case 1. A Year in Fashion
- •1. This story is set in a fashion house. To find out some background about the world of fashion, read this background box: Background: Fashion houses
- •2. This story looks at problems caused when borrowing money. If you’d like to think about the ethics of money lending, discuss this point:
- •Problem
- •27 May May Week No. 22
- •6 June June Week No.23
- •18 August August Week No. 33
- •11 September September Week No. 35
- •15 September September Week No. 35
- •27 May: Get the facts straight
- •6 June: Getting the money
- •18 August: Why gloomy?
- •11 September: The risks
- •15 September: a letter from the bank
- •5. When you’ve read the first paragraph of this entry, read this letter from the bank summarising the meeting, and fill in the gaps using the words underneath.
- •6. Now, read Suzanne’s four options and then move on to make your decision! Decision time
- •Paired comparisons
- •Background: Bonds
- •The Characters
- •The situation
- •The decision
- •Role play Divide into pairs with members of another group, and role play the following situations:
- •So, should Cliff try to sell the bonds to Louise? If your discussions so far haven’t produced a consensus, take a vote on it. Now decide! Case 3. Angel Investments Background
- •Case study ‘Angel Investments’ card 1
- •Key points for product presentations
- •Proposals
- •Writing
- •Case study ‘Angel Investments’ card 2
- •Case 4. Camden Football Club Background
- •Current situation
- •Writing
- •Case study ‘Camden fc’ card 1 Camden fc negotiating team
- •Case study ‘Camden fc’ card 2 United Media negotiating team
- •Case 5. Group Bon Appetit plc Background
- •Group Bon Appetit: Key facts
- •Innovia Cafes
- •Recent developments
- •1. Task
- •Speaker a Business start-up: Penguin Park
- •Speaker b The Olive Shop (established 2000)
- •Speaker c Business start-up: Sweet Sleepers
- •Speaker d Business start-up: Ingredients.Com
- •2. You have decided to approach a venture capitalist to raise finance for one of the ventures in Exercise 1. Write the covering letter to accompany a detailed business plan.
- •Information for savers and investors
- •Useful language:
- •3. When you have finished preparing your questions, you should meet up with Student b. Make notes on the answers you receive and decide how you are going to invest your money. Student b
- •Role Play 3: Deciding where to invest
- •Introduction
- •1. Look at this list of possible criteria. Work with a partner, and choose what you think are the important criteria. At the same time, eliminate criteria you think are unimportant.
- •Situation
- •You must decide:
- •Worksheet
- •Roles: Role a: The President
- •Role b: The Investment Manager, West Africa
- •Role c: The Investment Manager, South Korea
- •Role d: The Investment Manager, North America
- •Role e: The Financial Research Officer
- •Role f: The Political Research Officer
- •Role g: The Head of Loan Scheduling
- •Role play 4. Selling off a line of business
- •Introduction
- •1. Do this quiz. Begin at number 1, make your choice, and then go to the number indicated in brackets.
- •Situation
- •Role b: The Sales Manager
- •Role c: The Claims Manager
- •Role d: The Investment Manager
- •Role e: The Marketing Manager
- •Role f: The Personnel Manager
- •Role g: The it Manager
- •Role play 5. A big new feature film
- •Introduction
- •1. You are a film producer, with your own company. Work with a partner. Read the questions and choose the best answer.
- •Situation
- •Role b: The Production Manager
- •Role c: The Company Accountant
- •Role d: The Production Assistant
- •Role e: The Head of Casting
- •Role f: The Head of Marketing
- •Role g: The Technical Adviser
- •Role play 6. Servicing a debt
- •Introduction
- •1. Look at this list and put a tick next to those who will suffer because of your company’s closure:
- •4. Will the people who suffer more be those who have the best protection, or those who receive compensation? Situation
- •5. You must decide:
- •Fact sheet
- •Roles: Role a: The Chair of the Consortium of Banks
- •Role b: The Secretary of the Association of Danegelt Shareholders
- •Role c: The Managing Director of Danegelt
- •Role d: The Chief Executive of the Sumitomo Bank
- •Role e: The Secretary of the Federation of Small Shareholders
- •Role f: The Financial Director of Danegelt
- •Role g: The President of the Trust Bank of New York
- •2. Write notes.
- •3. Study the balance sheet items below. Is a bs in your company presented in the same way?
- •2. Fill in the missing vowels in these words and then check the meaning.
- •3. Discuss. Reference list
- •117997, Москва, Стремянный пер., 36.
2. Write notes.
What are the important issues in your company at the moment in relation to the P&L account?
|
||
What is your operating profit in relation to |
||
your competitors?
|
the capital invested in the business?
|
the general state of the economy?
|
3. Discuss.
Framework 2: Balance sheet
1. Prepare.
1. Cross out the incorrect words in italics.
On a balance sheet (BS), things that you own are called assets / liabilities and things that you owe are called assets / liabilities.
2. Match the words and phrases (1—8) with the definitions (a—h).
1) fixed assets 2) current assets 3) intangible assets 4) loan capital 5) share capital 6) retained profit 7) accounts receivable 8) accounts payable |
a) assets that can be converted to cash within one year b) assets that the company will use over a long time period c) assets that are not physical and so cannot easily be valued e.g. copyrights, patents, franchises, goodwill, trade mark/brand name d) money that has come into the company from issuing shares e) money that has come into the company from its operations f) money that has come into the company from bank loans g) money owed to suppliers (= creditors) h) money owed by customers (= debtors) |
3. Study the balance sheet items below. Is a bs in your company presented in the same way?
Current assets Cash Accounts receivable Inventory (raw materials and stock) Shares intended for disposal within 1 year Fixed assets Vehicles and equipment Investments (= financial assets) Land and buildings Intangible assets Goodwill (of companies you have bought), patents etc. |
Current liabilities Loan capital (= bank debt) Accounts payable Accrued expenses (other items not yet paid e.g. unpaid utility bills, unpaid payroll taxes) Tax payable (tax on operating profit) |
Provisions Amount set aside for future liabilities (e.g. writing off a bad debt, restructuring costs, a court case) |
|
Shareholders’ equity Share capital Retained profit (= reserves) |
4. Complete this equation using phrases from the BS. Then answer the question: Why is working capital important to a business?
working capital = _____________________ - ______________________
2. Write notes.
What are the important issues in your company at the moment in relation to the BS?
What is your company doing to decrease the tax payable?
What plans do you think the Board of Directors or CEO have to improve the BS next year?
3. Discuss.
Framework 3: Managing cashflow
1. Brainstorm.
1. Complete the ideas maps.
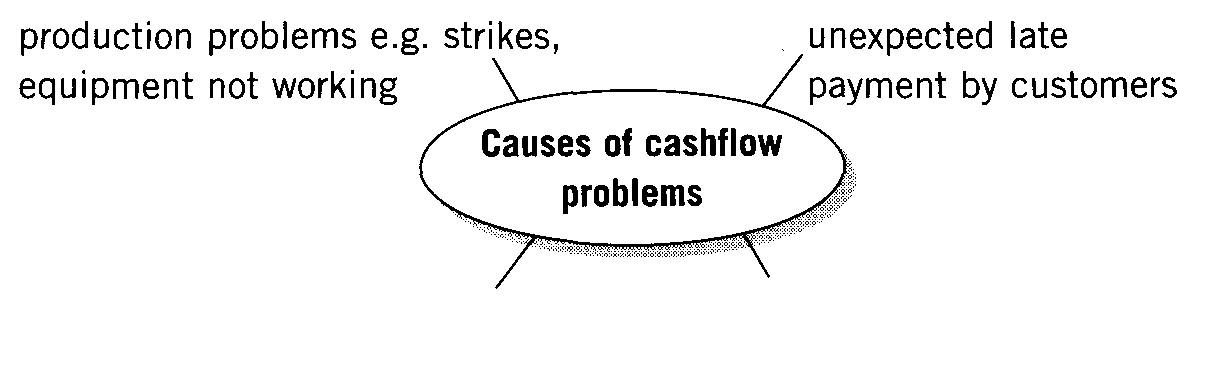
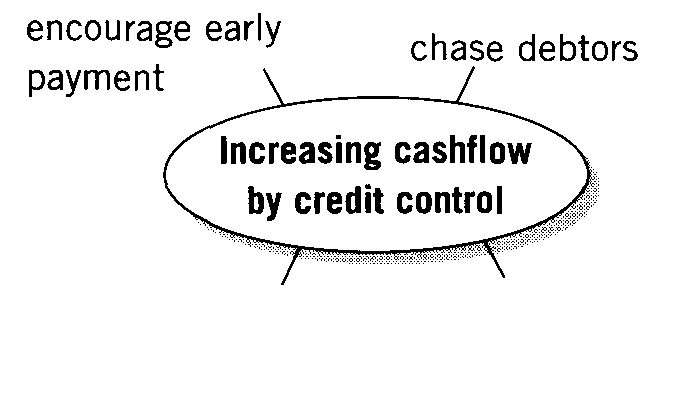
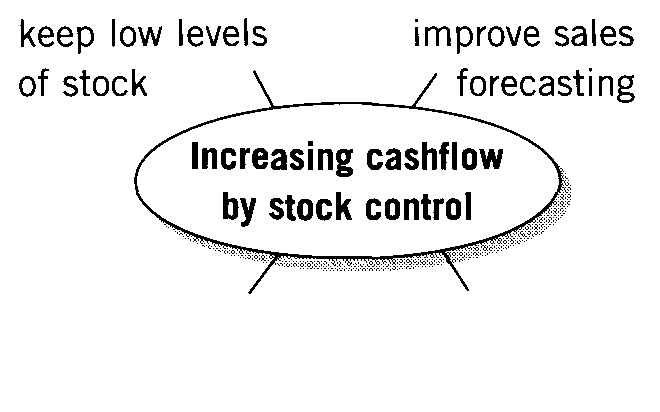
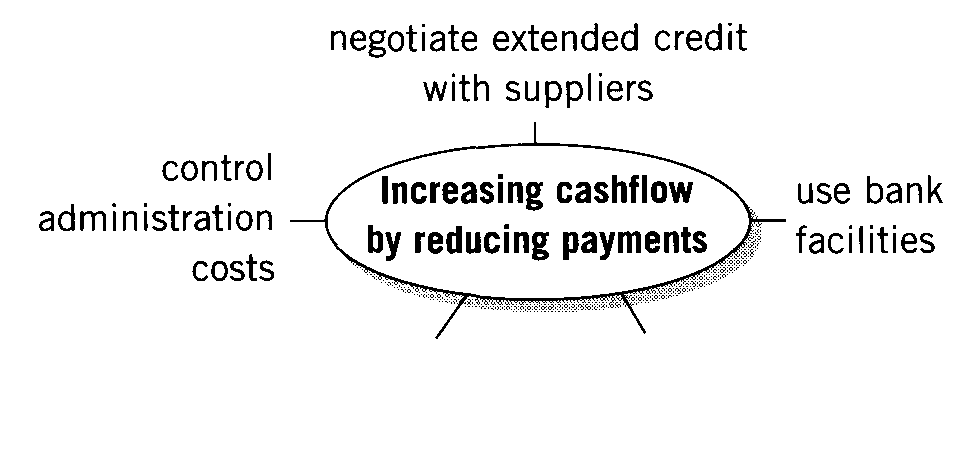
2. What other ways are there to increase cashflow?
__________________________________________________
2. Write notes.
1. What causes cashflow problems in your business? Give three real-life examples.
1.
2.
3.
2. How do you try to solve cashflow problems? What problems does this cause?
Methods we use to improve cashflow |
|
Problems associated with these methods |
1.
|
→ |
|
2.
|
→ |
|
3.
|
→ |
|
3. Discuss.
Framework 4: Company analysis
1. What do you need to know about a company to analyse its current performance and future potential? Brainstorm.
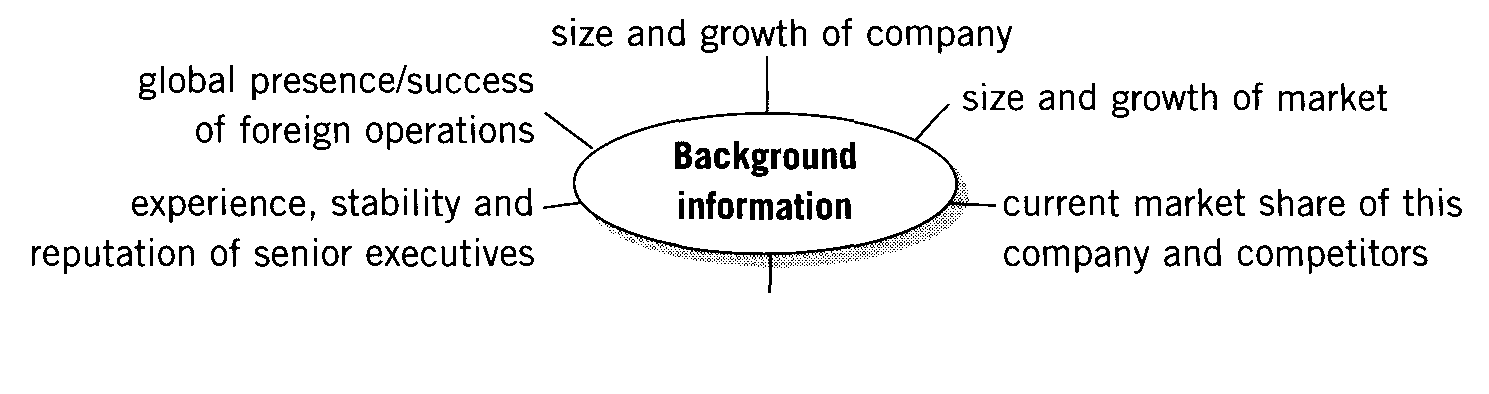
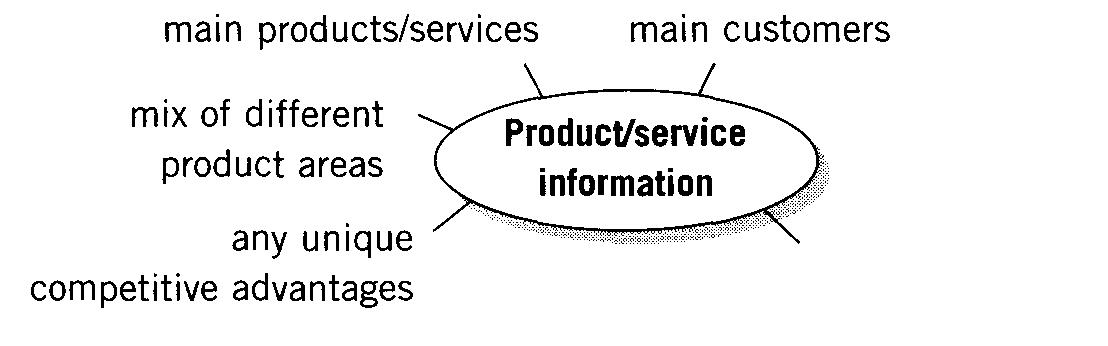

2. Write notes.
1. Choose a company you have recently analysed and complete the grids.
Name of company:_________________________________
Background information |
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. |
Product/service information |
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. |
Financial information |
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. |
2. Would you recommend this company to investors? Give three main reasons.
1.
2.
3.
3. Discuss.
Framework 5: Investment advice
1. Prepare.
1. Read the text and check the vocabulary.
Investment instruments include stocks (equities), bonds and cash. Most investors like to have a diversified portfolio of all three. Stocks offer a higher potential return over the long term, but at a higher risk. Bonds offer a fixed rate of interest, and have less risk. They can be issued by governments (in which case they are called gilts), or companies. Cash sits in a bank account earning interest. It is the safest investment, but offers the lowest returns.
Instead of investing in individual stocks, investors can spread their risk by investing in funds. These can be geographical funds (domestic / regional / international), sector funds (e.g. the technology / financial / health care / retail sectors), tracker funds (that ‘track’ or follow exactly a stock market index such as the S&P 500), emerging market funds or small company funds.
