
- •Amazon.Com case study Group project
- •4Th year student
- •4Th year student
- •Saint-Petersburg
- •Introduction
- •Product diversification and services Core business of the company
- •Market Growth Forecasts
- •Online Customers
- •Main players
- •Russian market and amazon.Com
- •Russians still pay in cash
- •Customs Issues
- •Post Blames Customs
- •Customs Blames Post
- •Who Takes an Advantage?
- •Theory 1. Swot-analysis.
- •Strengths
- •Weaknesses
- •Opportunities
- •Threats
- •International new ventures theory. Application to amazon.Com
- •Types of international new ventures
- •Strategies of amazon.Com on national markets
- •Entering the u.S. Market
- •Expansion into Europe. Case of Germany and the uk
- •French Market
- •Italian and Spanish markets
- •The Market of Canada
- •Expansion to Asia. Japanese Market.
- •Chinese market
- •Results and recommendations
- •Bibliography
- •59 Amazon buys into Chinese market . [Electronic resource] // Amazon. – Режим доступа: http://news.Cnet.Com/Amazon-buys-into-Chinese-market/2100-1030_3-5316255.Html свободный. – Загл. С экрана.
www.amazon.com;
www.amazon.co.uk;
www.amazon.de;
www.amazon.co.jp;
www.amazon.fr;
www.amazon.ca;
www.amazon.cn;
www.amazon.it;
www.amazon.es;
www.shopbop.com;
www.zappos.com;
www.endless.com;
www.javari.co.jp, etc.1
E-COMMERCE MARKET IN RUSSIA
The Russian E-Commerce market is the youngest and most dynamic market in Europe. With a population of about 140 million people, Russia represents a relatively large market for E-Commerce. Due to the growing middle class and the growing Internet penetration, many companies think about entering the Russian E-Commerce market, because the number of Internet users increases annually about 150%. This is the reason why Russia is one of the fastest growing Internet markets worldwide.2
Facts
The Internet penetration in Russia isn’t that high as in other European countries, but Russia is catching them up quickly. The average annual growth of the Internet users exceeded 15% over the last few years. Russia has already overtaken Germany as the market with the highest number of unique Internet users in Europe in September 2011. Furthermore in spring 2012 the total Russian Internet audience reached 80 million users (it consists of people aged 18 and up and including 20 million Russian speaking user in the former Soviet republics, Western Europe, Israel and North America. You have to consider that the Internet penetration in Russia is very uneven, there is a huge difference between the leading Regions and the lagging regions (67%-68% in the two capitals and in comparison 29% in Tyva and 34% in Mordovia).3
In 2011 the Russian online retail market accounted a total market volume of 310 billion rubles. This amount consists of the Internet sales of physical and digital goods and also of the online ticket sales (plane, train and cultural entertainment tickets). The volume of Internet sales in 2011 accounted for an approximate 1.7% of total Russian retail sales, which was 19 trillion rubles. The capitals and regions not only differ in the percentage of online shoppers, they also differ by the amount of the online spending. In 2011, the online shoppers from the capitals (Moscow and Saint-Petersburg) spend on average about two times more than users from the regions – around 15,000 rubles versus 7,000 rubles in a six-month period. That is the reason, why the two capitals accounted 55% of market turnover.4
In 2011 the sale volume of E-Commerce in Russia was similar to one in Italy, Spain or Bazil, but it is significantly behind of the USA and Europe sales. In comparison, the share of online retail in total retail amounted in the USA and the most Western European countries is between 7% and 9%, and in Russia only 2%.5
Market Growth Forecasts
There is an expectation that there would be a 2.5-fold market growth between 2010 and 2015. Moreover, the total e-commerce amount could be somewhere between 690 billion rubles and 900 billion rubles in 2015, at 2010 values. This represents 5% of total retail volume in Russia. Just for reference, the same level of e-commerce existed in the USA in 2008, Russia is behind approximately 10 years. It is expected that the fastest growth rate 3.6 fold or more will be found in the regions, with a flow of considerable new Internet users until 2015.6
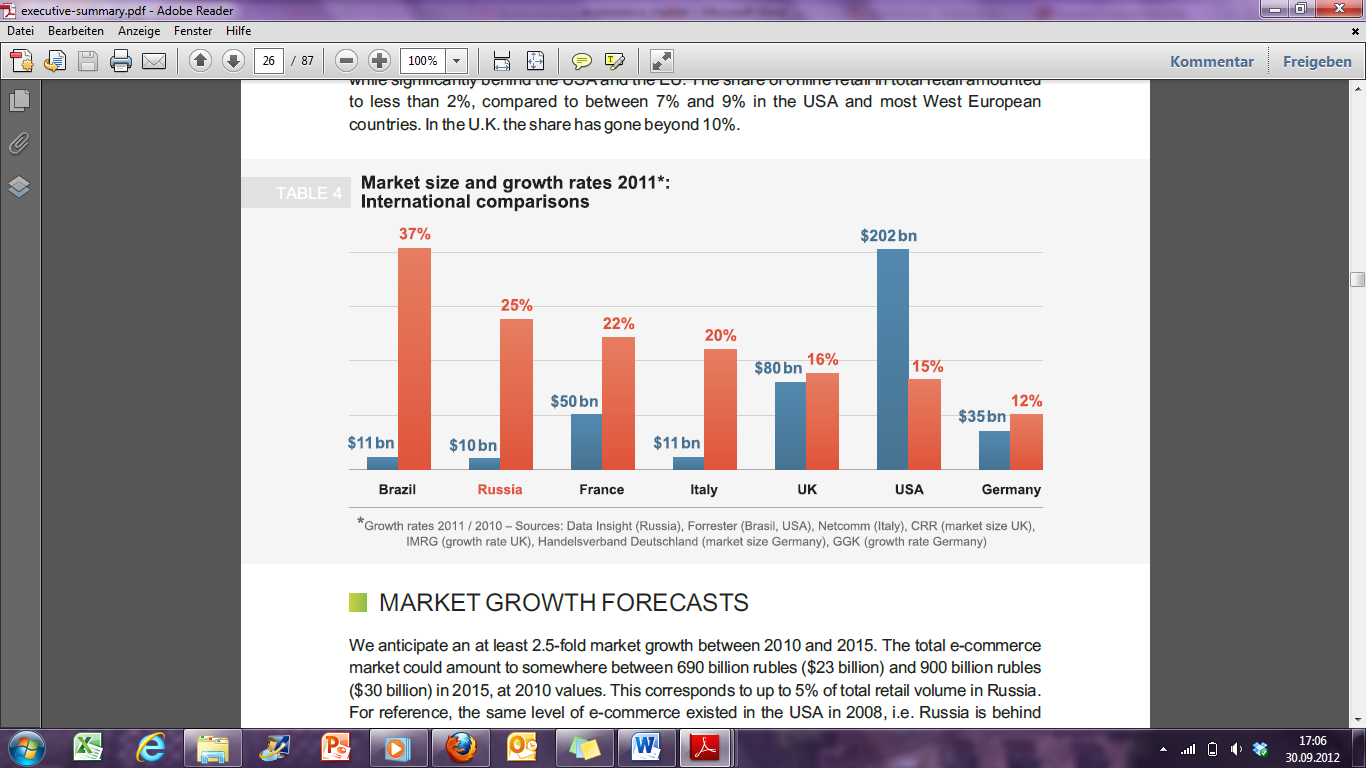
Picture 1 Market size and growth rates in 2011
Online Customers
In 2011, Data Insight counted 18 million online buyers (sixth month basis) consisting of approximately 30% of Russian Internet users and 15% of the Russian adult population. Due to detailed gender gap analysis there is no gap, but there a little variations in the online shopping behaviour between man and women. Differences can be recognized among age groups, the core customer group consist of people from the age between 18 and 44, and the differences are also reflected in the average spending.7
The most popular physical goods bought online are apparel and footwear, books, consumer electronics and computer hardware, cosmetics and beauty products, as well as home appliances. Moreover the customers prefer air and train tickets in the group of digital products, as well as event tickets and software. On daily deal and group buying sites, which are very popular in Russia the services or good most in demand are: beauty, service, entertainment and sports, dining and travel.8
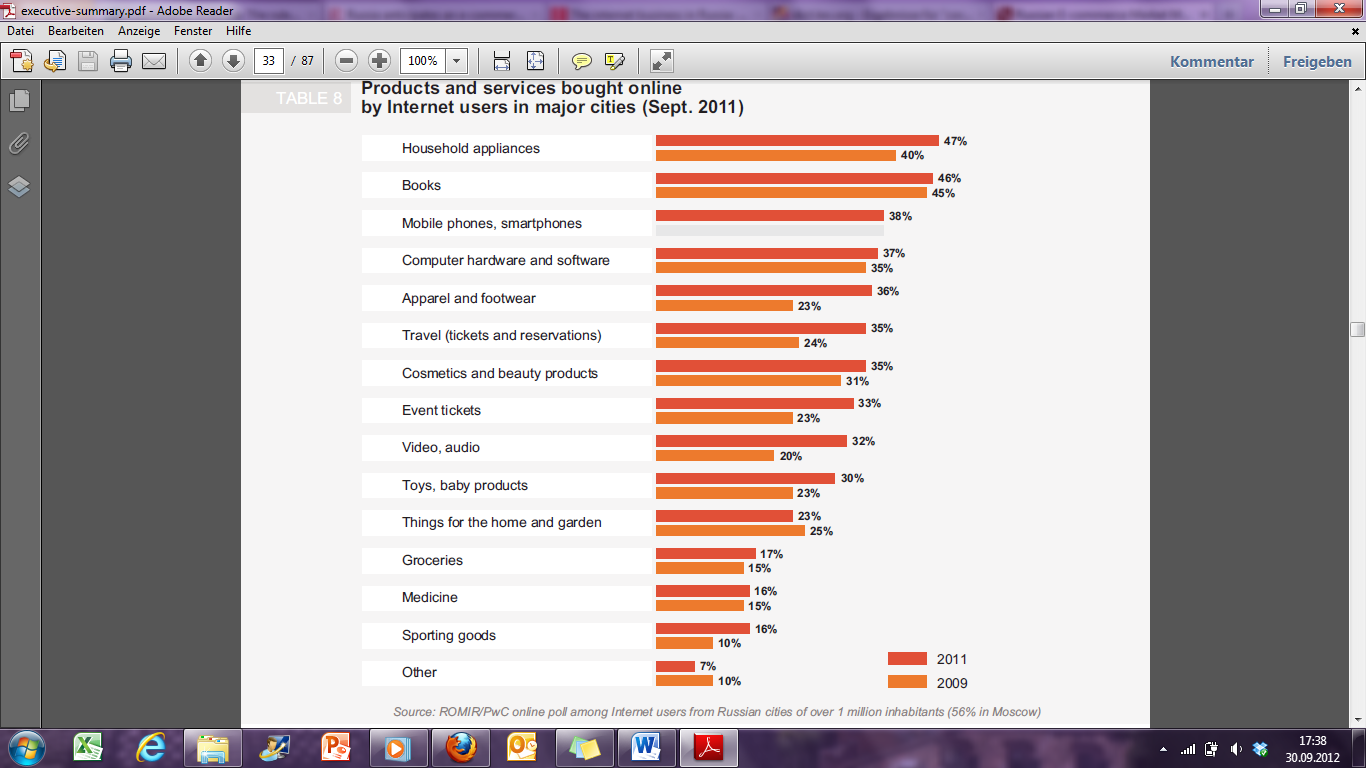
Picture 2 Ranking products and services bought online
Furthermore, according to different surveys, users prefer fast and comfortable delivery, lower prices, as well as satisfactory price and product information on the website. There could be some variations according to different user income. The high income group attach less importance to the cheapest price and focus more on comfortable delivery and trust. The main causes for dissatisfaction are the price, product information on the website, pricing as well as deliver conditions. The key issue for all online shoppers is that they can trust the online retailer.9
Main players
R
 ussian
companies dominate the Russian online retail market. For example
Yandex gets about 60% market share of online searches, while Google
only attract about a quarter, but its share is growing. Mail.ru is
currently the biggest e-mail service and gaming portal in Russia.
They also own 40% of Odnoklassniki, the second biggest social
network, and 40% of VKontakte the biggest Social network. Facebook
is only lies on the fourth place.
ussian
companies dominate the Russian online retail market. For example
Yandex gets about 60% market share of online searches, while Google
only attract about a quarter, but its share is growing. Mail.ru is
currently the biggest e-mail service and gaming portal in Russia.
They also own 40% of Odnoklassniki, the second biggest social
network, and 40% of VKontakte the biggest Social network. Facebook
is only lies on the fourth place.Furthermore, Ozon is the Russian answer to Amazon and Expedia and has the biggest market share in this sector. (The Economist (2012)) Even those that have formed alliances with Russian companies, likes Groupons’s partnership with Mail.ru, don’t have so much market share than their Russian competitors. In Russia global hegemony doesn’t count so much, so it isn’t a surprise, that Russia as the last Internet frontier of Europe.10
Trends

Picture 3 Foreign vs. Russian online retailers
There are a lot of trends for the Russian E-Commerce market. First of all the most important trend is, that the market will grow, by at least 25% per year. This would double or triple the sale of the online retailers.Second, the regions buy not so much online than the capitals, but this begins to change. The retailers gain more than half of their sales from the regions. Third, major offline retailers also start to enter the E-commerce market while online-offline concepts multiply. Fourth, the investment activities are increasing fast, on the other hand the exits are still exceptions and this situation wouldn’t change.11
Fifth, due to the fact, that logistics and delivery in the regions are the bottleneck of the companies, large retailers tend to build their own capacities in the regions. Sixth, cash on the delivery is the major way of paying, but the retailers find ways to cope with it. Seventh, there is big lack of good qualified employees for the entire Internet industry.
Last but not least is that the cross boarder sales increased constantly over the last few years, but foreign retailers are still confronted with two major walls: customs clearance and delivery across Russia.
Russian market and amazon.Com
Russians still pay in cash
To sustain online sales growth, Russia must address its poor financial and logistics infrastructure. Russians primarily buy with cash, as only one in five households has a credit card.12 Sometimes they do this at automatic kiosks made by QIWI, another Russian firm. Russians also like to be sure that their goods will turn up—and that they like them—before handing over their money. Sometimes they order from several suppliers and buy from the one that gets there first. Four-fifths of stuff bought from Ozon is paid for in cash on delivery.13
Figure 4 displays the distribution of customers’ awareness and major payment methods in the biggest and most advanced (technologically) city of Russia – Moscow. Even there only 29% of customers pays their purchases by a credit card.

Picture 4 Awareness and use of electronic payment methods among Moscow inhabitants (Feb. 2011)
In addition, the country is heavily reliant on rail for transporting goods, so products ordered online may take a week or longer for delivery to the outer provinces. As a result, 70 percent of Russia's e-commerce sales are concentrated in Moscow and St. Petersburg, and 20 percent are in second tier cities that have more than 1 million people.
Russia's e-commerce market is hampered by poor digital consumer protection laws and active, regular censorship of digital content, so the key to growth is building trust with Russian consumers. This is most often done through promotions and customer service. Ozon, for example, operates a 24-7 call center to field inquiries and M.video offers a 5 percent discount for online credit card orders.14
Customs Issues
Customs officers sorting through packages that are waiting for the go-ahead to be delivered. An astounding 13 forms need to be filled out for a shipping container from the United States to enter Russia, according to a World Bank investigation last year. By comparison, fellow BRICS nation India requires nine forms, while Mexico seeks five and France two.
The world’s biggest online retailer, Amazon.com, offers shipping to practically anywhere around the world, from Antarctica to Zimbabwe. But not in Russia.
It’s not because of a lack of enthusiasm for online shopping in Russia, where e-commerce has grown by leaps and bounds to top $8 billion last year. The problem is with long delivery times and regular gridlock at notoriously inefficient customs checkpoints — barriers that threaten to constrain further growth.
It takes an average of 36 days and $1,850 to get a container from the United States to Russia. These shipping troubles landed Russia in a dismal 166th place among 183 countries on the World Bank’s Trading Across Borders list. The Russian Post and the Federal Customs Service have reiterated promises to ease the shipping process and pointed the finger at each other for the difficulties. But frustrated shippers like Amazon, meanwhile, have limited or closed their Russian operations altogether. Amazon on its web site offers only priority shipping to Russia, which usually costs about the same as the purchase itself, and it ships only books, DVDs, VHS videos and music. People cannot order goods such as electronics, health-care products or children’s toys.
The shipping process was smoothed out temporarily last year when customs hired extra officers and extended their working hours, but at the start of this year Russia’s online shoppers were hit by a new wave of delays. “Our main delivery partner EMS stumbled at New Year’s, with delays of up to a month,” said Aaron Block, CEO of online retailer Bay.ru. EMS is the express delivery branch of the Russian Post.
Post Blames Customs
The postal service is the most obvious suspect, but its regular clients, both retail and wholesale, are mostly content with its current performance.
In a bid to smooth parcel deliveries, Russian Post/EMS, which remains the country’s biggest delivery service, announced in March that it was holding talks with online retailers to electronically regulate parcel data. Half of international deliveries get stuck at customs because the attached forms to determine weight, value and size of a shipment are filled out incorrectly.
Customs Blames Post
The Federal Customs Service said all international deliveries with correct paperwork are processed within a day and whatever delays happen are likely the fault of the postal service.
“The responsibility for loss of international mail, damage, incorrect packaging, non-delivery or breach of terms of sending international mail, lies with the postal administrations under the provisions of the Universal Postal Convention,” the customs agency said in an e-mailed statement. But it did not comment on the meticulously detailed customs forms, which shippers say are a guaranteed source of headache for anyone who tries to get their belongings over the Russian border.
The problems are not limited to overly detailed forms of UPS. Other issues include gaps in customs legislation, total control rather than control based on risk assessment, not enough customs employees to cope with the volume of customs declarations, and low work productivity. Customs has been focusing on easing regulations, implementing about 50 new rules on express deliveries in recent years aimed at streamlining the process.
Who Takes an Advantage?
One man’s delay, however, is another man’s business opportunity. At least, this is how it is for Aaron Block, whose company, BayRu, specializes in shipping things to Russia. While the business is tricky, it also offers huge opportunities, precisely because the shipping difficulties scare off competitors in a relatively embryonic market.
BayRu basically acts as a middleman between online behemoths such as Amazon and eBay and Russian consumers. After an order is placed from the site’s massive catalogue, which features products from a bevy of American retailers, the item is shipped from, say, Amazon to BayRu’s warehouse in Skokie, where it’s re-packaged for shipping to Russia via carriers such as USPS, FedEx, and UPS.15
Repackaging, the company has found, is crucial if orders are to survive the journey to the some 160 cities the company services in both Russia and former Soviet republics such as Kazakhstan and Azerbaijan.
The language barrier can limit foreign online sales, and for a country still rife with fraud and corruption, trust in online transactions is hard to come by. On top of that, cash is still king in Russia. “E-commerce is still very much a COD market,” Block says. “Credit card penetration is still very, very low.” To deal with this, BayRu works with a network of some half-million payment points where customers can put down cash for BayRu purchases.
Still, such companies as BayRu charges a healthy premium for getting goods through customs, and standard shipping time is about a month.16
Theory 1. Swot-analysis.
STRENGHTS
WEAKNESSES
Stable position on the market, strong brand and great level of experience.
Extending product line through strategic acquisitions
The strong position of Kindle on the market of e-books
Cultural clash
E-payments
Poor delivery system in Russia
OPPORTUNITIES
THREATS
Growing market of online retailing and e-books in Russia
Cooperation with authors and publishers
Russia’s entry into WTO
The increase of average salary rates in Russia
Customs rules
Customers’ loyalty to current main players
Unstable economic and political situation
Strengths
Stable position on the market, strong brand and great level of experience.
Now Amazon is the largest player on the market of online retailers. In 2010 it had the revenue of $34,204 million which is much bigger than the revenue of its closest competitor eBay with revenue of $9,156.3 million. Last year Amazon captured the 270th position in the Fortune’s Global 500 and 78th position in the Fortune 500 list of largest corporations in America.
High inventory turnover ratio allows Amazon to generate revenue from sales before its payments to suppliers come due. Additionally lower prices act as a compelling proposition in attracting more customers. The online retail format also enables Amazon to enhance customer satisfaction as it offers customers with broader selection and greater access to information. Amazon.com is one of the first movers which managed to take an advantage of Internet potential and the company used the opportunity to dynamically interact with a great number of clients. Leading and very stable market position enables Amazon to target a larger customer base. Thanks to well-developed recall system this organization has a very high level of customer loyalty throughout the World.
Owing to good relationships with suppliers Amazon products of Amazon are delivered in due time, which strongly reflects on company’s reputation.
In comparison with other online retailers, the considered company has a giant experience. Being presented in the market from 1995 company became the first retailer which serviced on-line. So Amazon management team owns very useful knowledge about specificity and other different aspects and tendencies of this market.
Extending product line through strategic acquisitions
Amazon has been expanding its business operations and product offering through various acquisitions. Among such acquisitions we want to strongly emphasize the merger of Zappos.com, an online retailer of apparel, footwear and accessories which gave Amazon the opportunity to sale goods of one of the largest shopping categories; the merger of Toucho’s technology and staff members into its Kindle hardware division. This acquisition expanded Amazon's platform to encompass more functionality and more content on Kindle. It also helps Amazon to address some of the form-factor issues with the Kindle. Further in October 2010, the company acquired BuyVIP.com, a fashion and lifestyle online buying community. This acquisition strengthened Amazon’s position in the retail of fashion apparel. This step helped Amazon to expand its consumer base, because BuyVIP.com has more than six million members in Spain, Germany, and Italy. The acquisition of Diapers.com in 2010 let Amazon to access an online baby care market. In addition, at the beginning of 2011, Amazon acquired the remaining shares in LOVEFiLM International, one of the leading European subscription entertainment service providers which offers online DVD, games rental-by-post, streams films and TV shows over the internet to personal computers, internet enabled TVs, and Playstation3.
The strong position of Kindle on the market of e-books
Thanks to the popularity and success of its e-reader device, Kindle, Amazon has been dominating on the fast-growing electronic book market through the past few years. In 2007, the company launched its e-reader, Kindle, in the US market. Kindle is Amazon's portable reader that wirelessly downloads books, blogs, magazines and newspapers to a high-resolution electronic paper display that looks like real paper. The US Kindle store offers over 950,000 books, which includes new releases and 109 of the 111 New York Times best sellers. Since the launch of the first version of Kindle in 2007, Amazon has launched other and more advanced versions of the e-reader device, including Kindle Touch, Kindle Touch 3G, Kindle Keyboard, Kindle Keyboard 3G. The latest in the list is Kindle Fire, launched in September 2011. Kindle Fire has a seven inch display and is sold for $199, compared with $499 for Apple’s cheapest iPad, Low pricing helps Amazon to attract more customers.
Weaknesses
Cultural clash
There are some cultural differences between Russia and the main market of Amazon the U.S. market. In Russia there is no equivalent of FedEx or United Parcel Service, which covers the whole Russia, so it is really tough for Amazon to deliver their packages in Russia on time. 17
Amazon also not provides a website in Russian, so it is really hard for Russians, who not speak English or another foreign language to order goods. Furthermore, not every Kindle provides Russian language and there are only a limited number of Russian books available in the online shop. The language is a reason why Amazon isn’t really popular in Russia, due to the fact that not everyone speaks English and this leads to lower interest in buying something at Amazon.18
Limited use of e-payments in Russia
Russians still prefer to pay in cash. Even if there is a small increase of online payment, the decrease in cash payment progress very slow. On the other hand various forms of electronic payment are in rise, but they are only used by a minority. There are some additional solutions to bank cards (the use of bank cards is growing slowly) which are intend to become very successful. Industry experts and e-commerce executives all predict that the use of electronic payments will continue to rise, with government encouragement, which will favour the development of online retail in Russia. Retailers especially those selling physical goods, like
Amazons main competitor Ozon.ru tend to believe today's situation will likely continue for the foreseeable future.19 The preference of Russians to pay in cash is a big weakness for Amazon, because they offer only credit card payment, bank account or their own gift card. So it is hard for them to purchase goods to Russia, due to their different payment habits.
Poor delivery system in Russia
The Russians are also not really trust the Russian post, so that is the reason, why Russians prefer, to get the goods delivered to the door and they really appreciate to receive the goods on time. So it would be very important, that Amazon establish warehouses in different parts of Russia and to develop their own logistic system or corporate with national courier service. But it is really expensive to build the warehouses, due to the fact that Russia is a big country, and it is really difficult to ensure that they deliver very fast to every part of Russia. It would be more expensive to establish a similar logistic system like in U.S. and could be therefore considered as a big weakness of Amazon. 20
In addition, the main potential rival, Ozon for 13 years of its operations has managed to build its own delivery system, which engages 3 thousand people and covers 70% of the Russian population (this system is used by 60 other companies).21 The system is rather expensive, but in the end it turns out to be even cheaper than services of the Russian Post that on top of everything else often loses track of parcels. Amazon, in contrary, cannot boast the same the same achievements.
Opportunities
Growing market of online retailing and e-books in Russia
According to the Federal Press and Mass Media Agency, legal sales of e-books in Russia increased almost 2.3 times in 2011, marking a third year of explosive growth, though remaining modest in absolute terms. The growth rate constitutes on average 120% per year, and for three years its volume has increased in 12 times. Sales of digital books stood at 135 million rubles ($4.4 million) in 2011, compared to 60 million rubles in 2010 and 11 million rubles in 2008, the first year for which statistics are available, the agency said in an annual report on the book industry in Russia22.
Russians began to prefer books in electronic format, which influences the market of printed books. According Rospechat, 30% of adult residents of large cities read e-books which price is about 20% of the cost of paper books. E The most common method of selling e-book is through online shopping and aggregators of information resources (43%), through electronic libraries (32%) and through their own websites (18%).
According to Rospechat, the proportion of legal e-books will grow. As calculated in the department, in 2015-2017, the sales of legitimate e-books can reach 3 billion rubles, compared with 135 million rubles in 2011. Such forecast creates very pleasant position for Kindle sailings23.
Russian online retail market is growing by 25 per cent per year and according to predictions online retail market could increase up to 5 per cent in 2015 24. That creates a great opportunity for Amazon to be effective player on the Russian market.
Cooperation with authors and publishers
In America Amazon has well-organized partnerships with the authors of different editions. Amazon Publishing pays authors 45 percent to 50 percent of the selling price when at the same time other publishers grant publishers about 20 percent (see picture 1). This fact helps Amazon to conclude very sturdy relationships with authors.

Picture 5 Amazon’s cooperation with authors in the USA Source: L. Kirshbaum Amazon’s Hitman. A tale of books, betrayal, and the (allegered) secret plot to destroy literature. – January, 30- February, 5, 2012, Bloomberg Businessweek.
We believe, that such scheme will also be very reasonable in Russia. Keeping good relations with authors will allow to arrange special appointments between famous writers and their fans, which also will grant the additional level of customer loyalty and credibility.
Russia’s entry into WTO
To our mind, the fact that Russia became the member of World Trade Organization would able to simplify the business of Amazon in this country. Amazon’s products will be more competitive in terms of price which in turn will provide a great number of customers for the company and will help to gain significant market share.
The increase of average salary rates in Russia
Thanks to the fact that salaries in Russia are getting higher, the conditions of life in the country are becoming better and purchasing power is growing as well. So potential clients get the good chance to buy more expensive product and the demand for foreign production will surge, and the Amazon products will stay very competitive.
Threats
Customs rules
13 forms need to be filled out for a shipping container from the United States to enter Russia, according to a World Bank investigation last year. By comparison, fellow BRICS nation India requires nine forms, while Mexico seeks five and France two. It takes an average of 36 days and $1,850 to get a container from the United States to Russia. These shipping troubles landed Russia in a dismal 166th place among 183 countries on the World Bank’s Trading Across Borders list.
It makes almost impossible for Amazon to provide fast delivery for Russian customers. But the simplicity and speed of purchasing process are in the list of the main features which compose company’s competitive advantage.
Lately, customs has been focusing on easing regulations, implementing about 50 new rules on express deliveries in recent years aimed at streamlining the process. But still, this process of improvement can last for a long time.
Customers’ loyalty to current main players
In all segments of electronic market from searching systems to online shops Russian companies dominates the market. For example, despite its best efforts, Google with just 27% market share has been forced into the unfamiliar position of playing second fiddle to Yandex, its Russian contemporary which holds a comfortable 61% share. The same situation with Amazon.com and Russian leader of online retail market – Ozon.
Ozon announced six-month results that show continued growth: they are up 78% on last year to $232 million (91% up in rouble terms to R7.1bn); these are pro-forma figures that are adjusted to include its acquisition of shoe/accessory site Sapato in February. It’s relatively little compared to Amazon, which posted revenues of $12.8 billion for last quarter. But Ozon is growing faster at the moment, and as Gavet points out, Russia is still a largely untapped opportunity: less than 20% of Russia’s population shops online at the moment.25
Unstable economic and political situation
In these latter months in Russia political situation is fairly unstable (more preciously, from December) due to a lot of anti-government rallies. The biggest ones took place, of course, in Moscow – on the Bolotnaya and Manegnaya Ploshyad’, on Poklonnaya Gora, as well as a series of rallies held in St. Petersburg.
International new ventures theory. Application to amazon.Com
The authors identify international new venture as a business organization that, from inception, seeks to derive significant competitive advantage from the use of resources and the sale of outputs in multiple countries. In contrast to organizations that evolve gradually from domestic firms to MNEs, these new ventures begin with a proactive international strategy. However, they do not necessarily own foreign assets; in other words, foreign direct investment is not a requirement. Strategic alliances may be arranged for the use of foreign resources such as manufacturing capacity or marketing26.
The foundation of the theoretical framework proposed is traditional in its reliance on transaction cost analysis, market imperfections, and the international internalization of essential transactions to explain the existence of the MNE. However, the framework also incorporates recently developed ideas from entrepreneurship scholars about how ventures gain influence over vital resources without owning them, and from strategic management scholars about how competitive advantage is developed and sustained. Together, all these elements describe the international new venture as a special kind of MNE27.
Element 1: Internalization of some transactions
The internalization element is most basic and is clearly part of traditional MNE theory. Organizations form where economic transactions are inefficiently governed by market prices (Coase, 1937; Williamson, 1985); in other words, where market imperfections exist. It is the defining element of all organizations, whether new or established, domestic or multinational.
When the transaction costs of constructing and executing a contract and monitoring the performance of the contracting parties are at their lowest in an organization, its hierarchical authority (not market prices or a hybrid contract) will be the governance mechanism chosen, and the transaction is said to have been internalized within an organization.
Amazon: Despite the fact that Amazon as highly automated logistics system with their own warehouses throughout the world, the company practically outsources delivery function (to DHL or FedEx) and then the company uses their own expertise in integration of storage, transportation and demand management functions altogether.
Element 2: Alternative governance structures
A major feature that distinguishes new ventures from established organizations is the minimal use of internalization and the greater use of alternative transaction governance structures. Due to their poverty of resources and power, new ventures may even use such structures when the risk of asset appropriation by hybrid partners is high. Hybrid partners share complementary assets to their mutual benefit.
In contrast to organizations that evolve gradually from domestic firms to MNEs, these new ventures begin with a proactive international strategy. However, they do not necessarily own foreign assets; in other words, foreign direct investment is not a requirement. Strategic alliances may be arranged for the use of foreign resources such as manufacturing capacity or marketing.28
Amazon: Amazon is actively using the strategy of cooperation. First, Amazon provides warehousing and order-fulfillment for third-party sellers. Second, Amazon provides the right for other retailers to operate on Amazon.com. They have an opportunity to independently conduct their pricing policy and govern their special conditions of selling and delivery. Therefore, more than one seller can be responsible for trading the same product. In addition, the company establishes strong relationships with books’ authors, on one hand, offering them higher share in sales of their books (in comparisons with publishing houses), and on the other – widening product range (e-books and printed books) of the website for customers.
Element 3: Foreign location advantage
The location advantage element of the framework distinguishes international from domestic organizations. Essentially, firms are international because they find advantage in transferring some moveable resources (e.g., raw material, knowledge, intermediate products) across a national border to be combined with an immobile, or less mobile, resource or opportunity (e.g., raw material, a market).
However, a firm conducting transactions in a foreign country has certain disadvantages vis-a-vis indigenous firms, such as governmentally instituted barriers to trade and an incomplete under-standing of laws, language, and business practices in foreign countries. As noted earlier, MNEs have often relied on the advantages of scale to overcome such obstacles. But international new ventures must usually rely on other resources.
Private knowledge is the most obvious alternative, and it has some interesting properties. The property that provides location advantage for modern MNEs, including international new ventures, is the great mobility of knowledge once it is produced. With modern communication infrastructures, valuable knowledge can be reproduced and can travel literally with the speed of light at minimal marginal cost.
Amazon: The company is just crazy about customer’s needs. Amazon.com applies a lot of features to satisfy customers’ needs and to simplify the whole ordering process: customer product reviews, multi-criteria ratings, individual recommendations based on previously purchased items, the option "Frequently Bought Together" and inline search. However, the company does not have any knowledge of Russian culture: it has to handle language issue (there is no website in Russian), the fact that credit-card usage habit is not common practice (and even vice versa). The following chapter of our work will provide Amazon’s internationalization practices. For Example, Chinese case is very similar to Russian and the company solved the problem of market penetration by acquisition of the main domestic player. In addition, the advantages, described above were copied and implemented by the main domestic players of Russian e-commerce market.
Element 4: Unique resources
The first three elements define the necessary conditions for the existence of an international new venture: internalization of some transactions, extensive use of alternative transaction governance structures, and some advantage over indigenous firms in foreign locations. However, these are not sufficient conditions for sustainable competitive advantage.
Sustainable competitive advantage for any firm requires that its resources be unique (Barney, 1991). Unfortunately, for the knowledge-based international new venture, knowledge is at least to some degree a public good. Knowledge may not remain unique for long. Thus, the ability to reproduce and move knowledge at nearly zero marginal cost is a simultaneously beneficial (as noted in Element 3) and troublesome property. The international new venture must limit the use of its knowledge by outsiders in many countries for it to have commercial value.
Amazon: The unique resources Amazon have and can be proud of: the expertise to build high-quality logistics systems and to establish relationship with other retailers and books’ authors to offer these products to customers at the best possible price. The problem with Russia is that Amazon does not have its own established logistics and it cannot organize delivery to every part of such a big country as Russia.
Types of international new ventures
New international market makers (Figure 3, quadrants I and II). New International Market Makers are an age-old type of firm. The most important value chain activities and, therefore, the ones most likely to be internalized are the systems and knowledge of inbound and outbound logistics. Transactions involving other activities tend to be governed by alternative structures. Direct investment in any country is typically kept at a minimum. The location advantage of such new ventures lies in their ability to discover imbalances of resources between countries and in creating markets where none existed.
Sustained competitive advantage depends on (1) unusual abilities to spot and act on (sometimes by charging high fees) emerging opportunities before increased competition reduces profits in markets they had previously established, (2) knowledge of markets and suppliers, and (3) the ability to attract and maintain a loyal network of business associates. New International Market Makers may be either Export/Import Start-ups or Multinational Traders. Export/Import Start-ups focus on serving a few nations with which the entrepreneur is familiar. Multinational Traders serve an array of countries and are constantly scanning for trading opportunities where their networks are established or where they can quickly be set up.
Geographically focused start-ups (Figure 3, quadrant III). Geographically focused start-ups derive advantages by serving well the specialized needs of a particular region of the world through the use of foreign resources. They differ from the Multinational Trader in that they are geographically restricted to the location of the specialized need, and more than just the activities of inbound and outbound logistics are coordinated. They differ from the export/import start-up only in the latter respect. In other words, competitive advantage is found in the coordination of multiple value chain activities, such as technological development, human resources, and production. Successful coordination may be inimitable because it is socially complex or involves tacit knowledge. That advantage may be further protected by a close and exclusive network of alliances in the geographical area served.

New international Market Makers
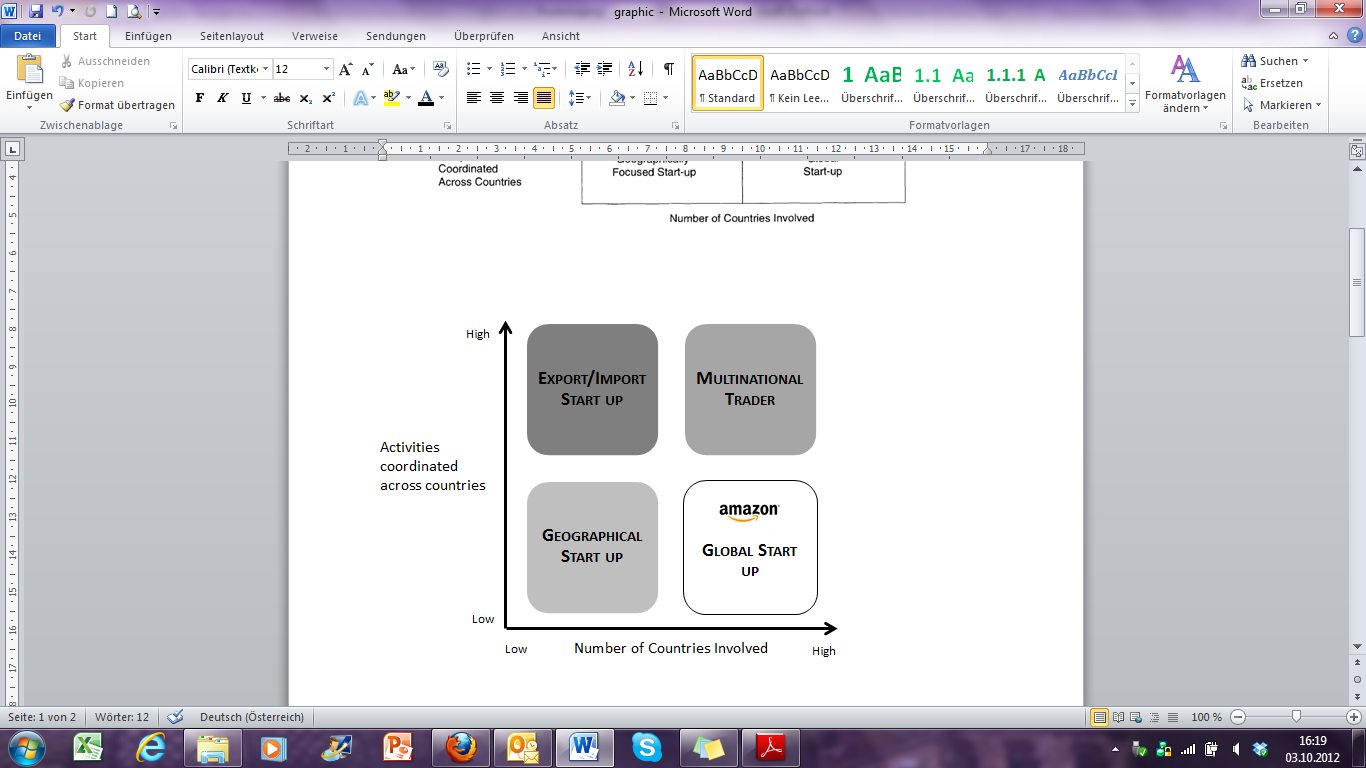
Picture 6 Types of International New Ventures and Amazon.com place. Source: Benjamin M. Oviatt and Patricia Phillips McDougall, Toward a theory of international new. – Journal of International Business Studies, Vol. 36, No. 1 (Jan., 2005), Oxford University Press, UK.
Global start-ups (Figure 3, quadrant IV). The phrase 'global start-up' is used because it is a common term of trade. It is the most radical manifestation of the international new venture because it derives significant competitive advantage from extensive coordination among multiple organizational activities, the locations of which are geographically unlimited. Such firms not only respond to globalizing markets, but also proactively act on opportunities to acquire resources and sell outputs wherever in the world they have the greatest value. Global start-ups may be the most difficult international new ventures to develop because they require skills at both geographic and activity coordination. However, once successfully established, they appear to have the most sustainable competitive advantages due to a combination of historically unique, causally ambiguous, and socially complex inimitability with close network alliances in multiple countries. Amazon company can be classified as Global Start-up.
Strategies of amazon.Com on national markets
The main feature of Amazon.com strategy is orientation on customer. The strategy is aimed at strengthening company's position and its development through continuous expansion and diversification. The company has built its business on the strong brand, growing customer database and innovative technologies.
Amazon’s business model creates customer value by providing the combination of the following benefits: easy product selection and purchasing process, speed, comprehensive information helping in decision making, a wide product selection, low price, reliable order processing and quality assurance.
Any of the elements of this business model, taken separately, cannot create a sustainable competitive advantage. Only the combination of all these features – information services, logistics and order processing – creates a unique value for customer and competitive advantage forAmazon.com.
Amazon provides business reporting, dividing all its operations into two regions: North America and International markets. In North America, Amazon operates through two web-sites: the main International (American) web-site – Amazon.Com and the web-site in Canada – Amazon.Ca. International market covers the remaining seven sites. It should be noted that each site is running on the foreign language of its home country, and all prices are presented in local currency.
Entering the u.S. Market
Amazon.com was founded by Jeff Bezos in 1994 and its website went online on the U.S. market in 1995. The company started off as an online bookstore but soon began selling other products as well. When entering the US market the company emphasized its wide product range The Seattle-based company offered more than one million different titles, 40 times more than typical mall bookstores, and more than 5 times as many as the country's largest book superstores. Amazon also stressed out the usability of the online bookstore: a customer was able to order products 24 hours a day, seven days a week, he can easily and quickly find and order any book, and Amazon will deliver it within 3-4 days29
Amazon.com always seeks to be the world's most customer-oriented company even at the very beginning its main target was to reduce the delivery costs. Therefore the company significantly expanded its US distribution infrastructure with the addition of new distribution facilities in Seattle, New Castle, Fernley Coffeyville, Kempbelsvil, Lexington, Macdonough and Grand Forks. 30It is interesting that, for example, warehouses in Fernley and in Newcastle were designed to reduce sales taxes. Domestic transport and distribution of goods were also attached with great importance. Warehousing costs were originally built into the price which was shown to a customer. 31
Agreements between Amazon and different websites, TV- programs and web- searchers can be treated as main driving force of the company. In 1997 Amazon and Netscape Communications Corporation made a strategic agreement. Under it, Amazon had an above-the-fold button on Netscape's popular Net Search page. This provided easy access for busy Internet users to search and browse Amazon's more than 2.5 million titles. In addition, Amazon.com received marketing and advertising within Netscape Netcenter. Specific feature of Amazon is introduction various innovations at the same time in all countries where it is presented. So, customers all over the world can enjoy all services of the company and get access almost to the entire range of products. 32
For over fifteen years, Amazon has been maintaining the loyalty of its customers, by launching new programs and expanding the product range. In 2007 the company released the only product under the Amazon's brand - hardware-software platform for e-book reading Amazon Kindle. In 2007, the product was sold out in a record-short time at a price of $ 399. In 2008, the Kindle price fell to 359 dollars, and later to 299. Amazon did benefit not from sales of the device, but because consumers buy Kindle books mostly from Amazon's bookstore - Kindle store. Thus, Amazon.com attached customers to their online store and in the long term profits compensated the low price of the device. 33
Amazon strives to Amazon strives to expand the scope of activities, not only by increasing the range and enter new markets, but also through the acquisition and development of new sites. In addition to the main site the company owns the following: www.shopbop.com, www.endless.com, www.zappos.com, Javari, www.a9.com, www.alexa.com and www.imdb.com and etc.34
Shopbop.com was bought in 2006 - it is an online store offering women's designer clothing and accessories. This site is based in the U.S., but ships to other countries as well.35 In 2007, the shoe site - Endless.com was created, but it was presented only in the United States. However, the online shoe shops have been opened in Japan, UK, France, and Germany, called Javari. 36In 2009, Amazon bought an online store- Zappos.com that specialized on shoes and accessories and served only in the U.S. market. 37For customer's convenience were opened sites which primary purpose was to assist clients in finding the right products for them. Thus, in 1999, Amazon opened Alexa.com and Imdb.com 2004 - A9.com.38
When Amazon has just appeared on the market of books, the company had no serious competitors, as there was no other firms influencing on the situation on the market. The most significant provider - the company Barnes & Noble - owned just one- tenth of the pie and also was not represented on the Internet. Although nowadays the book production is widely represented in the network such major companies as Barnes & Noble, as well as the second largest company - Borders, which went bankrupt in 2010, Amazon still enjoys the honorary right to be called a founder of networking industry. The company has expanded its product range, started selling CD, video production, toiletries, pet supplies and groceries, and began to provide services such as auction online and create greeting cards. This large scale has allowed the company to take up a leading position in the market, making it possible to compete with other firms in the network and beyond39.
Amazon operates on the rapidly evolving and intensely competitive market. The company indicates as its current and potential competitors the followings: physical-world retailers, publishers, vendors, distributors, manufacturers and producers of its products; other online and mobile e-commerce sites; media companies, Web portals; companies that provide e-commerce services; companies that design, manufacture, market or sell digital media devices and etc.40
Now in the context of developing Internet commerce main direct competitor of Amazon is eBay, which, unlike the Amazon is presented in 37 countries. However eBay operates by a somewhat different principle, acting like an intermediary between buyer and seller, guarantees execution of commitments and provides secure transfer of money. 41
Expansion into Europe. Case of Germany and the uk
In April 1998 Amazon launched its first international sites, Amazon.co.uk (United Kingdom) and Amazon.de (Germany). Strategies for entering a crowded e-commerce market of this two countries bear a great resemblance to each other.
Amazon began its expansion in the UK market through acquisition of Bookpages Ltd. (www.bookpages.co.uk), the UK's leading internet bookseller that submits more than 6 million titles and shipping to more than 100 countries. The new UK site propose more than 1.4 million titles, comprising all UK books in print (over 1.2 million titles - many unavailable in the US) and over 200,000 bestselling US-published titles. In terms of launching of a new joint website service offered everyday discounts of up to 40% off High Street prices on thousands of popular books. According to Dr Simon Murdoch, Managing Director of Amazon.co.uk this project was an absolutely new concept in shopping convenience for anyone and everyone in the UK.42
In 1998 Amazon.co.uk has concluded several agreements with various online companies to expand their activities. Amazon.co.uk has signed a contract with Virgin Net naming Amazon.co.uk as the exclusive supplier of books on Virgin's online service. According to the agreement, Amazon.co.uk got online Virgin Net right to post in a prominent placement through specific links that lead to Amazon.co.uk, and the ability to advertise throughout the site its products plus different range of new and unusual promotions including interactive demos in its free trial starter packs . This agreement allows Amazon to expand the audience and to draw Virgin's visitors attention its service. In 1998 Virgin Net had tens of thousands of regular visitors to its site, attracted by the wealth of UK exclusive content provided to consumers.43
In October 1998 the Internet bookstore Amazon.co.uk announced that it will join with the Sky News Book Show to make books featured on the popular program easier and more convenient to locate and to buy. Under the agreement, Amazon.co.uk sponsored the Book Show three times a week for a six-month period, and it included a 15-second spot at the beginning and end of each show with five-second break bumpers. This is the first-ever television sponsorship in the UK by an online company.44
In November 1998 Amazon.co.uk and Associated New Media (ANM) made an agreement naming Amazon.co.uk as the exclusive bookseller across ANM's award-winning websites. According to the terms of the agreement, UKplus gave visitors of their sites the opportunity to choose from Amazon.co.uk's 1.4 million titles. There will be easy access to this huge selection of books at everyday low prices via specific content links, buttons, banners, and promotions across all three sites.45
In 1999 Amazon.co.uk launched two services - Amazon.co.uk Auctions and Amazon.co.uk zShops .Amazon.co.uk customers gain the access to an additional half a million items from these new services. From this moment customers can not only find, discover and buy items in the store, but they also took the chance to sell their own items via auctions or zShops to the biggest and most experienced base of Internet shoppers. 46In the same year but a little bit later this two services started to operate in Germany.47
In 1999 Amazon.co.uk and Amazon.de started to offer its customers music goods48.
In Germany, Amazon acquired ABC Bucherdienst, after that project Amazon.de was launched. Amazon.de offers fast and free shipping to Germany, Austria, Switzerland, Luxembourg and Liechtenstein, as well as a 30-day money back guarantee for any reason, on the assumption of books’ excellent condition. Amazon.de also provided the ability to purchase gift certificates.49
The intensive development of the Amazon.de began in april 1999, from the offer to all site’s owners to create a partnership with the German Amazon, implying advertising Amazon.de by other party on their web pages. In 1996, the program was first introduced and successfully implemented on Amazon.com. Since then more than 230,000 partners worldwide were benefited from the program, and Amazon gained new customers. Due to the success of the program in the United States the same approach was implemented for Amazon.de in Germany.50
The main reason for entering the European market was the need to manage the company in the local markets in order to reduce the cost of books and other items through the elimination of the costs of shipping goods from the U.S.51
In connection with entering new markets two distribution centers were opened in the UK and in Germany. For 1999, the company has leased office space in these countries, the total area of 121,000 square feet of warehouse space and 690,000 square feet. 52Expected that these warehouses will serve not only the markets of these countries, but also markets of nearby countries. In the U.S. eight centers were opened. In aggregate distribution centers occupy 4,000,000 square feet of warehouse space. In 2000, Amazon UK rented additional warehouse of 500,000 square feet53. By 2011, the number of warehouses in the UK has risen to seven, and in Germany - to 4. In 2000, customer service centers were opened in the UK, Germany, Regenburge and the Netherlands54.
Agreements signed in 1998 - 1999, initiated the start of development of Amazon in the UK and Germany and in Europe in general. The company's strategy in these two countries is identical and implied access to the European market through extensive acquisitions and agreements with companies that can promote online retailer. Amazon follows this particular strategy till now.
French Market
Amazon.fr was set up in August 2000 in France. It is the third website of the Amazon.com Company in Europe. This time the company made its own website instead of purchasing already existing ones. This action that had not been taken by Amazon.com previously made its policy in France different from the company’s strategies in the others European markets. There are several reasons of this new course. First of all, the lack of appropriate websites in France could be an important cause. Secondly, the company’s activities were broadening and simple purchasing of web book stores with further introduction of new products and functions as it was made in Great Britain and Germany was not enough in this case.
Entering to electronic commerce market in France, Amazon.com offered not only books but music video and DVD also. In 2001 Amazon.fr in cooperation with American Amazon web sites began selling software and video games as well.
The company leased two premises – an office in Jeancourt and a storehouse in Orleans. Furthermore the Amazon Company purchased storage facilities in Blagny-sur-Brion, Saran, Loyre, Montelimar and Drom. Amazon.fr is destined for Belgian and Netherlandian customers.55
Italian and Spanish markets
In 2010 the third European Amazon.com web site called Amazon.it was set up in Italy. Amazon.es was founded in Spain one year later in September. This expansion was caused by the increased demand for Amazon services both in and out of Europe. The sites were developed in an independent way from the very beginning. It means that Amazon did not purchase already existing web sites but started their activity from the blank page. It should be noted that the Amazon Company had already have operating web sites in Europe that time thereby Amazon.it and Amazon.es were set up adopting other European sites’ practices. They offer the same choice of the goods as in the USA but a bit more specific orientated towards Italian and Spanish markets.
In Italy the storehouse was opened in Castel San Giovanni. As Amazon.es was set up not long ago the information about it is very limited. 56
The Market of Canada
In June 2002 Amazon.com set up a new North American web site in Canada – Amazon.ca. It offered a big choice of items – more than 1,5 million of books, CD, DVD, videos, both in English and French. Moreover Amazon.ca made it possible not only to make bargain purchases but also to get a free delivery if the price of the order was to the sum of 75 Canadian dollars or higher. The site was supposed to serve not only Canadian market but in addition to export its items widely abroad.
The fact that Amazon.ca did not have to involve the customers this time can be noted as Canadian web site’s specific feature. The point was that people who had used Amazon.com previously used the new site now. Amazon.ca enabled to reduce costs for goods delivery and to broaden a range of items orientating it toward Canadian market.
Amazon has only one storehouse in Canada. It is situated in Mississauga, Ontario. Amazon.ca shares it with courier company called Assured Logistics (this arrangement has been made not for the first time; thereby the joint ownership of storehouses in the regions without great demand can be considered as a part of the company’s strategy).
The policy of Amazon.ca setting up was not standing out of the traditional Amazon.com course because in the time of Canadian site’s making the experience of previous sites’ formation was used.57
Expansion to Asia. Japanese Market.
In November 2000 Amazon.com set up a new web site Amazon.co.jp in Japan. The company refused to purchase all existing platforms as it was made in France. Amazon.com.jp entered Japanese market offering 1,7 million books in Japanese and English. This Amazon.com market of online trading became the largest international market with 193 thousands of customers and 34$ million budget. Soon Amazon.co.jp came to the fore in Japanese web trading. It was the first Amazon Asian web site and its fourth international one.
Japanese web site’s promotion was started with 30% discount for many items. The Amazon Company usually practices this policy of sale’s advancement when setting up new web sites. Besides that, the site offered free delivery during the first working year. At the same time Amazon.co.jp concluded a deal with several Japanese publishing houses for the purpose of broadening choice of books in respective departments.58
Chinese market
Amazon started its activities in China with purchasing of the biggest Chinese web store called Joyo.com Limited in 2004. It was founded in 200 offering a large choice of books, videos, DVD, video games, gifts and other goods. Thereby Amazon.cn was set up on the basis of Joyo.com. The benefit of such purchase consisted in the fact that Amazon.com entered Chinese market not having anything but having got loyal customers, the choice of items already existing and a partnership with the companies which promoted and serviced Joyo.com previously.
Amazon.cn storage facilities are situated in Guangzhou, Suzhou and Beijing.59
Results and recommendations
Each element of Amazon strategy is intended for a customer. Following this policy the company enters any web trading market in the world. The leadership in innovations’ sphere is the main advantage of Amazon.com strategy. These are innovations that make it possible to broaden the range of items, to offer new services and to reduce the prices.
When entering a market in a new geographical area Amazon.com follows one of the two approaches: either purchases already existing web site, as it was made in Great Britain, Germany and China, and makes its Amazon site on the basis of an existing one; or it set up the business from total naught if there is no possibility to or necessity to buy a company, as it was in France, Japan, Canada, Italy and Spain. It should be noted that business specificity does not require the large developed system to organize a trade. For the web stores of such scale the limits are not essential at all.
Amazon improves its web sites at the same time. It means that if any new service like an auction is entered in the USA it will be entered in other Amazon resources in the near future.
Amazon.com enlisted the customer’s loyalty by creating the reputation of the “careful” company. The online store not only sells books, CD, video, pharmaceutical items and a lot of other but in addition it makes the customer to feel “at home”.
The main principles which are the company sticks to entering any international market are thrift, customer’s satisfaction and unless development owing to the consolidation of the brand, purchasing new companies and creating strategic alliances.
Russian website
The most important action for Amazon is to improve its own electronic resource in Russia. Firstly, Amazon should provide a website with Russian language, because a lot of Russians don’t speak English or another foreign language. It will help them to compete against their main Russian players as Ozon.ru. The customers got used to the Amazon design, because it is similar to the design of the national competitor. This design is approved all over the world, so the only important thing is that they translate it to Russian.
Due to the great development of the E-Book market in Russia, the company should keep in mind the Kindle selling’s and try to promote Russian books more. It could be an opportunity for Kindle to translate current bestsellers into Russian and to place advertisement of the bestsellers in Russian language on their homepage.
Customer service
Based on Brazilian experience Amazon can also use the import fee system in Russia, which will be very convenient for customers, because then they can be sure, that their order will be delivered and it doesn’t matter how long it takes or if the costs for the delivery increase. Furthermore Amazon will be able to deliver all items of their product range to Russia, so
The customers profit from a wider range of products in comparison with product ranges of Russian companies. Moreover, Russians prefer to pay in cash, so it would be a good idea to make cooperation with local providers of payment terminals so that they can pay their bill through the payment terminal. It is very important to say that Amazon mission strongly emphasizes the significance of in-time deliveries. This fact let clients to receive their orders faster. To ensure a quick and prompt delivery Amazon could start to supply Russia from the nearest established warehouse, for example they can send the goods from the warehouse in Beijing to the Region of Novosibirsk in Russia or they can supply Moscow or St. Petersburg from Europe. If this isn’t efficient enough they can build their own warehouses.
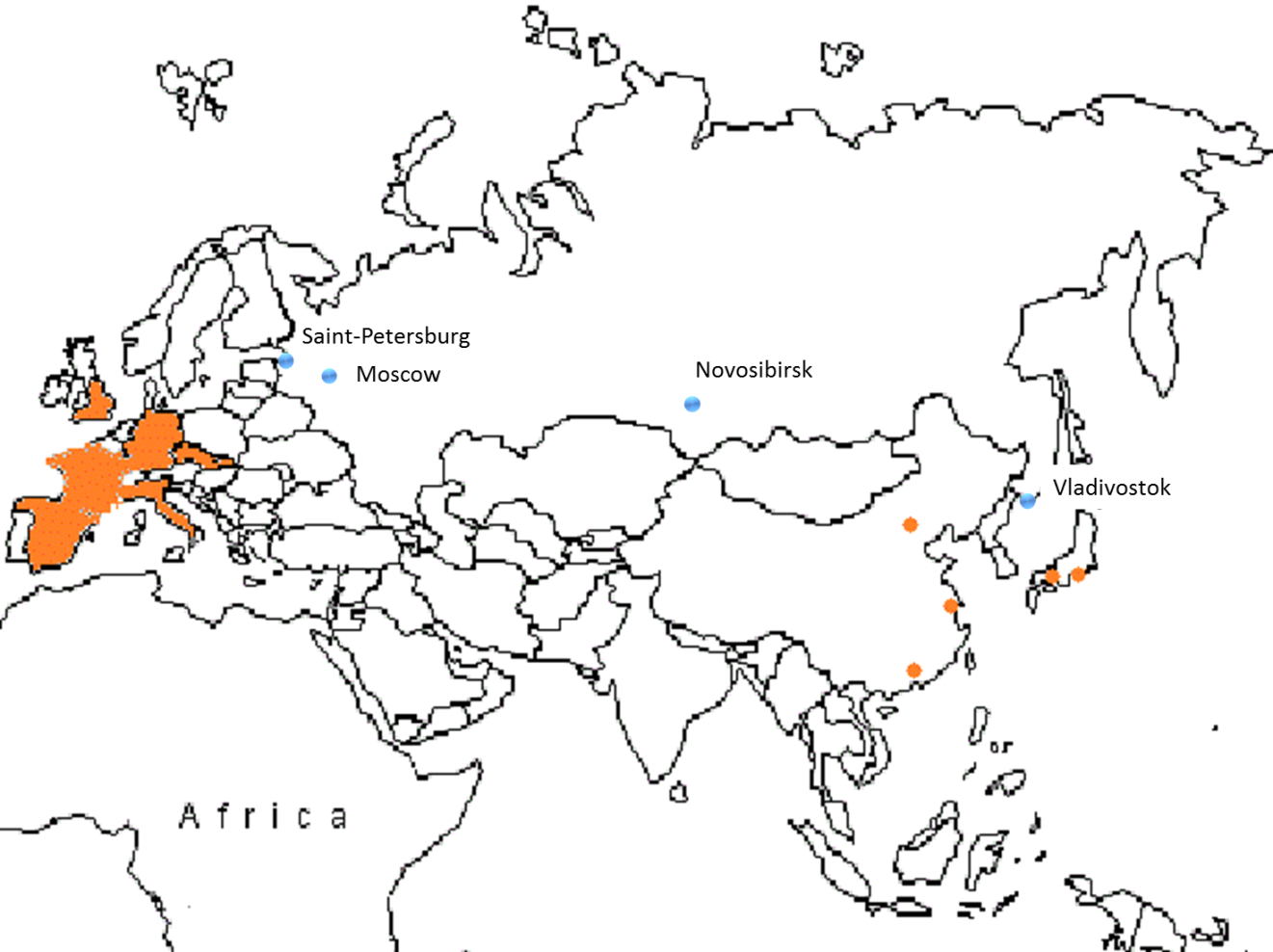
Picture 7 Location of the Biggest Russian Cities and Amazon's Warehouses
Suppliers
Amazon should try to improve their relationship with local suppliers and try to acquire more local suppliers and also authors. Because they currently have only few Russian products in their assortment.
Buying Ozon.ru
Our last recommendation is that Amazon can buy its main competitor Ozon.ru, as they did in China and they have now a bigger market share and also profit from the knowledge of their employees. But their market isn’t so big, because Chinese also prefer to pay in cash like Russian people. It could be really expensive to buy the main competitor and it isn’t ensured, that Amazon would be more successful in the Russian market.
Bibliography
Benjamin M. Oviatt and Patricia Phillips McDougall, Toward a theory of international new. – Journal of International Business Studies, Vol. 36, No. 1 (Jan., 2005), Oxford University Press, UK. p. 29-41
L. Kirshbaum Amazon’s Hitman. A tale of books, betrayal, and the (allegered) secret plot to destroy literature. – January, 30- February, 5, 2012, Bloomberg Businessweek.
Baiz, S. E‐Commerce in Russia: Accessing the Russian Market via the Internet [Electronic resource] // Department of Economics, Trinity College, Dublin. – 2012. – Access mode: http://www.languageconnections.com/descargas/White%20paper%20E%20marketing%20via%20the%20internet.pdf, free. – Accessed: 01.10.2012.
Europe’s great exception. Why local firms dominate the Russian internet [Electronic resource] // The Economist. – 19.05. 2012. – Access mode: http://www.economist.com/node/21555560, free. – Accessed: 01.10.2012.
Gavet, M. E-commerce in Russia: The rules are different [Electronic resource] // CNN Money. – 27.06.2012. – Access mode: http://tech.fortune.cnn.com/2012/06/27/e-commerce-in-russia-the-rules-are-different/, free. – Accessed: 01.10.2012.
Henni, A. E-Commerce in Russia [Electronic resource] // East-West Digital News. – August 2012. – Access mode: http://www.ewdn.com/e-commerce/executive-summary.pdf, free. – Accessed: 01.10.2012.
Mosmuller H. Amazon Will Deliver to Iraq Before Russia. [Electronic resource] // The Moscow Times. – 12.05.2011. – Access mode: http://www.themoscowtimes.com/news/article/amazon-will-deliver-to-iraq-before-russia/436669.html. – Accessed: 01.10.2012.
E-Commerce Is the Next Frontier in Global Expansion. [Electronic resource] // AT-Kearney. – June 2012. – Access mode: http://www.atkearney.com/paper/-/asset_publisher/dVxv4Hz2h8bS/content/id/351896. – Accessed: 01.10.2012.
Amazon's International Story: Margin Anchor Or Growth Motor? [Electronic resource] // Stock Market News & Fianncial Analysis – Seeking Aplha. – 14.05.2012. – Access mode: http://seekingalpha.com/article/587831-amazon-s-international-story-margin-anchor-or-growth-motor. – Accessed: 01.10.2012.
How A Tiny Chicago Suburb Sells Amazon And eBay To Russia. [Electronic resource] // Fast Company. – 12.06.2012. – Access mode: http://www.fastcompany.com/1839996/how-tiny-chicago-suburb-sells-amazon-and-ebay-russia. – Accessed: 01.10.2012.
Ozon: Russia’s Answer To Amazon Prepares For Clouds, Won’t Tackle ‘Kindle’ Soon, Says CEO. [Electronic resource] // Tech Crunch. – 04.09.2012. – Access mode: http://techcrunch.com/2012/09/04/ozon-russian-amazon-result/. – Accessed: 03.10.2012.
Russia is like Universe: it is huge and cold, smells like oil and constantly expands. [Electronic resource] // BCGroup. – 04.09.2012. – Access mode: http://www.bcgroup.su/news/russia-is-like-universe:-it-is-huge-and-cold,-smells-like-oil-and-constantly-expands/. – Accessed: 03.10.2012.
1 Amazon.com Overview Q2 2011 [Электронный ресурс] // Amazon
Режим доступа: http://amazon.com, свободный. – Загл. с экрана.
2 Baiz, S. E‐Commerce in Russia: Accessing the Russian Market via the Internet [Electronic resource] // Department of Economics, Trinity College, Dublin. – 2012. – Access mode: http://www.languageconnections.com/descargas/White%20paper%20E%20marketing%20via%20the%20internet.pdf, free. – Accessed: 01.10.2012.
3 Henni, A. E-Commerce in Russia [Electronic resource] // East-West Digital News. – August 2012. – p.22. – Access mode: http://www.ewdn.com/e-commerce/executive-summary.pdf, free. – Accessed: 01.10.2012.
4 Henni, A. E-Commerce in Russia [Electronic resource] // East-West Digital News. – August 2012. – p.23. – Access mode: http://www.ewdn.com/e-commerce/executive-summary.pdf, free. – Accessed: 01.10.2012.
5 Henni, A. E-Commerce in Russia [Electronic resource] // East-West Digital News. – August 2012. – p.26. – Access mode: http://www.ewdn.com/e-commerce/executive-summary.pdf, free. – Accessed: 01.10.2012.
6 ib.
7 Henni, A. E-Commerce in Russia [Electronic resource] // East-West Digital News. – August 2012. – p.31. – Access mode: http://www.ewdn.com/e-commerce/executive-summary.pdf, free. – Accessed: 01.10.2012.
8 ib.
9 Henni, A. E-Commerce in Russia [Electronic resource] // East-West Digital News. – August 2012. – p.32. – Access mode: http://www.ewdn.com/e-commerce/executive-summary.pdf, free. – Accessed: 01.10.2012.
10 Gavet, M. E-commerce in Russia: The rules are different [Electronic resource] // CNN Money. – 27.06.2012. – Access mode: http://tech.fortune.cnn.com/2012/06/27/e-commerce-in-russia-the-rules-are-different/, free. – Accessed: 01.10.2012.
11 Henni, A. E-Commerce in Russia [Electronic resource] // East-West Digital News. – August 2012. – p. 19. – Access mode: http://www.ewdn.com/e-commerce/executive-summary.pdf, free. – Accessed: 01.10.2012.
12 E-Commerce Is the Next Frontier in Global Expansion. [Electronic resource] // AT-Kearney. – June 2012. – Access mode: http://www.atkearney.com/paper/-/asset_publisher/dVxv4Hz2h8bS/content/id/351896. – Accessed: 01.10.2012.
13 Europe’s great exception. Why local firms dominate the Russian internet [Electronic resource] // The Economist. – 19.05. 2012. – Access mode: http://www.economist.com/node/21555560, free. – Accessed: 01.10.2012.
14 E-Commerce Is the Next Frontier in Global Expansion. [Electronic resource] // AT-Kearney. – June 2012. – Access mode: http://www.atkearney.com/paper/-/asset_publisher/dVxv4Hz2h8bS/content/id/351896. – Accessed: 01.10.2012.
15 How A Tiny Chicago Suburb Sells Amazon And eBay To Russia. [Electronic resource] // Fast Company. – 12.06.2012. – Access mode: http://www.fastcompany.com/1839996/how-tiny-chicago-suburb-sells-amazon-and-ebay-russia. – Accessed: 01.10.2012.
16 Mosmuller H. Amazon Will Deliver to Iraq Before Russia. [Electronic resource] // The Moscow Times. – 12.05.2011. – Access mode: http://www.themoscowtimes.com/news/article/amazon-will-deliver-to-iraq-before-russia/436669.html. – Accessed: 01.10.2012.
17Stone B. Russia’s Amazon.com Makes Deal to Expand – September 2011 – Access mode: http://www.businessweek.com/magazine/russias-amazoncom-makes-deal-to-expand-09152011.html - Accessed: 01.10.2012
18 Kindle Russia – November 2011 – Access mode: http://www.the-ebook-reader.com/kindle-russia.html Accessed: 01.10.2012
19 Henni, A. E-Commerce in Russia [Electronic resource] // East-West Digital News. – August 2012. – p.43. – Access mode: http://www.ewdn.com/e-commerce/executive-summary.pdf, free. – Accessed: 01.10.2012.
20 The Economist - The internet business in Russia – May 2012 – Access mode: http://www.economist.com/node/21555560 Accessed 29.09.2012
21 Russia is like Universe: it is huge and cold, smells like oil and constantly expands. [Electronic resource] // BCGroup. – 04.09.2012. – Access mode: http://www.bcgroup.su/news/russia-is-like-universe:-it-is-huge-and-cold,-smells-like-oil-and-constantly-expands/. – Accessed: 03.10.2012.
22E-book market in Russia doubles in 2011/ RIANovosti [Electronic resource]: http://en.rian.ru/russia/20120510/173368178.html, free – (03.10.2012)
23E-book market in Russia has grown 12 times for three years / bookrelay.com: http://www.bookrelay.com/2012/06/20/e-book-market-in-russia-has-grown-12-times-for-three-years/, free – (03.10.2012)
24 Russian online retailing market is slowly growing Council on Czech Competiveness [Electronic resource]:http://www.czechcompete.cz/policy-pipeline/us-globe/898-russian-online-retail-market-is-slowly-growing-, free – (03.10.2012)
25 Ozon: Russia’s Answer To Amazon Prepares For Clouds, Won’t Tackle ‘Kindle’ Soon, Says CEO. [Electronic resource] // Tech Crunch. – 04.09.2012. – Access mode: http://techcrunch.com/2012/09/04/ozon-russian-amazon-result/. – Accessed: 03.10.2012.
26 Benjamin M. Oviatt and Patricia Phillips McDougall, Toward a theory of international new. – Journal of International Business Studies, Vol. 36, No. 1 (Jan., 2005), Oxford University Press, UK. p. 31
27 Benjamin M. Oviatt and Patricia Phillips McDougall, Toward a theory of international new. – Journal of International Business Studies, Vol. 36, No. 1 (Jan., 2005), Oxford University Press, UK. p. 33
28 Benjamin M. Oviatt and Patricia Phillips McDougall, Toward a theory of international new. – Journal of International Business Studies, Vol. 36, No. 1 (Jan., 2005), Oxford University Press, UK. p. 31
29 World’s Largest Bookseller Opens on the Web [Electronic resource] // Amazon. –
Режим доступа: http://www.urlwire.com/news/100495.html, свободный. – Загл. с экрана.
30 Annual report. 1999 [Electronic resource] // Annual Reports. – Режим доступа: http://www.getfilings.com/o0000891020-00-000622.htmlсвободный. – Загл. с экрана.
31 Rebecca Saunders. Business the Amazon.com way. – Capstone Publishing Ltd., 2001. – 227
32 Amazon.com and Netscape Announce Strategic Online Commerce Deal [Electronic resource] // Amazon. – Режим доступа:http://phx.corporate-ir.net/phoenix.zhtml?c=97664&p=irol-newsArticle_Print&ID=231885&highlight=&erp=earningsDisclosure_Print, свободный. – Загл. с экрана.
33 Introducing Amazon Kindle [Electronic resource] // Amazon. – Режим доступа: http://www.amazon.com/gp/mpd/permalink/m2S5YCKCJJ64W8, свободный. – Загл. с экрана
34 Overview [Электронный ресурс] // Amazon. – Режим доступа: http://phx.corporate-ir.net/phoenix.zhtml?c=176060&p=irol-Mediakit, свободный. – Загл. с экрана.
35 Amazon.com Acquires Shopbop.com [Electronic resource] // Amazon. – Режим доступа: http://phx.corporate-ir.net/phoenix.zhtml?c=97664&p=irol-newsArticle&ID=822227&highlight= , свободный. – Загл. с экрана.
36 About Us. [Электронный ресурс] // Endless. – Режим доступа: http://www.endlessllp.com/about-us.aspx, свободный. – Загл. с экрана.
37 Amazon.com to Acquire Zappos.com. [Electronic resource] // Amazon. – Режим доступа: http://www.businesswire.com/news/home/20090722006145/en/Amazon.com-Acquire-Zappos.com, свободный. – Загл. с экрана
38 Overview. [Electronic resource] // Amazon. – Режим доступа: http://phx.corporate-ir.net/phoenix.zhtml?c=176060&p=irol-Mediakit, свободный. – Загл. с экрана.
39 Rebecca Saunders. Business the Amazon.com way. – Capstone Publishing Ltd., 2001. – 227
40 Annual report. 2010. [Electronic resource] // Annual Reports. –
Режим доступа: http://phx.corporate-ir.net/phoenix.zhtml?c=97664&p=irol-reportsannual, свободный. – Загл. с экрана.
41 About eBay. [Electronic resource] // Amazon. – Режим доступа: http://pages.ebay.co.uk/aboutebay.html, свободный. – Загл. с экрана.
42 Amazon.co.uk launches in the UK with huge selection and keen pricing [Electronic resource] // Amazon. – Режим доступа: http://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/press/pr/19981015, свободный. – Загл. с экрана.
43 Amazon.co.uk nets deal with Virgin Net. [Electronic resource] // Amazon. –
Режим доступа: http://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/press/pr/19981026, свободный. – Загл. с экрана.
44 Amazon.co.uk and Sky News' Book Show Join to Make Featured Books More Convenient to Find and Enjoy. [Electronic resource] // Amazon. – Режим доступа: http://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/press/pr/19981023 свободный. – Загл. с экрана.
45 Amazon.co.uk and Associated New Media strike exclusive bookselling deal. [Electronic resource] // Amazon. – Режим доступа: http://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/press/pr/19981105, свободный. – Загл. с экрана.
46 Amazon.co.uk launches auctions and zShops for UK shoppers and sellers. [Electronic resource] // Amazon. – Режим доступа: http://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/press/pr/19991105, свободный. – Загл. с экрана.
47 Amazon.de öffnet virtuelle Pforten zu zShops [Electronic resource] // Amazon. – Режим доступа: http://www.amazon.de/gp/press/pr/19991104 свободный. – Загл. с экрана.
48 Amazon.co.uk launches the ultimate music store. [Electronic resource] // Amazon. – Режим доступа: http://phx.corporate-ir.net/phoenix.zhtml?c=251199&p=irol-newsArticle&ID=1707506&highlight= свободный. – Загл. с экрана.
49 Amazon.co.uk launches the ultimate music store [Electronic resource] // Amazon. – Режим доступа: http://phx.corporate-ir.net/phoenix.zhtml?c=251199&p=irol-newsArticle&ID=1707506&highlight=свободный. – Загл. с экрана.
50 Amazon.de bietet lukrative Zusammenarbeit bei Anzeigen im Bereich E-Commerce. [Electronic resource] // Amazon. – Режим доступа: http://www.amazon.de/gp/press/pr/19990427 свободный. – Загл. с экрана.
51 Focus on I-Commerce. Amazon.com sets sites in Europe // InfoWorld. –October 26, 1998
52 Annual report. 1999. Amazon.com. [Electronic resource] // Annual Reports. –Режим доступа: http://phx.corporate-ir.net/phoenix.zhtml?c=97664&p=irol-reportsannual свободный. – Загл. с экрана.
53 Annual report. 1999. [Electronic resource] // Annual Reports. –Режим доступа: http://phx.corporate-ir.net/phoenix.zhtml?c=97664&p=irol-reportsannualсвободный. – Загл. с экрана.
54 Annual report. 2010. [Electronic resource] // Annual Reports. –Режим доступа: http://phx.corporate-ir.net/phoenix.zhtml?c=97664&p=irol-reportsannual, свободный. – Загл. с экрана.
55 Amazon.com Will Launches French Store Featuring Books, Music, DVDs and Videos; Amazon.fr is Third European Site, Serves Global French-Speaking Market . [Electronic resource] // Amazon. – Режим доступа: http://phx.corporate-ir.net/phoenix.zhtml?c=176060&p=irol-newsArticle_Print&ID=502828&highlight= свободный. – Загл. с экрана.
56 History and time line. [Electronic resource] // Amazon. – Режим доступа: http://phx.corporate-ir.net/phoenix.zhtml?c=176060&p=irol-corporateTimelineсвободный. – Загл. с экрана.
57 History and time line. [Electronic resource] // Amazon. – Режим доступа: http://phx.corporate-ir.net/phoenix.zhtml?c=176060&p=irol-corporateTimelineсвободный. – Загл. с экрана.
58 Major League Baseball Advanced Media and Amazon.com Team Up to Sell Seattle Mariners Goods to Customers in Japan. [Electronic resource] // Amazon. – Режим доступа: http://phx.corporate-ir.net/phoenix.zhtml?c=176060&p=irol-newsArticle_Print&ID=502800&highlight=свободный. – Загл. с экрана.
