
- •Cytology
- •The cell
- •Plasma membrane or plasmalemma
- •Intercellular connections
- •The membranous organelles Endoplasmic reticulum (e. R.)
- •Rough e. R. (rEr)
- •Smooth e. R. (sEr)
- •Golgi apparatus
- •Lysosomes
- •Peroxisomes (microbodies)
- •Mitochondria
- •Microtubules
- •Cilia and flagella
- •Filaments
- •Inclusions
- •Nucleus
- •Chromatin
- •Nucleolus
- •Nucleoplasm
- •Cell cycle
- •Mitosis
- •Embryology
- •The spermatozoon
- •Ovums or ovocytes
- •Fertilization
- •Penetration of Zona Pellucida
- •Fusion of Pronuclei
- •Cleavage
- •Blastocyst Formation Compaction
- •Cavitation
- •Gastrulation
- •Human developmental periods
- •Progenesis
- •Derivations of the ectoderm
- •Derivations of the mesoderm
- •Derivations of the endoderm
- •Fetal membranes
- •Placenta
- •Placental barrier
- •Umbilical cord
- •Amniotic fluid
- •Tissues
- •Classification of epithelium
- •Functions of a blood
- •Red blood cells
- •White blood cells
- •Neutrophils
- •Eosinophils
- •Basophils
- •Lymphocytes
- •Monocytes
- •Platelets
- •Hematopoiesis
- •Hematopoiesis in embryonic and fetal life
- •Pluripotential hematopoietic stem cells
- •Connective tissue
- •Loose connective tissue
- •Dense connective tissue
- •Connective tissue (c.T.) with special properties
- •Brown adipose c.T.:
- •Connective tissue fibers
- •Collagen fibers
- •Reticular fibers
- •Elastic fibers
- •Ground substance
- •Connective tissue cells
- •Fibroblasts and myofibroblasts
- •Macrophages
- •Mast cells
- •Hyaline cartilage
- •Fibro cartilage
- •Bone cells Osteoblasts
- •Osteocytes
- •Osteoclast
- •Classification of bone tissue
- •General structures of bones
- •Cartilage Arises From Mesenchyme
- •Bone formation
- •Intramembranous Ossification
- •In Intramembranous Ossification, Bone Is Formed by Differentiation of Mesenchymal Cells Into Osteoblasts
- •Endochondral Ossification
- •Growth of Endochondral Bone
- •Muscle tissue
- •Classification of muscle
- •Skeletal muscle
- •Skeletal muscle fibers
- •Myofibrils and myofilaments
- •Organization of a skeletal muscle
- •Cardiac muscle
- •Smooth muscle
- •Contraction and its control
- •Nervous tissue
- •Dendrites and axons
- •Synapses
- •Axonal transport systems
- •N euroglia
- •Functions of neuroglia
- •Schwann cells and the myelin sheath
- •Literature
Cell cycle
The reproduction cycle of a cell is termed the cell cycle.
For renewing cell populations and growing cell populations including embryonic cells, cells in tissue culture and even tumor cells a cell cycle may be described that two principal phases mitosis (M phase) and interphase which include three phases G1, S and G2 .
G1 phase (presynthesis, gap 1) of interphase is usually a period of cell growth and may last only a few hours in a rapidly dividing cell or may last a lifetime in a nondividing cell. The cell that leaves the cycle in G1, to begin “terminal” differentiation is considered to begin the G0 phase “0” for outside the cycle.
During the S (synthesis) phase DNA of the cell is doubled. The centrioles often self-duplicate during this stage.
During G2 phase (postsynthesis, gap 2) the final preparations for cell division occur; these include repair of damaged DNA, synthesis of tubulin for the spindle apparatus and ATP accumulation for the energy-expensive mitosis.
Mitosis
Mitosis follows the G2 phase and consists of four phases:
-prophase
-metaphase
-anaphase
-telophase
Mitosis is a cell division process that produces two daughter cells with the same chromosome number and DNA content as the original cell.
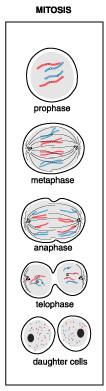
During prophase chromatin coils form chromosomes. The nuclear membrane and nucleolus start to disappears. The mitotic spindle apparatus begins to assembly between the centriole pairs. The two centriole pairs migrate to opposite poles of the cell.
During metaphase chromosomes becomes shorter, thicker and line up at the cell equator between the centriole pairs, and each chromosome has a centromere to which microtubules of the spindle apparatus attach.
The daughter cells are 2n in DNA content and 2n in chromosome number.
Embryology
The embryology is a science, which studies lows of formation of an embryos and process of his development. The individual development of living organisms is an ontogenesis.
In individual development are two basic stages:
Prenatal ontogenesis is development till birth
Postnatal ontogenesis is development from birth up to death of an individual
So, the embryogenes is a part of ontogenesis.
In development of embryos some stages characterized by certain quantitative and qualitative changes are observed:
1. Fertilization is fusion of a female and male gamete.
2. Cleavage is the series of rapid cell divisions of the zygote with the formation of blastula
3. Gastrulation is the formative process by which the three germ embryonic layers are established in embryos (ectoderm, mesoderm and endoderm).
4. Histogenesis-development of tissues
5. Organogenesis development of organs
6. Systemogenesis development of systems
Two types of sex cells are distinguished:
Male cell is spermatozoon or sperm
Female cell is ovum or ovocyte
