
- •Cytology
- •The cell
- •Plasma membrane or plasmalemma
- •Intercellular connections
- •The membranous organelles Endoplasmic reticulum (e. R.)
- •Rough e. R. (rEr)
- •Smooth e. R. (sEr)
- •Golgi apparatus
- •Lysosomes
- •Peroxisomes (microbodies)
- •Mitochondria
- •Microtubules
- •Cilia and flagella
- •Filaments
- •Inclusions
- •Nucleus
- •Chromatin
- •Nucleolus
- •Nucleoplasm
- •Cell cycle
- •Mitosis
- •Embryology
- •The spermatozoon
- •Ovums or ovocytes
- •Fertilization
- •Penetration of Zona Pellucida
- •Fusion of Pronuclei
- •Cleavage
- •Blastocyst Formation Compaction
- •Cavitation
- •Gastrulation
- •Human developmental periods
- •Progenesis
- •Derivations of the ectoderm
- •Derivations of the mesoderm
- •Derivations of the endoderm
- •Fetal membranes
- •Placenta
- •Placental barrier
- •Umbilical cord
- •Amniotic fluid
- •Tissues
- •Classification of epithelium
- •Functions of a blood
- •Red blood cells
- •White blood cells
- •Neutrophils
- •Eosinophils
- •Basophils
- •Lymphocytes
- •Monocytes
- •Platelets
- •Hematopoiesis
- •Hematopoiesis in embryonic and fetal life
- •Pluripotential hematopoietic stem cells
- •Connective tissue
- •Loose connective tissue
- •Dense connective tissue
- •Connective tissue (c.T.) with special properties
- •Brown adipose c.T.:
- •Connective tissue fibers
- •Collagen fibers
- •Reticular fibers
- •Elastic fibers
- •Ground substance
- •Connective tissue cells
- •Fibroblasts and myofibroblasts
- •Macrophages
- •Mast cells
- •Hyaline cartilage
- •Fibro cartilage
- •Bone cells Osteoblasts
- •Osteocytes
- •Osteoclast
- •Classification of bone tissue
- •General structures of bones
- •Cartilage Arises From Mesenchyme
- •Bone formation
- •Intramembranous Ossification
- •In Intramembranous Ossification, Bone Is Formed by Differentiation of Mesenchymal Cells Into Osteoblasts
- •Endochondral Ossification
- •Growth of Endochondral Bone
- •Muscle tissue
- •Classification of muscle
- •Skeletal muscle
- •Skeletal muscle fibers
- •Myofibrils and myofilaments
- •Organization of a skeletal muscle
- •Cardiac muscle
- •Smooth muscle
- •Contraction and its control
- •Nervous tissue
- •Dendrites and axons
- •Synapses
- •Axonal transport systems
- •N euroglia
- •Functions of neuroglia
- •Schwann cells and the myelin sheath
- •Literature
Hyaline cartilage
Figure 24. Photomicrograph of a typical hyaline cartilage; DCT, dense connective tissue; P, perichondrium; GC, growing cartilage; N, nuclei; TM, territorial matrix; IM, interterritorial matrix, isogenous groups
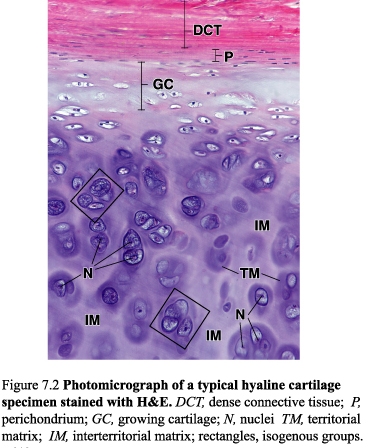
Hyaline cartilage is distinguished by a homogeneous, amorphous matrix. The matrix consists of two components: collagen fibrils and ground substance.
In developing bone, the matrix calcifies before it is replaced by bone matrix.
Hyaline cartilage is located in the articular surfaces of the movable joints, in the walls of larger respiratory passages (nose, larynx, trachea, bronchi) in the ventral ends of ribs, where they articulate with sternum, and in the epiphyseal plate, where it is responsible for the longitudinal growth of bone.
Cartilage matrix does calcify.
Cartilage matrix is highly hydrated. From 60% to 78% of the net weight of hyaline cartilage is water.
40% of the dry weight of hyaline cartilage consists of collagen embedded in a firm, hydrated gel of proteoglycans and structural glycoproteins. The collagen component of the matrix is in the form of relatively thin fibrils. The ground substance of hyaline cartilage contains three kinds of glycosaminoglycans:
-hyaluronic acid
-chondroitin sulfate
-keratan sulfate
The chondroitin and keratan sulfates of cartilage are joined to a core protein to form a proteoglycan monomer.
T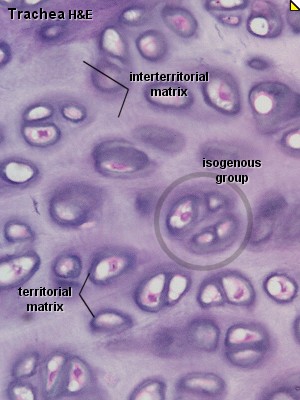 he
cartilage matrix surrounding each chondrocyte is rich in
glycosaminoglycan and poor in collagen. This peripheral zone, called
the
territorial or capsular matrix.
The cartilage matrix which located between the capsules called the
interterritorial
matrix.
he
cartilage matrix surrounding each chondrocyte is rich in
glycosaminoglycan and poor in collagen. This peripheral zone, called
the
territorial or capsular matrix.
The cartilage matrix which located between the capsules called the
interterritorial
matrix.
Except in the articular cartilage of joints, all hyaline cartilage is covered by a layer of dense connective tissue, the perichondrium. The perichondrium appears to be divided into an inner cellular layer, which gives rise to cartilage cells, and an outer fibrous layer.
The cells in the inner layer of the perichondrium are chondroblasts and easily differentiate into chondrocytes.
Chondrocytes are round and may appear in groups of up to eight cells originating from mitotic divisions of a single chondrocyte.
These groups are called isogenous.
Chondrocytes fill the lacunae completely. Chondrocytes synthesize collagen, proteoglycans, hyaluronic acid and chondronectin.
E lastic
cartilage
lastic
cartilage
Elastic cartilage is found in the external ear, in the walls of the external auditory canal and the auditory (Eustachian) tube, in the epiglottis and in the larynx. Like hyaline cartilage elastic possesses a perichondrium. The matrix of elastic cartilage does not calcify. Elastic cartilage contains elastic fibers in addition to collagen type II fibrils.
Fibro cartilage
Fibro cartilage is typically present in the intervertebral discs, the symphysis pubis, the articular discs of the sternoclavicular and temporomandibular joints, the meniscs of the knee joint, and certain places where tendons attach to bones.
Fibro cartilage consists of chondrocytes and their territorial matrix in combination with dense connective tissue. The chondrocytes are very often arranged in long rows. There is no identifiable perichondrium in fibro cartilage
Bone
Bone is a connective tissue characterized by a mineralized matrix. Bone consists of extracellular matrix and three cell types: osteocytes, osteoblasts and osteoclasts.
Bone matrix consists of type I collagen and ground substance containing proteoglycans and noncollagenous glycoproteins. The association of hydroapatite with collagen fibers is responsible for the hardness and resistance of bone tissue.
Within the bone matrix are spaces called lacunae, each of which contains a bone cell, the osteocyte. The osteocyte extends numerous processes into little tunnels called canaliculi.
