
- •Cytology
- •The cell
- •Plasma membrane or plasmalemma
- •Intercellular connections
- •The membranous organelles Endoplasmic reticulum (e. R.)
- •Rough e. R. (rEr)
- •Smooth e. R. (sEr)
- •Golgi apparatus
- •Lysosomes
- •Peroxisomes (microbodies)
- •Mitochondria
- •Microtubules
- •Cilia and flagella
- •Filaments
- •Inclusions
- •Nucleus
- •Chromatin
- •Nucleolus
- •Nucleoplasm
- •Cell cycle
- •Mitosis
- •Embryology
- •The spermatozoon
- •Ovums or ovocytes
- •Fertilization
- •Penetration of Zona Pellucida
- •Fusion of Pronuclei
- •Cleavage
- •Blastocyst Formation Compaction
- •Cavitation
- •Gastrulation
- •Human developmental periods
- •Progenesis
- •Derivations of the ectoderm
- •Derivations of the mesoderm
- •Derivations of the endoderm
- •Fetal membranes
- •Placenta
- •Placental barrier
- •Umbilical cord
- •Amniotic fluid
- •Tissues
- •Classification of epithelium
- •Functions of a blood
- •Red blood cells
- •White blood cells
- •Neutrophils
- •Eosinophils
- •Basophils
- •Lymphocytes
- •Monocytes
- •Platelets
- •Hematopoiesis
- •Hematopoiesis in embryonic and fetal life
- •Pluripotential hematopoietic stem cells
- •Connective tissue
- •Loose connective tissue
- •Dense connective tissue
- •Connective tissue (c.T.) with special properties
- •Brown adipose c.T.:
- •Connective tissue fibers
- •Collagen fibers
- •Reticular fibers
- •Elastic fibers
- •Ground substance
- •Connective tissue cells
- •Fibroblasts and myofibroblasts
- •Macrophages
- •Mast cells
- •Hyaline cartilage
- •Fibro cartilage
- •Bone cells Osteoblasts
- •Osteocytes
- •Osteoclast
- •Classification of bone tissue
- •General structures of bones
- •Cartilage Arises From Mesenchyme
- •Bone formation
- •Intramembranous Ossification
- •In Intramembranous Ossification, Bone Is Formed by Differentiation of Mesenchymal Cells Into Osteoblasts
- •Endochondral Ossification
- •Growth of Endochondral Bone
- •Muscle tissue
- •Classification of muscle
- •Skeletal muscle
- •Skeletal muscle fibers
- •Myofibrils and myofilaments
- •Organization of a skeletal muscle
- •Cardiac muscle
- •Smooth muscle
- •Contraction and its control
- •Nervous tissue
- •Dendrites and axons
- •Synapses
- •Axonal transport systems
- •N euroglia
- •Functions of neuroglia
- •Schwann cells and the myelin sheath
- •Literature
Brown adipose c.T.:
Figure 24. Photomicrograph of brown adipose tissue
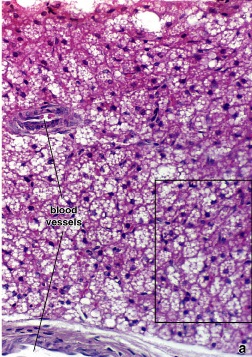
It is present in few sites in the body, namely; the mediastinum, perinephric fat and around the aorta.
It contains multilocular adipose cells.
Its main function is thermoregulation.
Connective tissue fibers
Each of the fiber types is produced by the fibroblast and is composed of protein formed by long peptide chains. Depending on their character and composition they are referred to as:
-collagen fibers
-reticular fibers
-elastic fibers
Collagen fibers
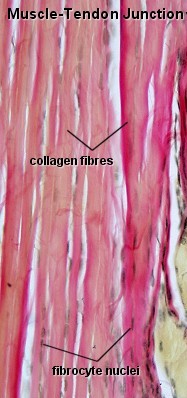 Collagen
fibers are the most numerous fibers in connective tissue. Although
fresh collagen fibers are colorless strands, when they are present in
great numbers the tissues in which they lie are white.
Collagen
fibers are the most numerous fibers in connective tissue. Although
fresh collagen fibers are colorless strands, when they are present in
great numbers the tissues in which they lie are white.
Collagen fibers are inelastic and because of their molecular configuration, have a tensile strength greater than that of steel.
Collagen fibers consist of closely packed thick fibrils, the collagen fibrils. The collagen fibrils consist of tropocollagen.
In many parts of the body, collagen fibers lie parallel to each other, forming collagen bundles.
Reticular fibers
Reticular fibers provide a supporting frame work for the cellular constituents of various tissues and organs of the body.
R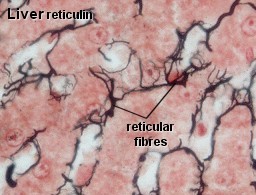 eticular
fibers are closely related to collagenous fibers, in that they both
consist of collagen fibrils. The individual fibrils that constitute
the reticular fiber are always narrow diameter, and typically,
fibrils do not bundle to form thick fibers.
eticular
fibers are closely related to collagenous fibers, in that they both
consist of collagen fibrils. The individual fibrils that constitute
the reticular fiber are always narrow diameter, and typically,
fibrils do not bundle to form thick fibers.
The reticular fiber is composed of type III collagen. The reticular fiber has a thread-like appearance. Reticular fibers are so called because they are arranged in a mesh-like pattern or network.
Elastic fibers
E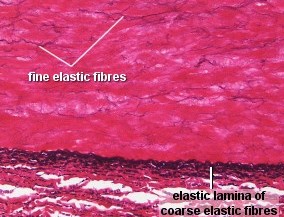 lastic
fibers provide tissues with the ability to respond to stretch and
distension.
lastic
fibers provide tissues with the ability to respond to stretch and
distension.
Elastic fibers are typically thinner than collagen fibers and are arranged in a branching pattern to form a three dimensional network.
Elastic fibers are composed of two structural components, elastin and microfibrils.
The random coiling of the elastin molecule gives the elastic fiber its ability to be stretched and then recoil back to its original state. Elastin also uniquely contains desmosine and isodesmosine.
In mature fibers, the microfibrils are located with elastic fiber and at the periphery of the fiber.
Ground substance
Ground substance is the component that occupies the space between the cells and fibers.
Ground substance is a viscous, clear substance that has a slippery feel. It has a high water content and that combined with its structure less nature at least above the macromolecular level.
Ground substance consists largely of proteoglycans and hyaluronic acid. The physical properties of ground substance and its ability to permit diffusion of oxygen and nutrients between the microvasculature and adjacent tissues is due to the proteoglycans that it contains.
Connective tissue cells
The types of cells found in loose connective tissue as well as their relative numbers reflect the tissues functional activity.
Connective tissue cells can be categorized as fixed or wandering.
The cells that comprise the fixed cell population include:
-fibroblasts and closely related cell type, the myofibroblasts
-macrophages
-adipose cells
-mast cells
-undifferentiated mesenchymal cells
The cells that comprise the wandering or transit population include:
-lymphocytes
-plasma cells
-neutrophils
-eosinophils
-basophils
-monocytes
