
- •Cytology
- •The cell
- •Plasma membrane or plasmalemma
- •Intercellular connections
- •The membranous organelles Endoplasmic reticulum (e. R.)
- •Rough e. R. (rEr)
- •Smooth e. R. (sEr)
- •Golgi apparatus
- •Lysosomes
- •Peroxisomes (microbodies)
- •Mitochondria
- •Microtubules
- •Cilia and flagella
- •Filaments
- •Inclusions
- •Nucleus
- •Chromatin
- •Nucleolus
- •Nucleoplasm
- •Cell cycle
- •Mitosis
- •Embryology
- •The spermatozoon
- •Ovums or ovocytes
- •Fertilization
- •Penetration of Zona Pellucida
- •Fusion of Pronuclei
- •Cleavage
- •Blastocyst Formation Compaction
- •Cavitation
- •Gastrulation
- •Human developmental periods
- •Progenesis
- •Derivations of the ectoderm
- •Derivations of the mesoderm
- •Derivations of the endoderm
- •Fetal membranes
- •Placenta
- •Placental barrier
- •Umbilical cord
- •Amniotic fluid
- •Tissues
- •Classification of epithelium
- •Functions of a blood
- •Red blood cells
- •White blood cells
- •Neutrophils
- •Eosinophils
- •Basophils
- •Lymphocytes
- •Monocytes
- •Platelets
- •Hematopoiesis
- •Hematopoiesis in embryonic and fetal life
- •Pluripotential hematopoietic stem cells
- •Connective tissue
- •Loose connective tissue
- •Dense connective tissue
- •Connective tissue (c.T.) with special properties
- •Brown adipose c.T.:
- •Connective tissue fibers
- •Collagen fibers
- •Reticular fibers
- •Elastic fibers
- •Ground substance
- •Connective tissue cells
- •Fibroblasts and myofibroblasts
- •Macrophages
- •Mast cells
- •Hyaline cartilage
- •Fibro cartilage
- •Bone cells Osteoblasts
- •Osteocytes
- •Osteoclast
- •Classification of bone tissue
- •General structures of bones
- •Cartilage Arises From Mesenchyme
- •Bone formation
- •Intramembranous Ossification
- •In Intramembranous Ossification, Bone Is Formed by Differentiation of Mesenchymal Cells Into Osteoblasts
- •Endochondral Ossification
- •Growth of Endochondral Bone
- •Muscle tissue
- •Classification of muscle
- •Skeletal muscle
- •Skeletal muscle fibers
- •Myofibrils and myofilaments
- •Organization of a skeletal muscle
- •Cardiac muscle
- •Smooth muscle
- •Contraction and its control
- •Nervous tissue
- •Dendrites and axons
- •Synapses
- •Axonal transport systems
- •N euroglia
- •Functions of neuroglia
- •Schwann cells and the myelin sheath
- •Literature
Connective tissue
Connective tissue consists of cells and an extracellular matrix that includes extracellular fibers, ground substance and tissue fluid.
Classification of connective tissue
Classification is based on the composition and organization of the cellular and extracellular components and on special functions.
The term “connective tissue” includes a variety of tissues with differing functional properties but with certain common characteristics that allow them to be grouped together.
Thus, connective tissue consist of
Connective tissue proper
Specialized connective tissue
The tissues that belong to last category are divided into next general types:
-adipose tissue
-blood
-bone
-cartilage
-lymphatic tissue
-hemopoietic tissue
Connective tissue proper
Consist of:
-loose connective tissue
-dense connective tissue
Loose connective tissue
Loose connective tissue, also called areolar tissue, is characterized by loosely arranged fibers and an abundance of cells. There are collagen, elastic and reticular fibers in this tissue.
The most numerous cells are fibroblasts and macrophages, but all the other types of connective tissue cells (such as adipose cells, lymphocytes, plasma cells, neutrophils, eosinophils, basophils and monocytes) are also present.
Dense connective tissue
Dense connective tissue can be subclassified into:
-dense irregular connective tissue
-dense regular connective tissue
The distinction between these two types is simply the arrangement of the fibers.
Dense regular connective tissue is characterized by ordered and densely packed arrays of fibers and cells.
Dense regular connective tissue is the main functional component of tendons, ligaments and aponeuroses.
Dense irregular connective tissue is characterized by an abundance of fibers and few cells. Typically, the fibers are arranged in bundles oriented in various directions (thus, it is irregular) to withstand stresses to which an organ or structure may be subjected. Similarly, skin contains a relatively thick layer of dense irregular connective tissue in the dermis. This is the reticular or deep layer of the dermis.
Connective tissue (c.T.) with special properties
1. Reticular С.Т.:
In this type of С.Т., the reticular fibers are dominating. It is formed of branching and anastomosing network of reticular fibers and reticular cells. This network of reticular fibers takes the arrangement of the parenchyma of the organ in which it is present.
It is present in the stroma filling the background of organs e.g.; spleen, lymph node, liver, kidney etc.
2. Mucoid С.Т.:
It is a type of C.T. proper in which the mucoid amorphous component of the intercellular substance is dominating, with mucoid cells and some few collagenous fibers.
It is an embryonic type of C.T. present very rarely in adults e.g. in Wharton’s jelly of the umbilical cord, and bulb of the tooth.
3. Pigmented С.Т.:
It is a type of C.T. proper in which the pigment cells are dominating. It can be seen in the uveal tract of the eye ball (the choroid, the ciliary body and iris).
4. Adipose C.T.:
It is a type of C.T. proper, in which the fat cells are dominating and
arranged in the form of lobules separated by septa of loose C.T. . There are two types of adipose C.T.
White adipose С.Т.:
Figure 23. Photomicrograph of white adipose tissue
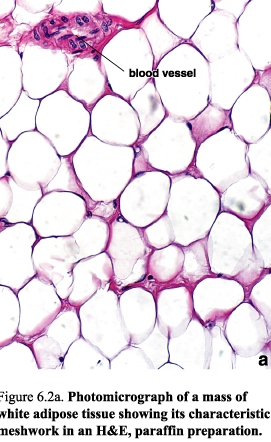
It is present in most of the fatty tissue of the body e.g. the subcutaneous adipose C.T., mammary glands of the adult females. It is characterized by containing unilocular adipose cells.
It performs many functions in the body, namely; energy storage, insulation of heat, supportive pads of fat for other organs and gives the body its characteristic contour (they are the functions of unilocular fat cells).
